Abstract
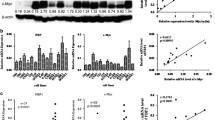
Gene expression profiling had revealed that TGF-β superfamily type I receptor (also known as activin receptor-like kinase-1, ALK1) and TGFβR2 (TGF-β type II receptor) were down-regulated in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) (P < 0.05, respectively). However, no study with significantly large clinical samples to address the relevance of ALK1 and TGFβR2 in NPC progression or in patient outcomes has been reported. This study aims to assess the possible correlations of ALK1 and TGFβR2 expression with NPC progression and their potential prognostic predictive ability in NPC outcomes. ALK1 and TGFβR2 mRNA and protein levels were detected by qRT-PCR and NPC tissue microarray (TMA), which included 742 tissue cores. Both mRNA and protein levels of ALK1 and TGFβR2 were significantly lower in the cancer tissues compared with the non-cancerous tissues (P < 0.05). Epstein-Barr virus small RNA (EBER-1) hybridization signals in NPC showed significant associations with ALK1 and TGFβR2 proteins (P = 0.000 and 0.003, respectively). In the final logistic regression analysis model, the abnormal expression of ALK1 and TGFβR2 were found to be independent contributors to nasopharyngeal carcinogenesis (P = 0.000 and 0.000, respectively). A survival analysis revealed that ALK1 (Disease Free Survival (DFS): P = 0.002, Overall Survival (OS): P = 0.007) and TGFβR2 (DFS: P = 0.072, OS: P = 0.045) could predict the prognosis of NPC patients. The positive expression of ALK1 and TGFβR2 were independent risk factors for DFS and OS in multivariate analyses (DFS: P = 0.001 and 0.420, respectively; OS: P = 0.018 and 0.047, respectively). These results suggest that ALK1 and TGFβR2 may be useful prognostic biomarkers in NPC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NPC:
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- TMA:
-
Tissue microarray
- DFS:
-
Disease free survival
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
References
Albiñana V, Sanz-Rodríguez F, Recio-Poveda L, Bernabéu C, Botella LM (2011) Immunosuppressor FK506 increases endoglin and activin receptor-like kinase 1 expression and modulates transforming growth factor-β1 signaling in endothelial cells. Mol Pharmacol 79(5):833–843
Attisano L, Cárcamo J, Ventura F, Weis FM, Massagué J, Wrana JL (1993) Identification of human activin and TGF beta type I receptors that form heteromeric kinase complexes with type II receptors. Cell 75(4):671–680
Carter KL, Cahir-McFarland E, Kieff E (2002) Epstein-Barr virus induced changes in B-lymphocyte gene expression. J Virol 76(20):10427–10436
Chang ET, Adami HO (2006) The enigmatic epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15(10):1765–1777
Fan SQ, Ma J, Zhou J, Xiong W, Xiao BY, Zhang WL, Tan C, Li XL, Shen SR, Zhou M, Zhang QH, Ou YJ, Zhuo HD, Fan S, Zhou YH, Li GY (2006) Defferential expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded RNA and several tumor-related genes in various types of nasopharyngeal epithelial lesions and nasopharyngeal carcinoma using tissuemicroarray analysis. Hum Pathol 37(5):593–605
Fang W, Li X, Jiang Q, Liu Z, Yang H, Wang S, Xie S, Liu Q, Liu T, Huang J, Xie W, Li Z, Zhao Y, Wang E, Marincola FM, Yao K (2008) Transcriptional patterns, biomarkers and pathways characterizing nasopharyngeal carcinoma of Southern China. J Transl Med 6:32
Fukai Y, Fukuchi M, Masuda N, Osawa H, Kato H, Nakajima T, Kuwano H (2003) Reduced expression of transforming growth factor-b receptors is an unfavorable prognostic factor in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 104(2):161–166
Garrigue-Antar L, Souza RF, Vellucci VF, Meltzer SJ, Reiss M (1996) Loss of transforming growth factor-b type II receptor gene expression in primary human esophageal cancer. Lab Invest 75(2):263–272
