Abstract
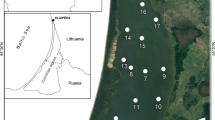
The Salton Sea currently suffers from several well-documented water quality problems associated with high nutrient loading. However, the importance of phosphorus regeneration from sediments has not been established. Sediment phosphorus regeneration rates may be affected by benthic macroinvertebrate activity (e.g. bioturbation and excretion). The polychaete Neanthes succinea (Frey and Leuckart) is the dominant benthic macroinvertebrate in the Salton Sea. It is widely distributed during periods of mixing (winter and spring), and inhabits only shallow water areas following development of anoxia in summer. The contribution of N. succinea to sediment phosphorus regeneration was investigated using laboratory incubations of cores under lake temperatures and dissolved oxygen concentrations typical of the Salton Sea. Regeneration rates of soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) were lowest (−0.23–1.03 mg P m−2 day−1) under saturated oxygen conditions, and highest (1.23–4.67 mg P m−2 day−1) under reduced oxygen levels. N. succinea most likely stimulated phosphorus regeneration under reduced oxygen levels via increased burrow ventilation rates. Phosphorus excretion rates by N. succinea were 60–70% more rapid under reduced oxygen levels than under saturated or hypoxic conditions. SRP accounted for 71–80% of the dissolved phosphorus excreted under all conditions. Whole-lake SRP regeneration rates predicted from N. succinea biomass densities are highest in early spring, when the lake is mixing frequently and mid-lake phytoplankton populations are maximal. Thus, any additional phosphorus regenerated from the sediments at that time has potential for contributing to the overall production of the lake.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller, R. C., 1978. Experimental studies of changes produced by deposit feeders on pore water, sediment, and overlying water chemistry. American Journal of Science 278: 1185–1234.
APHA, 1998. Method 4500-P. In Clesceri L. S., A. D. Eaton & Greenberg A. E. (eds), Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (17th Ed.). American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Pollution Control Federation, Washington, DC.
Bain, R. C., A. M. Caldwell, R. H. Clawson, H. L. Scotten & R. G. Wills, 1970. Salton Sea California: water quality and ecological management considerations. U.S. Department of the Interior, Federal Water Quality Administration, Pacific Southwest Region, 53 pp.
Bartoli, M., D. Nizzoli, D. T. Welsh & P. Viaroli, 2000. Short-term influence of recolonisation by the polychaete worm Nereis succinea on oxygen and nitrogen fluxes and denitrification: a microcosm simulation. Hydrobiologia 431: 165–174.
Björkman, K. M. & D. M. Karl, 2003. Bioavailability of dissolved organic phosphorus in the euphotic zone at station ALOHA, North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Limnology and Oceanography 48: 1049–1057.
Boström B., M. Jannson & C. Forsberg, 1982. Phosphorus release from lake sediments. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Beiheft Ergebnisse der Limnologie 18: 5–59.
Carpelan, L. H., 1958. The Salton Sea: physical and chemical characteristics. Limnology and Oceanography 3: 373–386.
Carpelan, L. H. & R. H. Linsley, 1961. The pile worm, Neanthes succinea (Frey and Leuckart). In Walker, B. W. (ed.), The ecology of the Salton Sea, California, in relation to the sportsfishery. California Department of Fish and Game, Fish Bulletin 113: 63–76.
Christensen, B., A. Vedel & E. Kristensen, 2000. Carbon and nitrogen fluxes in sediment inhabited by suspension-feeding (Nereis diversicolor) and non-suspension-feeding (N. virens) polychaetes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 192: 203–217.
Clavero, V., J. A. Fernández & F. X. Niell, 1992. Bioturbation by Nereis sp. and its effects on the phosphate flux across the sediment–water interface in the Palmones River Estuary. Hydrobiologia 235/236: 387–392.
