Abstract
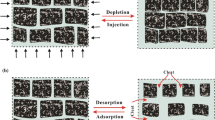
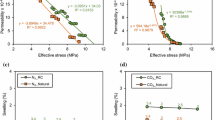
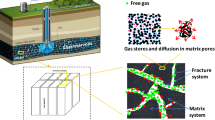
The kinetics of gas–coal interaction during coalbed methane (CBM) recovery and/or carbon dioxide sequestration in coal has been subject of investigation over past few years. Swelling of coal matrix due to gaseous phase CO2 injection is now well established through laboratory experiments and field validations. Further, fluid exchange or flow in coal alters effective stresses in the underground environment. These significantly affect the permeability characteristics of coal and therefore influence the gas recovery/injection projects. Most research works on coal seam sequestration have been carried out for gas or liquid phase CO2. Considering the pressure–temperature conditions of deep seated coal, studies are now being done on supercritical CO2 flow and adsorption in coal. A newly developed experimental set up was utilized to replicate the underground conditions in laboratory to investigate the (1) initial N2 permeability of coal, (2) supercritical CO2 permeability of coal, (3) effects of CO2 sorption on N2 permeability of coal. The temperature of the set up was maintained at 33 °C while CO2 injection pressures were varied between 11 and 15 MPa at a range of 16–24 MPa confinements, and N2 was used as a relatively neutral medium to estimate the loss in permeability due to supercritical CO2 flow. The results indicate that high adsorption of supercritical CO2 in coal led to significant reduction in permeability. On increasing the confining pressure, further decline in the permeability was recorded. CO2 becomes liquid-like with increasing confining pressures and the coal–fluid interactions change, causing high sorption and matrix swelling, leading to reduced permeability in coal. This explains why substantial decline in the injection rate of CO2 was observed progressively in most CO2 sinks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae J, Bhatia SK (2006) High-pressure adsorption of methane and carbon dioxide on coal. Energy Fuel 20:2599–2607
Botnen LS, Fisher DW, Dobroskok AA, Bratton TR, Greaves KH, McLendon TR et al (2009) Field test of CO2 injection and storage in lignite coal seam in North Dakota. J Energy Procedia 1(1):2013–2019
Chandra D (1992) Jharia coalfield. Mineral Resources of India, Geol Soc India, Bangalore, pp 1–149
Fokker PA, van der Meer LGH (2004) The injectivity of coalbed CO2 injection wells. Energy 29(9, 10):1423–1429
Fujioka M, Yamaguchi S, Nako M (2010) CO2-ECBM field tests in the Ishikari coal basin of Japan. Int J Coal Geol 82:287–298
Harpalani S, Chen G (1995) Estimation of changes in fracture porosity of coal with gas emission. Fuel 74(10):1491–1498
Kiyama T, Nishimoto S, Fujioka M, Xue Z, Ishijima Y, Pan Z et al (2011) Coal swelling strain and permeability change with injecting liquid/supercritical CO2 and N2 at stress-constrained conditions. Int J Coal Geol 85(1):56–64
Krooss BM, van Bergen F, Gensterblum Y, Siemons N, Pagnier HJM, David P (2002) High-pressure methane and carbon dioxide adsorption on dry and moisture equilibrated Pennsylvanian coals. Int J Coal Geol 51:69–92
Massarotto P, Golding SD, Bae JS, Iyer R, Rudolph V (2010) Changes in reservoir properties from injection of supercritical CO2 into coal seams—A laboratory study. Int J Coal Geol 82(3):269–279
Reeves S (2001) Geological sequestration of CO2 in deep, un-mineable coal beds: an integrated research and commercial-scale field demonstration project. In New Orleans, LA, USA: Society of Petroleum Engineers Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition
Shukla R, Ranjith PG, Haque A, Choi X (2010) A review of studies on CO2 sequestration and caprock integrity. Fuel 89(10):2651–2664
Siriwardane H, Haljasmaa I, McLendon R, Irdi G, Soong Y, Bromhal G (2009) Influence of carbon dioxide on coal permeability determined by pressure transient methods. Int J Coal Geol 77(1–2):109–118
Suehiro Y, Nakajima M, Yamada K, Uematsu M (1996) Critical parameters of xCO2 + (1 − x)CHF3 for x = (1.0000, 0.7496, 0.5013, and 0.2522). J Chem Thermodyn 28:1153–1164
Vishal V, Singh L, Pradhan SP, Singh TN, Ranjith PG (2013a) Numerical modeling of Gondwana coal seams in India as coalbed methane reservoirs substituted for carbon dioxide sequestration. Energy 49:384–394
Vishal V, Ranjith PG, Singh TN (2013b) CO2 permeability of Indian bituminous coals: implications for carbon sequestration. Int J Coal Geol 105:36–47
Vishal V, Ranjith PG, Pradhan SP, Singh TN (2013c) Permeability of sub-critical carbon dioxide in naturally fractured Indian bituminous coal at a range of down-hole stress conditions. Eng Geol 167:148–156
Vishal V, Singh TN, Ranjith PG (2015a) Influence of sorption time in CO2-ECBM process in Indian coals using coupled numerical simulation. Fuel 139:51–58
Vishal V, Jain N, Singh TN (2015b) 3-D modeling of propagation of hydraulic fractures in shale at different injection pressures. Sustain Environ Res 25(4):1–8
Vishal V, Sudhakaran A, Singh TN, Pradhan SP (2015c) Liquid and supercritical CO2 permeability of bituminous coal at multiple downhole stress conditions. Int J Coal Geol (submitted for publication)
Vishal V, Ranjith PG, Singh TN (2015d) An experimental investigation on behaviour of coal under fluid saturation, using acoustic emission. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 22:428–436
White CM, Smith DH, Jones KL, Goodman AL, Jikich SA, LaCount RB et al (2005) Sequestration of carbon dioxide in coal with enhanced coalbed methane recovery: a review. Energy Fuel 19(3):659–724
Acknowledgments
This research was conducted as a part of the DST INSPIRE Faculty Award Grant (IFA-13-EAS-07). VV is thankful to the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi for the research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vishal, V., Singh, T.N. A Laboratory Investigation of Permeability of Coal to Supercritical CO2 . Geotech Geol Eng 33, 1009–1016 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9882-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9882-8