Gobbi H, Arteaga CL, Jensen RA, Simpson JF, Dupont WD, Olson SJ, Schuyler PA, Plummer WD Jr, Page DL (2000) Loss of expression of transforming growth factor b type II receptor correlates with high tumour grade in human breast in situ and invasive carcinomas. Histopathology 36(2):168–177
Goumans MJ, Valdimarsdottir G, Itoh S, Rosendahl A, Sideras P, ten Dijke P (2002) Balancing the activation state of the endothelium via two distinct TGFbeta type I receptors. EMBO J 21(7):1743–1753
Goumans MJ, Valdimarsdottir G, Itoh S, Lebrin F, Larsson J, Mummery C, Karlsson S, ten Dijke P (2003) Activin receptor-like kinase (ALK)1 is an antagonistic mediator of lateral TGFbeta/ALK5 signaling. Mol Cell 12(4):817–828
Gu Y, Jin P, Zhang L, Zhao X, Gao X, Ning Y, Meng A, Chen YG (2006) Functional analysis of mutations in the kinase domain of the TGFβ receptor ALK1 reveals different mechanisms for induction of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Blood 107(5):1951–1954
Guo RJ, Wang Y, Kaneko E, Wang DY, Arai H, Hanai H, Takenoshita S, Hagiwara K, Harris CC, Sugimura H (1998) Analyses of mutation and loss of heterozygosity of coding sequences of the entire transforming growth factor b type II receptor gene in sporadic human gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis 19(9):1539–1544
Heng DM, Wee J, Fong KW, Lian LG, Sethi VK, Chua ET, Yang TL, Khoo Tan HS, Lee KS, Lee KM, Tan T, Chua EJ (1999) Prognostic factors in 677 patients in Singapore with nondisseminated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 86(10):1912–1920
Hong MH, Mai HQ, Min HQ, Ma J, Zhang EP, Cui NJ (2000) A comparison of the Chinese 1992 and fifth-edition international union against cancer staging systems for staging nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 89(2):242–247
Izumoto S, Arita N, Ohnishi T, Hiraga S, Taki T, Tomita N, Ohue M, Hayakawa T (1997) Microsatellite instability and mutated type II transforming growth factor-b receptor gene in gliomas. Cancer Let 112(2):251–256
Jones JO, Arvin AM (2003) Microarray analysis of host cell gene transcription in response to varicella-zoster virus infection of human T cells and fibroblasts in vitro and SCIDhu skin xenografts in vivo. J Virol 77(2):1268–1280
Kawamata H, Furihata T, Omotehara F, Sakai T, Horiuchi H, Shinagawa Y, Imura J, Ohkura Y, Tachibana M, Kubota K, Terano A, Fujimori T (2003) Identification of genes differentially expressed in a newly isolated human metastasizing esophageal cancer cell line, T.Tn-AT1, by cDNA microarray. Cancer Sci 94(8):699–706
Kim IY, Ahn HJ, Zelner DJ, Shaw JW, Lang S, Kato M, Oefelein MG, Miyazono K, Nemeth JA, Kozlowski JM, Lee C (1996) Loss of expression of transforming growth factor b type I and type II receptors correlates with tumor grade in human prostate cancer tissues. Clin Cancer Res 2(8):1255–1261
Kim IY, Ahn HJ, Lang S, Oefelein MG, Oyasu R, Kozlowski JM, Lee C (1998) Loss of expression of transforming growth factor-b receptors is associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 4(7):1625–1630
Kim WS, Park C, Hong SK, Park BK, Kim HS, Park K (2000) Microsatellite instability (MSI) in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is highly associated with transforming growth factor-b type II receptor (TGF-b RII) frameshift mutation. Anticancer Res 20(3A):1499–1502
Lim CC, Yahaya H (2003) Second report of the national cancer registry cancer incidence in Malaysia. National Cancer Registry, Ministry of Health, Malaysia
Lynch MA, Nakashima R, Song H, DeGroff VL, Wang D, Enomoto T, Weghorst CM (1998) Mutational analysis of the transforming growth factor b receptor type II gene in human ovarian carcinoma. Cancer Res 58(19):4227–4232
Ma BB, Poon TC, To KF, Zee B, Mo FK, Chan CM, Ho S, Teo PM, Johnson PJ, Chan AT (2003) Prognostic significance of tumor angiogenesis, Ki67, p53 oncoprotein, epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2 receptor protein expression in undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a prospective study. Head Neck 25(10):864–872