Cooke, G. D., E. B. Welch, S. A. Peterson & P. R. Newroth, 1993. Management and restoration of lakes and reservoirs. Lewis Publishing and CRC Press, Boca Raton, 548 pp.
Devine, J. & M. J. Vanni, 2002. Spatial and seasonal variation in nutrient excretion by benthic invertebrates in a eutrophic reservoir. Freshwater Biology 47: 1107–1121.
Detwiler, P., M. F. Coe & D. M. Dexter, 2002. Benthic invertebrates of the Salton Sea: distribution and seasonal dynamics. Hydrobiologia 473 (Developments in Hydrobiology 161): 139–160.
Fukuhara, H. & M. Sakamoto, 1987. Enhancement of inorganic nitrogen and phosphate release from lake sediment by tubificid worms and chironomid larvae. Oikos 28: 312–320.
Fukuhara, H. & K. Yasuda, 1985. Phosphorus excretion by some zoobenthos in a eutrophic freshwater lake and its temperature dependency. Japanese Journal of Limnology 46: 287–296.
Gallepp, G. W., 1979. Chironomid influence on phosphate release in sediment water microcosms. Ecology 60: 547–556.
Gamenick, I., A. Jahn, K. Vopel & O. Giere, 1996. Hypoxia and sulphide as structuring factors in a macrozoobenthic community on the Baltic Sea shore: colonisation studies and tolerance experiments. Marine Ecology Progress Series 144: 73–85.
Gardner, W. S., T. F. Nalepa, M. A. Quigly & J. M. Malczyk, 1981. Release of phosphorus by certain benthic invertebrates. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 38: 978–981.
Granéli, W., 1979. The influence of Chironomus plumosus larvae on the exchange of dissolved substances between sediment and water. Hydrobiologia 66: 149–159.
Guérin, C. & L. Labroue, 1991. A laboratory study of the effect of Tubifex tubifex Mulleri (Tubificidae, Oligochaeta) on the release of phosphorus through the sediment. Annales de Limnologie 27: 253–265 (in French).
Hargrave, B. T. & G. H. Geen, 1968. Phosphorus excretion by zooplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 13: 332–342.
Holdren, G. C. & D. E. Armstrong, 1980. Factors affecting phosphorus release from intact lake sediment cores. Environmental Science and Technology 14: 79–87.
Holdren, G. C. & A. Montaño, 2002. Chemical and physical characteristics of the Salton Sea, California. Hydrobiologia 473(Developments in Hydrobiology 161): 1–21.
Hoover, F. & J. St. Armant, 1970. Establishment of Tilapia mossambica Peters in Bard Valley, Imperial County, California. California Fish and Game 56: 70–71.
Jørgensen, B. B., 1980. Seasonal oxygen depletion in bottom waters of a Danish fjord and its effects on the benthic community. Oikos 34: 68–76.
Kristensen, E., 1981. Direct measurement of ventilation and oxygen uptake in three species of tubicolous polychaetes (Nereis spp.). Journal of Comparative Physiology 145: 45–50.
Kristensen, E., 1983a. Comparison of polychaete (Nereis spp.) ventilation in plastic tubes and natural sediment. Marine Ecology Progress Series 12: 307–309.
Kristensen, E., 1983b. Ventilation and oxygen uptake by three species of Nereis (Annelida: Polychaeta). I. Effects of hypoxia. Marine Ecology Progress Series 12: 289–297.
Kristensen, E., S. I. Ahmed & A. H. Devol, 1995. Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition of organic matter in marine sediment: which is fastest? Limnology and Oceanography 40: 1430–1437.
Martin, J. M., 1974. The effects of dissolved oxygen, salinity, and temperature on two populations of the polychaetous annelid Neanthes succinea. Master’s Thesis, California State University, Long Beach, 89 pp.
Matisoff, G. & X. Wang, 1998. Solute transport in sediments by freshwater infaunal bioirrigators. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 1487–1499.
