Abstract
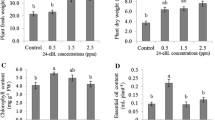
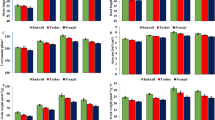
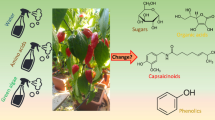
The effects of spraying two brassinosteroid analogues, DI-31 and DI-100, were evaluated at concentrations of 4, 8 and 12 ppm together with a seaweed extract and amino acid mixture called Tomex Amin (2.5 l/ha) to enhance their activity. These were sprayed ten times to foliage of pepper var. Orlando grown under greenhouse conditions. Treatment with DI-31 at a dose of 12 ppm (30 mg/ha) resulted in the highest production increases, which were 13.55 % relative to the control with Tomex Amin (T02). Correlation between net photosynthesis increase and yield increase due to DI-31 treatment, which produced the maximum yield increase and also the highest net photosynthesis with significant differences with respect to the control, was observed. This increased yield was caused by an increase in pepper/plant number. The physic-chemical variables related to pepper quality, such as fresh weight, h/d ratio, lobe number/fruit, firmness, colour and ripening index, were similar in the control and treated peppers. Total antioxidant activity and phenolic content was higher in pepper treated over T02. The results showed that sprayed DI-31 may play an important role in increasing the yield of field grown pepper due to an increase in fruits number per plant without any undesirable effects on their nutritive and organoleptic properties.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BB16:
-
Biobrás 16
- BR:
-
Brassinosteroid
- BRs:
-
Brassinosteroids
- RI:
-
Ripening index
- TAA:
-
Total antioxidant activity
- TSS:
-
Total soluble solids
References
Akbudak N, Akbudak B, Seniz V (2007) Foliar applied harpin effects on fruit quality of peppers. Acta Agric Scand Sec B Soil Plant Sci 57:82–86. doi:10.1080/09064710600571622
Ali B, Hayat S, Aiman Hasan S, Ahmad A (2006) Effect of root applied 28-homobrassinolide on the performance of Lycopersicon esculentum. Sci Hortic 110:267–273. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2006.07.015
Ali B, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2007) 28-Homobrassinolide ameliorates the saline stress in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Environ Exp Bot 59:217–223. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2005.12.002
Amorós A, Pretel MT, Almansa MS, Botella MA, Zapata PJ, Serrano M (2009) Antioxidant and nutritional properties of date fruit from Elche grove as affected by maturation and phenotypic variability of date palm. Food Sci Technol Int 15:65–72. doi:10.1177/1082013208102758
Cano A, Hernández-Ruíz J, García-Canovas F, Acosta M, Arnao MB (1998) And end-point method for estimation of the total antioxidant activity in plant material. Phytochem Anal 9:196–202
Churikova VV, Chozhainova GN, Eprintsev AT (1999) The action of epin on the activity of malatdehydrogenase in seedlings of cucumber plants. In: Shevelucha VS, Karlov GI, Karsunkina NP, Salnikova EI, Skorobogatova IV, Siusheva AG (eds) Regulators of plant growth and development 5. Agricultural Academy, Moscow, p 141
Coll MF, Jomarrón RIM, Robaina RCM, Alonso BEM, Cabrera PMT (1995) Polyhydroxyspirostanones as plant growth regulators. PCT Int. Appl. CO 7 J 71.100. AOIN 45.00 WO 97.13780
Del Amor FM (2006) Growth, photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence of sweet pepper plants as affected by the cultivation method. Ann App Biol 148:133–139. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7348.2006.00048.x
Esposito D, Komarnytsky S, Shapses S, Raskin I (2011) Anabolic effect of plant brassinosteroid. FASEB J 25:3708–3719. doi:10.1096/fj.11-181271
Fariduddin Q, Hasan SA, Ali B, Hayat S, Ahmad A (2008) Effect of modes of application of 28-homobrassinolide on mung bean. Turkish J Biol 32:17–21
Flores P, Navarro JM, Garrido C, Rubio JS, Martínez V (2004) Influence of Ca2+, K+ and NO3 − fertilisation on nutritional quality of pepper. J Sci Food Agric 84:569–574. doi:10.1002/jsfa.1694
Flores P, Castellar I, Hellín P, Fenoll J, Navarro J (2007) Response of pepper plants to different rates of mineral fertilizers after soil biofumigation and solarisation. J Plant Nutr 30:367–379. doi:10.1080/01904160601171264
