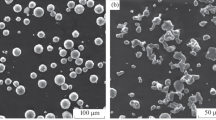
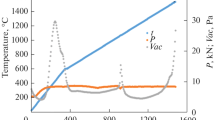
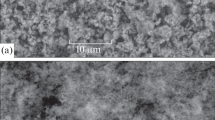
The dependences of the microstructure and physical-mechanical properties of Si3N4–TiN-based ceramic in a wide range of mass ratios of the components are examined. The sintering process and the accompanying physical and chemical processes, viz. the dependence of the hardness and density of the material on the ratios of the conducting phase of titanium nitride and the dielectric phase of silicon nitride with values above and below the percolation threshold, are examined. A ceramic based on pure titanium nitride with high physical-mechanical characteristics (H = 21.5 GPa) is obtained.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ching-Huan Lee, Horng-Hwa Lu and Chang-An Wang, et al., “Microstructure and mechanical properties of TiN/Si3N4 nanocomposites by spark plasma sintering (SPS),” J. Alloys Compounds, 508, 540 – 545 (2010).
Y. G. Gogotsi, “Particulate silicon nitride-based composites,” J. Mater. Sci., 29(10), 2541 – 2556 (1994).
J. L. Huang, S. Y. Chen, and M. T. Lee, “Microstructure, chemical aspects and mechanical properties of TiB2/Si3N4 and TiN/Si3N4 composites,” J. Mater. Res., 9(9), 2349 – 2354 (1994).
Z. Guo, G. Blugan, R. Kirchner, et al., “Microstructure and electrical properties of Si3N4/TiN composites sintered by hot pressing and spark plasma sintering,” Ceram. Int., 33, 1223 – 1229 (2007).
S. Balakrishnan, J. S. Burnellgray, and P. K. Datta, “Preliminary studies of TiN particulate-reinforced Si3N4 matrix composite (SYALON 501) following exposure in oxidizing and oxychloridizing environments,” Key Eng. Mater., 99(1), 279 – 290 (1995).
C. C. Liu and J. L. Huang, “Effect of the electrical discharge machining on strength and reliability of TiN/Si3N4 composites,” Ceram. Int., 29(6), 679 – 687 (2003).
M. Yoshimura, O. Komura, and A. Yamakawa, “Microstructure and tribological properties of nano-sized Si3N4,” Scr. Mater., 44(8 – 9), 1517 – 1521 (2001).
S. Kawano, J. Takahashi, and S. Shimada, “Highly electroconductive TiN/Si3N4 composite ceramics fabricated by spark plasma sintering of Si3N4 particles with a nano-sized TiN coating,” J. Mater. Chem., 12(2), 361 – 365 (2002).
L. Gao, J. G. Li, T. Kusunose, and K. Niihara, “Preparation and properties of TiN–Si3N4composites,” J. Europ. Ceram. Soc., 24(2), 381 – 386 (2004)
S. Kawano, J. Takahashi, and S. Shimada, “Fabrication of TiN/Si3N4 ceramics by spark plasma sintering of Si3N4 particles coated with nanosized TiN prepared by controlled hydrolysis of Ti(O-i-C3H7)4 ,” J. Amer. Ceram. Soc., 86(4), 701 – 705 (2003).
M. Tokita, “Mechanism of spark plasma sintering,” J. Mater. Sci., 5(45), 78 – 82 (2004).
V. I. Lysenko, A. G. Anisimov, and V. I. Mali, “Microhardness of ceramic obtained from oxide nanopowders by the conventional and SPS methods,” Steklo Keram., No. 12, 15 – 17 (2014); V. I. Lysenko, A. G. Anisimov, and V. I. Mali, “Microhardness of ceramic obtained from oxide nanopowders by the conventional and SPS methods,” Glass Ceram., 71(11 – 12), 431 – 433 (2014).
A. V. Hmelov and I. Shteins, “Properties of mullite-zirconium ceramic obtained by spark plasma sintering,” Steklo Keram., No. 12, 17 – 22 (2011); A. V. Hmelov and I. Shteins, “Properties of mullite-zirconium ceramic obtained by spark plasma sintering,” Glass Ceram., 68(11 – 12), 399 – 404 (2011).
E. Ayas, A. Kara, and F. Kara, “A novel approach for preparing electrically conductive α/β SiAlON–TiN composites by spark plasma sintering,” J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn., 116(7), 812 – 814 (2008).
A. A. Sivkov, A. S. Saigash, A. Ya. Pak, and A. A. Evdokimov, “Direct production of nanodisperse powders and compositions in a hypersonic jet of electric-discharge plasma,” Nanotekhnika, No. 2(18), 38 – 43 (200).
J. Wan, R.-G. Duan, and A. K. Mukherjee, “Spark plasma sintering of silicon nitride/silicon carbide nano-composites with reduced additive amounts,” Scr. Mater., 53, 663 – 667 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 10, pp. 32 – 37, October, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evdokimov, A.A., Sivkov, A.A. & Gerasimov, D.Y. Obtaining Ceramic Based on Si3N4 and TiN by Spark Plasma Sintering. Glass Ceram 72, 381–386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-016-9794-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10717-016-9794-y