Abstract
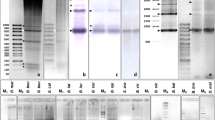
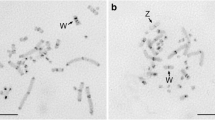
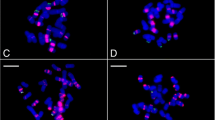
In the subfamily Arvicolinae (Cricetidae, Rodentia) the satellite DNA Msat-160 has been so far described in only some species from the genus Microtus and in one species from another genus, Chionomys nivalis. Here we cloned and characterized this satellite in two new arvicoline species, Microtus (Terricola) savii and Arvicola amphibius (terrestris). We have also demonstrated, by PCR and FISH, its existence in the genomes of several other species from both genera. These results suggest that Msat-160 already occurred in the common ancestor of the four genera/subgenera of Arvicolinae (Microtus, Chionomys, Arvicola, and Terricola). In Arvicola and Terricola, Msat-160 showed the basic monomer length of 160 bp, although a higher-order repeat (HORs) of 640 bp could have been probably replacing the original monomeric unit in A. a. terrestris. Msat-160 was localized by FISH mostly on the pericentromeric regions of the chromosomes, but the signal intensity and the number of carrier chromosomes varied extremely even between closely related species, resulting in a species-specific pattern of chromosomal distribution of this satellite. Such a variable pattern most likely is a consequence of a rapid amplification and contraction of particular repeats in the pericentromeric regions of chromosomes. In addition, we proposed that the rapid variation of pericentromeric repeats is strictly related to the prolific species radiation and diversification of karyotypes that characterize Arvicolinae lineage. Finally, we performed phylogenetic analysis in this group of related species based on Msat-160 that results to be in agreement with previously reported phylogenies, derived from other molecular markers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta MJ, Marchal JA, Martínez S et al (2007) Characterization of the satellite DNA Msat-160 from the species Chionomys nivalis (Rodentia, Arvicolinae). Genetica 130:43–51
Acosta MJ, Marchal JA, Fernández-Espartero CH et al (2008) Retroelements (LINEs and SINEs) in vole genomes: differential distribution in the constitutive heterochromatin. Chromosome Res 16:949–959
Acosta MJ, Marchal JA, Mitsainas GP et al (2009) A new pericentromeric repeated DNA sequence in Microtus thomasi. Cytogenet Genome Res 124:27–36
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA et al (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Arnason U, Grétarsdóttir S, Widegren B (1992) Mysticete (baleen whale) relationships based upon the sequence of the common cetacean DNA satellite. Mol Biol Evol 9:1018–1028
Bachmann L, Sperlich D (1993) Gradual evolution of a specific satellite DNA family in Drosophila ambigua, D. tristis, and D. obscura. Mol Biol Evol 10:647–659
Benson G (1999) Tandem repeats finder: a program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 27:573–580
Burgos M, Jiménez R, de la Díaz GR (1986) A rapid, simple and reliable combined method for G-banding mammalian and human chromosomes. Stain Technol 61:257–260
Burgos M, Jiménez R, de la Díaz GR (1988) Comparative study of G- and C-banded chromosomes of five species of Microtidae: a chromosomal evolution analysis. Genome 30:540–546
Burgos M, Jiménez R, de la Díaz GR (1989) Comparative study of G- and C-banded chromosomes of five species of Microtidae. Genetica 78:3–12
Burgos M, Olmos DM, Jiménez R et al (1990) Fluorescence banding in four species of Microtidae: an analysis of the evolutive changes of the constitutive heterochromatin. Genetica 81:11–16
Burgos M, Sánchez A, Jiménez R et al (1991) Cytogenetic studies in Pitymys duodecimcostatus. Cytobios 66:173–177
Castiglia R, Annesi F, Aloise G et al (2008) Systematics of the Microtus savii complex (Rodentia, Cricetidae) via mitochondrial DNA analyses: paraphyly and pattern of sex chromosome evolution. Mol Phylogenet Evol 46:1157–1164
Chaline J (1977) Rodents, evolution, and prehistory. Endeavour 1:44–51
Chaline J, Graf JD (1988) Phylogeny of the Arvicolinae (Rodentia): biochemical and paleontological evidence. J Mamm 69:22–33
Chaline J, Brunet-Lecomte P, Motuire S et al (1999) Anatomy of the arvicoline radiation (Rodentia): paleaogeographical, paleaoecological history and evolutionary data. Ann Zool Fennici 36:239–267
Charlesworth B, Sniegowski P, Stephan W (1994) The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 371:215–220
Ciobanu D, Grechko VV, Darevsky IS et al (2004) New satellite DNA in Lacerta s. str. lizards (Sauria: Lacertidae): evolutionary pathways and phylogenetic impact. J Exp Zoolog (Mol Dev Evol) 302B:505–516