Ma BB, Leungm SF, Hui EP, Mo F, Kwan WH, Zee B, Yuen J, Chan AT (2004) Prospective validation of serum CYFRA 21-1, beta-2-microglobulin, and ferritin levels as prognostic markers in patients with nonmetastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma undergoing radiotherapy. Cancer 101(4):776–781
Markowitz S, Wang J, Myeroff L, Parsons R, Sun L, Lutterbaugh J, Fan RS, Zborowska E, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1995) Inactivation of the type II TGF-b receptor in colon cancer cells with microsatellite instability. Science 268(5215):1336–1338
McDermott AL, Dutt SN, Watkinson JC (2001) The aetiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 26(2):82–92
Myeroff LL, Parsons R, Kim SJ, Hedrick L, Cho KR, Orth K, Mathis M, Kinzler KW, Lutterbaugh J, Park K (1995) A transforming growth factor b receptor type II gene mutation common in colon and gastric but rare in endometrial cancers with microsatellite instability. Cancer Res 55(23):5545–5547
Nagai M, Kawarada Y, Watanabe M, Iwase T, Muneyuki T, Yamao K, Fukutome K, Yatani R (1999) Analysis of microsatellite instability, TGF-b type II receptor gene mutations and hMSH2 and hMLH1 allele losses in pancreaticobiliary maljunction-associated biliary tract tumors. Anticancer Res 19(3A):1765–1768
Parsons R, Myeroff LL, Liu B, Willson JK, Markowitz SD, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1995) Microsatellite instability and mutations of the transforming growth factor b type II receptor gene in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 55(23):5548–5550
Sakata K, Hareyama M, Tamakawa M, Oouchi A, Sido M, Nagakura H, Akiba H, Koito K, Himi T, Asakura K (1999) Prognostic factors of nasopharynx tumors investigated by MR imaging and the value of MR imaging in the newly published TNM staging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 43(2):273–278
Schneider J, Gonzalez-Roces S, Pollán M, Lucas R, Tejerina A, Martin M, Alba A (2001) Expression of LRP and MDR1 in locally advanced breast cancer predicts axillary node invasion at the time of rescue mastectomy after induction chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res 3(3):183–191
Seki T, Yun J, Oh SP (2003) Arterial endothelium-specific activin receptorlike kinase 1 expression suggests its role in arterialization and vascular remodeling. Circ Res 93(7):682–689
Shanmugaratnam K, Chan SH, de-Thé G, Goh JE, Khor TH, Simons MJ, Tye CY (1979) Histopathology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlations with epidemiology, survival rates and other biological characteristics. Cancer 44(3):1029–1044
Taheri-Kadkhoda Z, Magnusson B, Svensson M, Mercke C, Björk-Eriksson T (2009) Expression modes and clinical manifestations of latent membrane protein1, Ki-67, cyclin-B1, and epidermal growth factor receptor in nonendemic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 31(4):482–492
Tani M, Takenoshita S, Kohno T, Hagiwara K, Nagamachi Y, Harris CC, Yokota J (1997) Infrequent mutations of the transforming growth factor b-type II receptor gene at chromosome 3p22 in human lung cancers with chromosome 3p deletions. Carcinogenesis 18(5):1119–1121
Tatsumi-Tamori A, Yoshizaki T, Miwa T, Furukawa M (2000) Clinical evaluation of staging system for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: comparison of fourth and fifth editions of UICC TNM classification. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 109(12 Pt 1):1125–1129
Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G (2001) Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(9):5116–5121
Wang LF, Chai CY, Kuo WR, Tai CF, Lee KW, Ho KY (2006) The prognostic value of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and p53 protein expression in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Acta Otolaryngol 126(7):769–774
Xiang Y, Yao H, Wang S, Hong M, He J, Cao S, Min H, Song E, Guo X (2006) Prognostic value of survivin and livin in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope 116(1):126–130