Miron, G. & E. Kristensen, 1993. Behavioural responses of three nereid polychaetes to injection of sulfide inside burrows. Marine Ecology Progress Series 101: 147–155.
Nalepa, T. F., D. S. White, C. M. Pringle & M. A. Quigley, 1980. The biological component of phosphorus exchange and cycling in lake sediments. In D. Scavia & R. Moll (eds), Nutrient cycling in the Great Lakes. Great Lakes Research Division Special Report 83. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, 93–110.
Osgood, R. A., 1988. Lake mixis and internal phosphorus dynamics. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 113: 629–638.
Prairie, Y. T., C. De Montigny & P. A. del Giorgio, 2001. Anaerobic phosphorus release from sediments: a paradigm revisited. Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung für Theoretische und Angewandte Limnologie 27, 4013–4020.
Reish, D. J. & T. L. Richards, 1966. A technique for studying the effects of varying concentrations of dissolved oxygen on aquatic organisms. International Journal of Air and Water Pollution 10: 69–71.
Riedel, G. F., J. G. Sanders & R. W. Osman, 1997. Biogeochemical control on the flux of trace elements from estuarine sediments: water column oxygen concentrations and benthic infauna. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 44: 23–38.
Riedel, R., L. Caskey & B. A. Costa-Pierce, 2002. Fish biology and fisheries ecology of the Salton Sea, California. Hydrobiologia 473(Developments in Hydrobiology 161): 229–244.
Roden, E. E. & J. W. Edmonds, 1997. Phosphate mobilization in iron-rich anaerobic sediments: microbial Fe(III) oxide reduction versus iron–sulfide formation. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 139: 347–378.
Rosenberg, R., B. Hellman & B. Johansson, 1991. Hypoxic tolerance of marine benthic fauna. Marine Ecology Progress Series 79: 127–131.
Schroeder R. A., W. H. Orem & Y. K. Kharaka, 2002. Chemical evolution of the Salton Sea: nutrient and selenium dynamics. Hydrobiologia 473 (Developments in Hydrobiology 161): 23–45.
Søndergaard, M., P. Kristensen & E. Jeppesen, 1992. Phosphorus release from resuspended sediment in the shallow and wind-exposed Lake Arresø, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 228: 91–99.
Swan, B. K., 2003. The role of Neanthes succinea in phosphorus cycling in the Salton Sea. Master’s Thesis, San Diego State University, 92 pp.
Theede, H., J. Schaudinn & F. Saffé, 1973. Ecophysiological studies on four Nereis species of the Kiel Bay. Oikos 15: 246–252.
Tiffany, M. A., B. K. Swan, J. M. Watts & S. H. Hurlbert, 2002. Metazooplankton dynamics in the Salton Sea, California, 1997–1999. Hydrobiologia 473 (Developments in Hydrobiology 161): 103–120.
Van Rees, K. C. J., K. R. Reddy & P. C. S. Rao, 1996. Influence of benthic organisms on solute transport in lake sediments. Hydrobiologia 317: 31–40.
Watts, J. M., B. K. Swan, M. A. Tiffany & S. H. Hurlbert, 2001. Thermal, mixing and oxygen regimes of the Salton Sea, California, 1997–1999. Hydrobiologia 466(Development in Hydrobiology 162): 159–176.
Welch, E. B. & G. D. Cooke, 1995. Internal phosphorus loading in shallow lakes: importance and control. Lake and Reservoir Management 11: 272–281.
Wilhelm, F. M., J. J. Hudson & D. W. Schindler, 1999. Contribution of Gammarus lacustris to phosphorus recycling in a fishless alpine lake. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 56: 1679–1686.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest Editor: John M. Melack
Saline Water and their Biota
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swan, B.K., Watts, J.M., Reifel, K.M. et al. Role of the polychaete Neanthes succinea in phosphorus regeneration from sediments in the Salton Sea, California. Hydrobiologia 576, 111–125 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0298-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0298-6