Conroy CJ, Cook JA (1999) MtDNA evidence for repeated pulses of speciation within arvicoline and murid rodents. J Mamm Evol 6:221–245
de la Díaz GR, Pretel A (1978) Karyotype and centric dissociation in water vole Arvicola sapidus spp sapidus Miller 1908 (Rodentia, Muridae). Experientia 34:706–708
De La Herrán R, Rejón CR, Rejón MR et al (2001) The molecular phylogeny of the Sparidae (Pisces, Perciformes) based on two satellite DNA familias. Heredity 87:691–697
Dover G (1986) Molecular drive in multigene families—how biological novelties arise, spread and are assimilated. Trends Genet 2:159–165
Dover G (2002) Molecular drive. Trends Genet 18:587–589
Elisaphenko EA, Nesterova TB, Duthie SM et al (1998) Repetitive DNA sequences in the common vole: cloning, characterization and chromosome localization of two novel complex repeats MS3 and MS4 from the genome of the East European vole Microtus rossiaemeridionalis. Chromosome Res 6:351–360
Ellingsen A, Slamovits CH, Rossi MS (2007) Sequence evolution of the major satellite DNA of the genus Ctenomys (Octodontidae, Rodentia). Gene 392:283–290
Fernández R, Barragán MJ, Bullejos M et al (2001) Molecular and cytogenetic characterization of highly repeated DNA sequences in the vole Microtus cabrerae. Heredity 87:637–646
Fry K, Salser W (1977) Nucleotide sequences of HS-alpha satellite DNA from kangaroo rat Dipodomys ordii and characterization of similar sequences in other rodents. Cell 12:1069–1084
Galewski T, Tilak M, Sanchez S, Chevret P, Paradis E, Douzery EJP (2006) The evolutionary radiation of Arvicolinae rodents (voles and lemmings): relative contribution of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA phylogenies. BMC Evol Biol 6:80
Galleni L, Stanyon R, Tellini A et al (1992) Karyology of the Savi pine vole, Microtus savii (De Sélys-Longchamps, 1838) (Rodentia, Arvicolidae): G-, C-, DA/DAPI-, and AluI-bands. Cytogenet Cell Genet 59:290–292
Galleni L, Tellini A, Stanyon R et al (1994) Taxonomy of Microtus savii (Rodentia, Arvicolidae) in Italy: cytogenetic and hybridization data. J Mammal 75:1040–1044
Jaarola M, Martinkova N, Gunduz I et al (2004) Molecular phylogeny of the speciose vole genus Microtus (Arvicolinae, Rodentia) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 33:647–663
Kalscheuer V, Singh AP, Nanda I et al (1996) Evolution of the gonosomal heterochromatin of Microtus agrestis: rapid amplification of a large, multimeric, repeat unit containing a 3.0-kb (GATA)11-positive, middle repetitive element. Cytogenet Cell Genet 73:171–178
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitution through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Lee C, Court DR, Cho C et al (1997) Higher-order organization of subrepeats and the evolution of cervid satellite I DNA. J Mol Evol 44:327–335
López-Flores I, De la Herrán R, Garrido-Ramos MA et al (2004) The molecular phylogeny of oysters based on a satellite DNA related to transposons. Gene 339:181–188
Lorite P, Carrillo JA, Tinaut A et al (2004) Evolutionary dynamics of satellite DNA in species of the Genus Formica (Hymenoptera, Formicidae). Gene 332:159–168
Marchal JA, Acosta MJ, Bullejos M et al (2003) Sex chromosomes, sex determination, and sex-linked sequences in Microtidae. Cytogenet Genome Res 101:266–273
Marchal JA, Acosta MJ, Bullejos M et al (2006) Distribution of L1-retroposons on the giant sex chromosomes of Microtus cabrerae (Arvicolidae, Rodentia): functional and evolutionary implications. Chromosome Res 14:177–186
Maruyama T, Imai HT (1981) Evolutionary rate of the mammalian karyotype. J Theor Biol 90:111–121
Mayorov VI, Adkison LR, Vorobyeva NV et al (1996) Organization and chromosomal localization of a B1-like containing repeat of Microtus subarvalis. Mamm Genome 7:593–597
Mayorov VI, Rogozin IB, Adkison LR (1999) Characterization of several LINE-1 elements in Microtus kirgisorum. Mamm Genome 10:724–729
Mazurok NA, Rubtsova NV, Isaenko AA et al (2001) Comparative chromosome and mitochondrial DNA analyses and phylogenetic relationships within common voles (Microtus, Arvicolidae). Chromosome Res 9:107–120
Meylan A (1970) Caryotypes et distribution de quelques Pitymys européens (Mammalia, Rodentia). Note préliminaire. Rev Suisse Zool 77:562–575
Mitsainas GP, Rovatsos MTh, Giagia-Athanasopoulou EB (2010) Heterochromatin study and geographical distribution of Microtus species (Rodentia, Arvicolinae) from Greece. Mamm Biol 75:261–269
Modi WS (1987a) Phylogenetic Analyses of chromosomal banding-patterns among the Nearctic Arvicolidae (Mammalia, Rodentia). Syst Zool 36:109–136