Flores P, Hellín P, La Casa A, López A, Fenoll J (2009) Pepper antioxidante compositions affected by organic, low-input and soilles cultivation. J Sci Food Agric 89:2267–2274. doi:10.1002/jsfa.3719
Garcia-Closas R, Berenguer A, Tormo MJ et al (2004) Dietary sources of vitamin C, vitamin E and specific carotenoids in Spain. Brit J Nutr 91:1005–1011. doi:10.1079/BJN20041130
Gomes MMA, Compostrini E et al (2006) Brassinosteroid analogue effects on the yield of yellow passion fruit plants (Passiflora edulis f. flavicarpa). Sci Hortic 110:235–240. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2006.06.030
Hayat S, Ahmad A (2003) Soaking seeds of Lens culinaris with 28-homobrassinolide increased nitrate reductase activity and grain yield in the field in India. Ann Appl Biol 143:121–124. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7348.2003.tb00276.x
Hayat A, Ahmad A, Mobin M, Fariduddin Q, Azam ZM (2001) Carbonic anhydrase, photosynthesis, and seed yield in mustard plants treated with phytohormones. Plant Physiol Sec 39:111–114
Hayat S, Ali B, Hasan A, Ahmad A (2007) Brassinosteroid enhanced the level of antioxidants under cadmium stress in Brassica juncea. Environ Exp Bot 60:33–41. doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.06.002
Holá D, Rothová O, Koĉová M, Kohout L, Kvasnic M (2010) The effect of brassinosteroids on the morphology, development and yield of field-grown maize. Plant Growth Regul 61:29–43. doi:10.1007/s10725-010-9446-0
Hutton MG, Handley DT (2007) Bell pepper cultivar performance under short, variable growing seasons. Hort Technol 17:136–141
Janeczko A, Biesaga-Kościelniak J, Oklešt′ková J et al (2010) Role of 24-epibrassinolide in wheat production: physiological effects and uptake. J Agron Crop Sci 196:311–321. doi:10.1111/j.1439-037X.2009.00413.x
Kandelinskaya OL, Topunov AF, Grishchenko ER (2007) Biochemical aspects of growth-stimulating effects of steroid phytohormones on lupine plants. Appl Biochem Micro 43:324–331. doi:10.1134/S0003683807030155
Kang YY, Guo SR (2011) Role of brassinosteroids on horticultural crops. In: Hayat S, Ahmad A (eds) Brassinosteroids,a class of plant hormone. Springer, Berlin, pp 269–288
Kartal G, Temel A, Arican E, Gozukirmizi N (2009) Effects of brassinosteroids on barley root growth, antioxidant system and cell division. Plant Growth Regul 58:261–267. doi:10.1007/s10725-009-9374-z
Lisso J, Altmann T, Müssing C (2006) Metabolic changes in fruits of the tomato dx mutant. Phytochemistry 67:2232–2238. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.07.008
Lycoskoufis IH, Savvas D, Mavrogianopoulos G (2005) Growth, gas exchange, and nutrient status in pepper (Capsicum annum L.) grown in recirculating nutrient solution as affected by salinity imposed to half of the root system. Sci Hortic 106:147–161. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2005.02.022
Madeira AC, De Varennes A (2005) Use of chlorophyll meter to assess the effect of nitrogen on sweet pepper development and growth. J Plant Nutr 28:1133–1144. doi:10.1081/PLN-200063133
Marcelis LFM, Heuvelink E, Hofman-Eijer LRB, Bakker JD, Xue LB (2004) Flower and fruit abortion in sweet pepper in relation to source and sink strength. J Exp Bot 55:2261–2268. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh245
Mazorra LM, Núñez M, Nápoles MC, Yoshida S, Robaina C, Coll F, Asami T (2004) Effects of structural analogs of brassinosteroids on the recovery of growth inhibition by a specific brassinosteroid biosynthesis inhibitor. Plant Growth Regul 44:183–185
Montoya T, Nomura T, Yokota T et al (2005) Patterns of dwarf expression and brassinosteroid accumulation in tomato reveal the importance of brassinosteroid synthesis during fruit development. Plant J 42:262–269. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02376.x
Navarro JM, Flores P, Garrido C, Martinez V (2006) Changes in the contents of antioxidants compounds in pepper fruits at different ripening stages, as affected by salinity. Food Chem 96:66–73. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.01.057
Núñez M, Torres W, Coll F (1995) Efectividad de un análogo de brasinoesteroide sobre el rendimiento de plantas de papa y tomate. Cultivos Tropicales 16:26–27
