Abstract
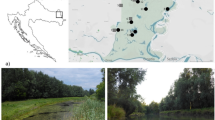
Temporary pools are numerous in coastal plains of Atlantic Morocco and have a rich and diverse flora. These habitats are increasingly under pressure by man impact through grazing by domestic livestock and the development of annual crops in their catchments. The objectives of this work were to evaluate the species richness and the species composition of the vegetation of a sample of 30 pools in this region, in order to assess the structure of the vegetation within pools and to evaluate the role of environmental and anthropogenic factors in their richness and species composition. The results highlighted the species richness of the pools with 300 species found among which annual species were heavily dominant. The structure of the vegetation varied within pools according to a topographical/flooding gradient and between pools in relation with the land use in the surrounding areas. Three vegetation belts were recognized from the centre to the periphery of the pool. The total species richness per pool was not found significantly related to environmental or anthropogenic factors. The species characteristics of the pools were found mostly in the centre and their number affected by hydrological factors and land use in the pool and in the surrounding areas. The species characteristics of woodland habitats and of agriculture crops were found mostly in the peripheral zone. Temporary pools maintain specific communities of both aquatic and amphibious species, probably because of the selection induced by water level variations. The peripheral zone, although often dominated by terrestrial species, is clearly interpreted as part of the pool. It contains amphibious species highly characteristic of the pool for which the irregular flooding is a key environmental factor which decreases competition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. J. Anderson B. Vondracek (1999) ArticleTitleInsects as indicators of land use in three ecoregions in the Prairie Pothole Region Wetlands 19 648–664 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF03161702
E. T. Bauder (2000) ArticleTitleInundation effects on small-scale plant distributions in San Diego, California vernal pools Aquat. Ecol. 34 43–61 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1009916202321
Braun-Blanquet, J., 1936. Un joyau floristique et phytosociologique, L’Isoetion méditerranéen. SIGMA, Comm 42
J. S. Brewer J. M. Levine M. D. Bertness (1997) ArticleTitleEffects of biomass removal and elevation on species richness in a New England Salt marsh Oikos 80 333–341
A. Bonis J. Lepart P. Grillas (1995) ArticleTitleSeed bank dynamics and coexistence of annual macrophytes in a temporary and variable habitat Oikos 74 81–92
G. Chevassut P. Quézel (1956) ArticleTitleContribution à l’étude des groupements végétaux des mares transitoires à Isoetes velata et des dépressions humides à Isoetes histrix en Afrique du nord Bull. Soc. Hist. Nat. Afrique du Nord 47 59–73
K. Crosslé M.A. Brock (2002) ArticleTitleHow do water regime and clipping influence plant establishment from seed banks and subsequent reproduction? Aquat. Bot. 74 43–56 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0304-3770(02)00034-7
Fennich, M.F., 1990. Etude des groupements d’adventices dans les principales cultures de la province de Benslimane. (Study of Groupings of Adventitious Plants in the Main Agricultural Areas of the Province of Benslimane.) Thèse de 3ème cycle, Université Mohammed V, Rabat, 243
L. Gough J. B. Grace (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of flooding, salinity and herbivory on coastal plant communities, Louisiana, United States Oecologia 117 527–535 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050689
N. M. Hill P. Keddy (1992) ArticleTitlePrediction of rarities from habitat variables : Coastal plain plants on Nova Scotian lakeshores Ecology 73 1852–1859 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1940036
Jahandiez, E. & R. Maire, 1931 (Vol. I), 1932 (Vol. II), 1934 (Vol. III). Catalogue des plantes du Maroc. Minerva, Alger
J. Lenssen F. Menten W. V. D. Putten K. Bloom (1999) ArticleTitleControl of plant species richness and zonation of functional groups along a freshwater flooding gradient Oikos 86 523–534
Maire R., 1952–1987. Flore de l’Afrique du Nord (Flora of North Africa). Vol. 16. Lechevalier, Paris
F. Médail H. Michaud J. Molina G. Paradis R. Loisel (1998) ArticleTitleConservation de la flore et de la végétation des mares temporaires dulçaquicoles et oligotrophes de France méditerranéenne Ecol. Mediter. 24 119–134
Metge, G., 1986. Etude des écosystèmes hydromorphes (dayas et merjas) de la meseta occidentale marocaine. Thèse de Doctorat ès Sciences, Université d’Aix-Marseille III, 280 pp
P. Quézel (1998) ArticleTitleLa végétation des mares transitoires à Isoetes en région méditerranéenne, intérêt patrimonial et conservation Ecol. Mediter. 24 111–117
Rhazi, L., 1990. Sur le traitement de l’information phyto-écologiques de quelques dayas temporaires de la province de Benslimane ‘‘Ouest Marocain ’’. Thèse de 3ème cycle Université Mohammed V Rabat
L. Rhazi P. Grillas A. Mounirou Touré L. Tan Ham (2001a) ArticleTitleImpact of land use and activities on water, sediment and vegetation of temporary pools in Morocco C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris. Life Sciences 324 165–177 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7ovFChsA%3D%3D
L. Rhazi P. Grillas L. Tan Ham D. El Khyari (2001b) ArticleTitleThe seed bank and the between years dynamics of the vegetation of a Mediterranean temporary pool (NW Morocco) Ecol. Mediter. 27 69–88
Thiery, A., 1987. Les crustacés branchiopodes des milieux limniques temporaires (dayas) au Maroc. Taxonomie, biogéographie, écologie. Thèse Doctorat ès Sciences, Univ. d’Aix Marseille III, 405 pp
P. H. Zedler (1987) ArticleTitleThe ecology of Southern California Vernal Pools: a Community Profile U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Biological Report 85 7–11
Zidane, L., 1990. Etude bioclimatique et étude phyto-écologique des forêts de la province de Benslimane “Ouest marocain”. (Bioclimatic Study and Phyto-ecological Study of the Woodland of the West Moroccan Province of Benslimane.). Thèse 3ème cycle Univ. Mohammed V, Rabat, 187 pp
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhazi, L., Rhazi, M., Grillas, P. et al. Richness and structure of plant communities in temporary pools from western Morocco: influence of human activities. Hydrobiologia 570, 197–203 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0180-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0180-6