Xiong W, Zeng ZY, Xia JH, Xia K, Shen SR, Li XL, Hu DX, Tan C, Xiang JJ, Zhou J, Deng H, Fan SQ, Li WF, Wang R, Zhou M, Zhu SG, Lü HB, Qian J, Zhang BC, Wang JR, Ma J, Xiao BY, Huang H, Zhang QH, Zhou YH, Luo XM, Zhou HD, Yang YX, Dai HP, Feng GY, Pan Q, Wu LQ, He L, Li GY (2004) A susceptibility locus at chromosome 3p21 linked to familial nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res 64(6):1972–1974
Xiong W, Wu X, Starnes S, Johnson SK, Haessler J, Wang S, Chen L, Barlogie B, Shaughnessy JD Jr, Zhan F (2008) An analysis of the clinical and biologic significance of TP53 loss and the identification of potential novel transcriptional targets of TP53 in multiple myeloma. Blood 112(10):4235–4246
Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Zhang W, Li X, Xiong W, Liu H, Fan S, Qian J, Wang L, Li Z, Shen S, Li G (2006) Family-based association analysis validates chromosome 3p21 as a putative nasopharyngeal carcinoma susceptibility locus. Genet Med. 8(3):156–160
Zeng ZY, Zhou YH, Zhang WL, Xiong W, Fan SQ, Li XL, Luo XM, Wu MH, Yang YX, Huang C, Cao L, Tang K, Qian J, Shen SR, Li GY (2007a) Gene expression profiling of nasopharyngeal carcinoma reveals the abnormally regulated Wnt signaling pathway. Hum Pathol 38(1):120–133
Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Xiong W, Luo X, Zhang W, Li X, Fan S, Cao L, Tang K, Wu M, Li G (2007b) Analysis of gene expression identifies candidate molecular markers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma using microdissection and cDNA microarray. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 133(2):71–81
Zeng Z, Huang H, Zhang W, Xiang B, Zhou M, Zhou Y, Ma J, Yi M, Li X, Li X, Xiong W, Li G (2011) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: advances in genomics and molecular genetics. Sci China Life Sci 54(10):966–975
Zhang HT, Chen XF, Wang MH, Wang JC, Qi QY, Zhang RM, Xu WQ, Fei QY, Wang F, Cheng QQ, Chen F, Zhu CS, Tao SH, Luo Z (2004) Defective expression of transforming growth factor b receptor type II is associated with CpG methylated promoter in primary non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10(7):2359–2367
Zhang W, Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Xiong W, Fan S, Xiao L, Huang D, Li Z, Li D, Wu M, Li X, Shen S, Wang R, Cao L, Tang K, Li G (2009) Identification of aberrant cell cycle regulation in Epstein-Barr virus-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma by cDNA microarray and gene set enrichment analysis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 41(5):414–428
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Ear, Nose and Throat (ENT) department at Xiangya Hospital, the Second Xiangya Hospital and the Tumor Hospital of Hunan Province for providing our NPC samples. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 30871282, 30871365, 81172189, 81071644, 30971147, 81171930, 81071820), the 111 Project (Grant No. 111-2-12), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Grant Nos. 10JJ7003), the Fok Ying Tong Education Foundation (121036) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2011JQ020).
Conflicts of interest
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10735_2012_9392_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig 1 Our cDNA microarray data was reanalyzed using SAM software. The results suggested that there were 488 down-regulated genes and 278 up-regulated genes in NPC. Among these differentially expressed genes, ALK1 and TGFβR2 were both down-regulated in NPC. (TIFF 761 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zeng, Z., Fan, S. et al. Evaluation of the prognostic value of TGF-β superfamily type I receptor and TGF-β type II receptor expression in nasopharyngeal carcinoma using high-throughput tissue microarrays. J Mol Hist 43, 297–306 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9392-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-012-9392-4