Abstract
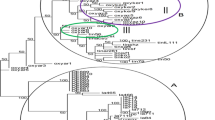
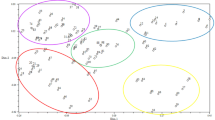
Genetic diversity and relationships among 48 safflower accessions were evaluated using 22 inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSR) primers. A total of 429 bands were amplified, and 355 bands (about 82.7%) were polymorphic. Five to forty-one polymorphic bands could be amplified by each primer, with an average of 16.1 polymorphic bands per primer. The results showed that the polymorphism of the safflower germplasm was higher at the DNA level. All the 48 accessions could be distinguished by ISSR markers and were divided into 9 groups based on ISSR GS by using UPGMA method. The genetic relationships among the accessions from different continents were closer. Comparatively, the genetic diversity of the accessions originated from Asia was higher, from Europe assembled. The results also showed that the genetic variation of accessions from Indian and Middle Eastern safflower diversity centers were relatively higher. ISSR is an effective and promising marker system for detecting genetic diversity among safflower and give some useful information on its phylogenic relationships.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amiri RM, Azdi SB, Ghanadha MR, Abd MC (2001) Detection of DNA polymorphism in landrace populations of safflower in Iran using RAPD-PCR technique. Iranian J Agri Sci 32(4):737–745
Ash GJ, Raman R, Crump NS (2003) An investigation of genetic variation in Carthamus lanatus in New South Wales, Australia, using intersimple sequence repeats (ISSR) analysis. Weed Res Oxford 43(3):208–213
Blair MW, Panaud O, McCouch SR (1999) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) amplication for analysis of microsatellite motif frequency and fingerprinting in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 98(5):780–792
Budak H, Shearman RC, Parmaksiz I, Dweikat I (2004) Comparative analysis of seeded and vegetative biotype buffalograsses based on phylogenetic relationship using ISSRs, SSRs, RAPDs, and SRAPs. Theor Appl Genet 109(2):280–288
Casaoli M, Mattion C, Cherubini M, Villani F (2001) A genetic linkage map of European chestnut (Castanea sativa Mill.) based on RAPD, ISSR and isozyme markers. Theor Appl Genet102(8):1190–1199
Cekic C, Battey NH, Wilkinson MJ (2001) The potential of ISSR-PCR primer-pair combinations for genetic linkage analysis using the seasonal flowering locus in Fragaria as a mode. Theor Appl Genet103(4):540–546
Eiadthong W, Yonemori K, Sugiura A, Utsunomiya N, Subhadrabandhu S, Suranant S (1999) Identification of mango cultivars of Thailand and evaluation of their genetic variation using the amplified fragments by simple sequence repeat-(SSR-)anchored primers. Sic Hort 82(1–2):57–66
Fang DQ, Krueger RR, Roose ML, Fang DQ (1998) Phylogenetic relationships among selected Citrus germplasm accessions revealed by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. J Am Soc Hort Sci 123(4):612–617
Fang DQ, Roose ML (1997) Identification of closely related citrus cultivars with inter-simple sequence repeat markers. Theor Appl Genet 95(3):408–417
Guo ML, Jiang W, Zhang ZZ, Zhang G, Mao JF, Yin M, Su ZW (2003) Randomly amplified polymorphic DNA technique in molecular identification of germplasms of Carthamus tinctorius L. Acad J Sec Mil Med Univ 24(10):1116–1119 (In Chinese)
Guo ML, Zhang ZY, Zhang HM, Li HF, Su ZW (1999) Studies on the pollen feature, bands of isozyme and contents of chemical components on cultivated population of safflower. Chin Pharm J 34(11):728–730 (In Chinese)
Joshi SP, Gupta VS, Aggarwal RK, Ranjekar PK, Brar DS (2000) Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship as revealed by inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism in the genus Oryza. Theor Appl Genet 100(8):1311–1320
Nagaoka T, Ogihara Y (1997) Applicability of inter-simple sequence repeat markers in wheat for use as DNA markers in comparison to RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 94(5):597–602
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Pomper KW, Crabtree SB, Browm SP, Jones SC, Bonney TM, Layne DR (2003) Assessment of genetic diversity of pawpaw (Asimina triloba) cultivars with intersimple sequence repeat markers. J Am Soc Hort Sci 128(4):521–525
Potter D, Gao FY, Aliello G, Leslie C, McGranahan G (2002) Intersimple sequence repeat markers for fingerprinting and determining genetic relationships of walnut (Juglans regia) cultivars. Am Soc Hort Sic 127(1):75–81
Qian W, Ge S, Hong DY (2000) Assessment of genetic variation of Oryza granulata detected by RAPDs and ISSRs. Acta Botanica Sinica 42(7):741–750 (In Chinese)
Rohlf FJ (1993) NTSYS-pc version 11.80. Distribution by Exeter Software, Setauket, New York
Saghai-Maroof MA, Biyashev RM, Yang GP, Zhang Q, Allard RW (1984) Extraordarily polymorphic microsatellite DNA in barly: species diversity, chromosomal locations, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:5466–5470
Sanguinelti CJ, Neto ED, Simpson AJG (1994) Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. BioTechniques 17:915–919
Tanyolac B (2003) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) and RAPD variation among wild barely (Hordeum vulgare subsp. spontaneum) populations from west Turkey. Genet Resour Crop Evol 50(6):611–614
Wu W, Zheng YL, Chen L, Wei YM, Yang RW, Yan ZH (2005) Evaluation of genetic relationships in the genus Houttuynia Thunb. in China based on RAPD and ISSR markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 33:1141–1157
Yuan GB, Han YZ, Li DJ, Wu ZR, Fan ZX (1989). Safflower’s germplasm resources and its exploitation. Science Press, Beijing, pp 30–42
Zhang ZW (2000) Studies on genetic diversity and classification of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) germplasm by isozyme techniques. J Plant Gene Res1(4):6–13 (In Chinese)
Zietkiwicz E, Rafaliski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplication. Genomics 20(2):176–183
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Bradley of American Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) for kindly providing 42 safflower accessions, Mr. Han Xinnian of Xinjiang Agricultural Academy of Science for providing Xinghong 1, Xinghong 4 and UC 26, Ms. Tang Li of Yaan Sanjiu Medicine Co. Ltd. for providing Chuanhong 1 and Jianyanghonghua accessions used in this experiment. And the experiment was accomplished in the lab of Gene Resource and Molecular Breeding in Sichuan Agricultural University. This work is financial supported by the Youth Science and Technology Foundation of Sichuan Province in China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, YX., Wu, W., Zheng, YL. et al. Genetic diversity and relationships among safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) analyzed by inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSRs). Genet Resour Crop Evol 54, 1043–1051 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-006-9192-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-006-9192-3