Modi WS (1987b) C-banding analyses and the evolution of heterochromatin among Arvicolid Rodents. J Mammal 68:704–714
Modi WS (1992) Nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of a tandem satellite array from the rock vole Microtus chrotorrhinus (Rodentia). Mamm Genome 3:226–232
Modi WS (1993a) Comparative analyses of heterochromatin in Microtus: sequence heterogeneity and localized expansion and contraction of satellite DNA arrays. Cytogenet Cell Genet 62:142–148
Modi WS (1993b) Heterogeneity in the concerted evolution process of a tandem satellite array in meadow mice (Microtus). J Mol Evol 37:48–56
Modi WS (1993c) Rapid, localized amplification of a unique satellite DNA family in the rodent Microtus chrotorrhinus. Chromosoma 102:484–490
Modi WS (1996) Phylogenetic history of LINE-1 among arvicolid rodents. Mol Biol Evol 13:633–641
Modi WS, Serdyukova NA, Vorobieva NV et al (2003) Chromosomal localization of six repeated DNA sequences among species of Microtus (Rodentia). Chromosome Res 11:705–713
Modi WS, Ivanov S, Gallagher DS (2004) Concerted evolution and higher-order repeat structure of the 1.709 (satellite IV) family in bovids. J Mol Evol 58:460–465
Nadachowski A (1991) Systematics, geographic variation, and evolution of snow voles (Chionomys) based on dental characters. Acta Theriol 36:1–45
Neitzel H, Kalscheuer V, Henschel S et al (1998) Beta-heterochromatin in mammals: evidence from studies in Microtus agrestis based on the extensive accumulation of L1 and non-L1 retroposons in the heterochromatin. Cytogenet Cell Genet 80:165–172
Neitzel H, Kalscheuer V, Singh AP et al (2002) Copy and paste: the impact of a new non-L1 retroposon on the gonosomal heterochromatin of Microtus agrestis. Cytogenet Genome Res 96:179–185
Palomeque T, Lorite P (2008) Satellite DNA in insects: a review. Heredity 100:564–573
Pfunder M, Holzgang O, Frey JE (2004) Development of microarray-based diagnostics of voles and shrews for use in biodiversity monitoring studies, and evaluation of mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I vs. cytochrome b as genetic markers. Mol Ecol 13:1277–1286
Plohl M, Luchetti A, Meštrovic N et al (2008) Satellite DNAs between selfishness and functionality: structure, genomics and evolution of tandem repeats in centromeric (hetero)chromatin. Gene 409:72–82
Pons J, Gillespie RG (2004) Evolution of satellite DNAs in a radiation of endemic Hawaiian spiders: does concerted evolution of highly repetitive sequences reflect evolutionary history? J Mol Evol 59:632–641
Pons J, Bucur R, Vogler AP (2003) Higher-order repeats in the satellite DNA of the cave beetle Pholeuon proserpinae glaciale (Coleoptera: Cholevidae). Hereditas 139:28–34
Sánchez A, Bullejos M, Burgos M et al (1996) An alternative to blunt-end ligation for cloning DNA fragments with incompatible ends. Trends Genet 12:44
Shevchenko AI, Mazurok NA, Slobodyanyuk SY et al (2002) Comparative analysis of the Msat-160 repeats in four species of common vole (Microtus, Arvicolidae). Chromosome Res 10:117–126
Stewart WA, Piertney SB, Dallas JF (1998) Isolation and characterization of highly polymorphic microsatellites in the water vole, Arvicola terrestris. Mol Ecol 7:1258–1259
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M et al (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Vanlerberghe F, Bonhomme F, Hutchison CA 3rd et al (1993) A major difference between the divergence patterns within the lines-1 families in mice and voles. Mol Biol Evol 10:719–731
Yamada K, Nishida-Umehara C, Matsuda Y (2004) A new family of satellite DNA sequences as a major component of centromeric heterochromatin in owls (Strigiformes). Chromosoma 112:277–287
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Junta de Andalucia for capture permits of A. sapidus and M. duodecimcostatus; Junta de Castilla-León for capture permits of A. terrestris and M. lusitanicus. This work was supported by the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia y Tecnología through project numbers: CGL2006-05308 and CGL2009-07754 (cofunded by the European Regional Development Fund), by the Junta de Andalucía throughout the programme “Ayudas a grupos de investigación”, group number: CVI 220, and by funds of “Ateneo Federato della Scienza e della Tecnologia” to R. C. (AST 2008, pr. C26F08W5R2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acosta, M.J., Marchal, J.A., Fernández-Espartero, C. et al. Characterization of the satellite DNA Msat-160 from species of Terricola (Microtus) and Arvicola (Rodentia, Arvicolinae). Genetica 138, 1085–1098 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-010-9496-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-010-9496-2