Núñez M, Robaina C, Coll F (2003) Synthesis and practical applications of brassinosteroid analogs. In: Hayat S, Ahmad A (eds) Brassinosteroids: bioactivity and crop productivity. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Papadopoulou E, Grumet R (2005) Brassinosteroid-induced femaleness in cucumber and relationship to ethylene production. Hortic Sci 40:1763–1767
Peng J, Tang X, Feng H (2004) Effects of brassinolide on the physiological properties of litchi pericarp (Litchi chinensis cv. Nuomoci). Sci Hortic 101:407–416. doi:10.1016/j.sicienta.2003.11.012
Pirogovskaya GV, Bogdevitch IM, Naumova GV, Khripach VA, Azizbekyan SG, Krul LP (1996) New forms of mineral fertilizers with additives of plant growth regulators. Proc Plant Growth Regul Soc Am 23:146–151
Singh I, Shono M (2005) Physiological and molecular effects of 24-epibrassinolide, a brassinosteroid on thermotolerance of tomato. Plant Growth Regul 47:111–119. doi:10.1007/s10725-005-3252-0
Swamy KN, Rao SSR (2008) Influence of 28-homobrassinolide on growth, photosynthesis metabolite and essential oil content of geranium [Pelargonium graveolens (L.) Herit]. Am J Plant Physiol 3:173–174
Symons GM, Davies C, Shavrukov Y, Dry IB, Reid JB, Thomas, MR (2006) Grapes on steroids. Brassinosteroids are involved in grape berry ripening. Plant Physiol 140: 150–158. doi/10.1104/pp.105.070706
Turner AD, Wien HC (1994) Photosynthesis, dark respiration and bud sugar concentrations in pepper cultivars differing in susceptibility to stress-induced bud abscission. Ann Bot 73:623–628
Vardhini BV, Rao SSR (1998) Effect of brassinosteroids on growth, metabolite content and yield of Arachis hypogaea. Phytochemistry 48:927–930
Vardhini BV, Rao SSR (2002) Acceleration of ripening of tomato pericarp discs by brassinosteroids. Phytochemistry 61:843–847
Vardhini BV, Anuradha S, Rao SSR (2006) Brassinosteroids-new class of plant hormones with potential to improve crop productivity. Indian J Plant Physiol 11:1–12
Warusavitharana AJ, Tambe TB, Kshirsagar DB (2008) Effect of cytokinins and brassinosteroid with gibberellic acid on yield and quality of Thompson seedless grapes. Acta Hortic 785:217–224
Wood JE, Senthilmohan ST, Peskin AV (2002) Antioxidant activity of procyanidin-containing plant extracts at different pHs. Food Chem 77:155–161
Wu CY, Trieu A, Radhakrishnan P, Kwok SF, Harris S, Zhang K, Wang J, Wan J, Zhai H, Takatsuto S, Matsumoto S, Fujioka S, Feldmann KA, Pennell RI (2008) Brassinosteroids regulate grain filling in rice. Plant Cell 20:2130–2145. doi:10.1105/tpc.107.055087
Wubs AM, Heuvelink E, Marcelis LFM (2009) Abortion of reproductive organs in sweet pepper (Capsicum annum L.): a review. J Hortic Sci Biotech 84:467–475
Xia XJ, Huang LF, Zhou YH, Mao WH, Shi K, Wu JX, Asami T, Chen Z, Yu JQ (2009) Brassinosteroids promote photosynthesis and growth by enhancing activation of rubisco and expression of photosynthetic genes in Cucumis sativus. Planta 230:1185–1196. doi:10.1007/s00425-009-1016-1
Yu JQ, Huang LF, Hu WH, Zhou YH, Mao WH, Ye SF, Nogues S (2004) A role for brassinosteroids in the regulation of photosynthesis in Cucumis sativus. J Exp Bot 55:1135–1143. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh124
Zhu JH, Li XL, Christie P, Li JL (2005) Environmental implications of low nitrogen use efficiency in excessively fertilized hot pepper (Capsicum frutescens L.) cropping systems. Agr Ecosyst Environ 111:70–80. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2005.04.025
Zullo MAT, Adam G (2002) Brassinosteroid phytohormones–structure, bioactivity and applications. Braz J Plant Physiol 14:143–181
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Consellería de Educación of the Generalitat Valenciana for financial support (GV07/016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serna, M., Hernández, F., Coll, F. et al. Brassinosteroid analogues effects on the yield and quality parameters of greenhouse-grown pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Plant Growth Regul 68, 333–342 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-012-9718-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-012-9718-y