Abstract
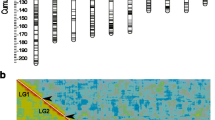
The mo (hereditary mosaic) mutation is one of the most famous and interesting mutations of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Females homozygous for mo generate mosaic and gynandromorphic offspring due to non-elimination of polar bodies and subsequent double fertilization events, irrespective of the genotype of the mated males. Although mo was first reported in 1927, the locus has not been mapped to linkage groups, as the mutation is unstable and appears to be sensitive to genetic background. In this study, linkage analysis of mo was performed using PCR-based markers on single nucleotide polymorphism linkage maps. Bombyx mandarina was used as the mating partner for the B. mori mo strain, as it is easier to identify polymorphic markers between B. mori and B. mandarina than within B. mori strains. Surprisingly, we identified two homozygous linkage groups (LGs) in all of the 12 B1 (first backcross generation) moths that had deposited mosaic eggs. It was revealed that +mo is located on the M chromosome of B. mandarina, which corresponds to two linkage groups of B. mori, LG 14 and 27. Based on further linkage analysis using B. mori as a mating partner, mo was mapped to LG 14. Additionally, we found that mo activity could be modified by a gene(s) on LG 17.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe H, Kobayashi M, Watanabe H (1990) Mosaic infection with a densonucleosis virus in the midgut epithelium of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Invertebr Pathol 55:112–117
Abe H, Yokoyama T, Oshiki T, Kobayashi M (1993) Analysis of the mechanism of nonsusceptibility to the densonucleosis virus (densovirus) type-2 in the silkworm, Bombyx mori, using a genetic mosaic. J Seric Sci Jpn 62:38–44 (in Japanese with English summary)
Banno Y, Nakamura T, Nagashima E, Fujii H, Doira H (2004) M chromosome of the wild silkworm, Bombyx mandarina (n = 27), corresponds to two chromosomes in the domesticated silkworm, Bombyx mori (n = 28). Genome 47:96–101
Banno Y, Fujii H, Kawaguchi Y, Yamamoto K, Nishikawa K (2005) A guide to the silkworm mutants: 2005 gene name and gene symbol. Kyusyu University, Fukuoka (in Japanese)
Banno Y, Yamamoto K, Nishikawa K, Tamura K, Yamamoto K, Aso Y (2010) Integration of the twenty-fourth and twenty-seventh linkage groups of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Insect Biotech Sericol 79:67–70
Ebinuma H, Kobayashi M, Kobayashi J, Shimada T, Yoshitake N (1988) The detection of mosaics and polyploids in the hereditary mosaic strain of the silk moth, Bombyx mori, using egg colour mutants. Genet Res 51:223–229
Goldschmidt R, Katsuki K (1931) Vierte mitteilung uber erblichen gynandromorphismus und somatische mosaikbildung bei Bombyx mori L. Biologisches Zentralblat 51:58–74
Goto K, Kobayashi M (1997) Genetical analysis of the mosaic lethal mutant in Bombyx mori. J Ser Sci Jpn 66:123–127 (in Japanese with English summary)
Hasimoto H (1933) The role of the W-chromosome in the sex determination of Bombyx mori. Jpn J Genet 4:113–114 (in Japanese)
Hasimoto H (1934) Genetical studies on the tetraploid female in the silkworm. II. Bull Sericult Exp Station Jpn 8:505–523 (in Japanese with English summary)
International Silkworm Genome Consortium (2008) The genome of a lepidopteran model insect, the silkworm Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 38:1036–1045
Katsuki K, Akiyama T (1927) A new case of silkworm mosaics appeared in a silk worm. Sangyo Shimpo 35:426–436 (in Japanese)
Kawaguchi E (1926) Polyspermy in Bombyx mori L. Sangyo Simpo 34:38–41 (in Japanese)
Kawaguchi E (1928) Zytologische Untersuchungen am Seidenspinner und seinen Verwandten. I. Gametogenese von Bombyx mori L. und B. mandarina M. und ihrer Bastar. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 7:519–552
Kawaguchi Y, Doira H, Kusakabe T, Koga K (2001) Genetic analysis of the maternally conditioned “mosaic of Tanaka” mutation in Bombyx mori. J Insect Biotech Seric 70:193–197
Kobayashi M (1991) Mutation of meiotic division and fertilization. Iden 45:14–18 (in Japanese)
Murakami A, Imai HT (1974) Cytological evidence for holocentric chromosomes of the silkworms, Bombyx mori and B. mandarina (Bombycidae, Lepidoptera). Chromosoma 47:167–178
Shimada T (2000) Importance of the genome analysis of the Bombyx mori. Agricult Horticult 75:1112–1115 (in Japanese)
Shimada T, Kobayashi M (1992) Homeotic transformation in E Nk mutant cells is not affected by neighboring normal cells in genetic mosaic of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. J Ser Sci Jpn 61:444–450
Shimada T, Ebinuma H, Kobayashi M (1986) Expression of homeotic genes in Bombyx mori estimated from asymmetry of dorsal closure in mutant/normal mosaics. J Exp Zool 240:335–342
Takami T (1946) Experimental studies on the embryo formation in Bombyx mori. V. Presumptive mesodermal and neural regions of the egg. Seibutu 1:208–211 (in Japanese)
Tazima Y (1947) Mosaic caused by mosaic genes. Mosaic of the Bombyx mori. Hokuryukan, Tokyo, pp 52–68 (in Japanese)
Tazima Y (1964a) Biology of the silkworm. The genetics of the silkworm. Logos Press, London, pp 1–17
Tazima Y (1964b) Parthenogenesis and polyploidy. The genetics of the silkworm. Logos Press, London, pp 165–175
Yamamoto K, Narukawa J, Kadono-Okuda K, Nohata J, Sasanuma M, Suetsugu Y, Banno Y, Fujii H, Goldsmith MR, Mita K (2006) Construction of a single nucleotide polymorphism linkage map for the silkworm, Bombyx mori, based on bacterial artificial chromosome end sequences. Genetics 173:151–161
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by KAKENHI (No. 22128004) and the Agrigenome Research Program (MAFF-NIAS). Tsuguru Fujii is a recipient of the JSPS Fellowship for Young Scientists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fujii, T., Abe, H., Yamamoto, K. et al. Interspecies linkage analysis of mo, a Bombyx mori locus associated with mosaicism and gynandromorphism. Genetica 139, 1323–1329 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-012-9634-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-012-9634-0