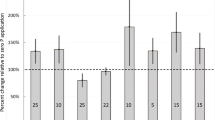
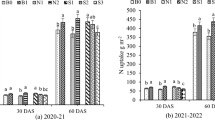
Abstract
Fertiliser application strategies for maize (Zea mays L.) production on sandy soils under high rainfall regimes need to be carefully designed to minimise nutrient losses through leaching and maximise crop yield. Experiments were conducted to determine N, P, and K leaching in sandy soils with 3–6% clay in surface layers under maize production, and the effectiveness of different N, P, and K fertiliser timing and splitting strategies on leaching of N, P, and K and on maize yield. In a column experiment on an Oxic Paleustult (Korat series) with 3% clay, leaching of N, P, and K from fertiliser (114N-17P-22K in kg ha−1) was significant under simulated rainfall, but decreased to negligible levels with 3–5 split applications of fertiliser. Maize N and K uptake increased with 3–5 split applications, but not P uptake. Despite continued intense rainfall and further fertilizer additions, leaching was not recorded after day 30, and this was attributed to the effect of plant water uptake on reducing deep drainage. Split applications of fertilizer maintained NP and K in the 0–30 cm layer during 30–60 days when maize nutrient demand was likely to be at its highest, while in the recommended fertilizer regime NPK in the surface layers declined after 30 days. In a field experiment on an Oxic Paleustult (Korat series) with 6% clay, 3–4 splits of fertiliser increased N and K uptake and increased maize yields from 3.3 to 4.5 Mg ha−1. Postponing basal fertiliser application from pre-planting to 7–15 days after emergence increased uptake of N, P, and K and grain yield emphasising the greater risk of nutrient losses from fertiliser applied at planting than later. Strategies designed to reduce the amount of nutrients applied as fertiliser at planting, such as split application and postponing basal application can decrease the risk of leaching of N, P, and K from fertiliser and improve nutrient use efficiency, and grain yield of maize on sandy soils under high growing season rainfall regimes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfaro MA, Jarvis SC, Gregory PJ (2004) Factors affecting potassium leaching in different soils. Soil Use Manage 20:182–189. doi:10.1079/SUM2004249
Allen SC, Nair VD, Graetz DA, Jose S, Nair PKR (2006) Phosphorus loss from organic versus inorganic fertilizers used in alleycropping on a Florida Ultisol. Agric Ecosyst Environ 117:290–298. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2006.04.010
Amberger A (1989) Research on dicyandiamide as a nitrification inhibitor and future outlook. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 20:1933–1955. doi:10.1080/00103628909368195
Baker JL, Timmons DR (1994) Fertilizer management effects on leaching of labeled nitrogen for no-till corn in field lysimeters. J Environ Qual 23:305–310
Berthelsen S, Noble AD, Ruaysoongnern S, Huan H, Yi J (2007) Addition of clay based ameliorants to light textured soils to reduce nutrient loss and increase crop productivity. In: Management of tropical sandy soils for sustainable development. Proceedings of the International Conference on the Management of tropical sandy soils, Khon Kaen, Nov. 2005. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok, pp 373–382
Blanchart E, Albrecht A, Bernoux M, Brauman A, Chotte JL, Feller C, Gany F, Hien E, Manlay R, Masse D, Sall S, Villenave C (2007) Organic matter and biofunctioning in tropical sandy soils and implications for its management. In: Management of tropical sandy soils for sustainable development. Proceedings of the International Conference on the Management of tropical sandy soils, Khon Kaen, Nov. 2005. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok, pp 224–241
Bolland MDA, Clarke MF, Yeates JS (1995) Effectiveness of rock phosphate, coastal superphosphate and single superphosphate for pasture on deep sandy soils. Fertil Res 41:129–143
Boumans LJM, Fraters D, Van Drecht G (2005) Nitrate leaching in agriculture to upper groundwater in the sandy regions of the Netherlands during the 1992–1995 period. Environ Monit Assess 102:225–241. doi:10.1007/s10661-005-6023-5
Cassman KG, Kropff MJ, Gaunt J, Peng S (1993) Nitrogen use efficiency of rice reconsidered: What are the key constraints? Plant Soil 155/156:359–362. doi:10.1007/BF00025057
Chardon WJ, Oenema O, del Castilho P, Vriesema R, Japenga J, Blaauw D (1997) Organic phosphorus in solutions and leachates from soils treated with animal slurries. J Environ Qual 26:372–378
Chen GC, He ZL, Stoffella PJ, Yang XE, Yu S, Calvert D (2006) Use of dolomite phosphate rock (DPR) fertilizers to reduce phosphorus leaching from sandy soil. Environ Pollut 139:176–182. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.12.016
Chikowo R, Mapfumo P, Nyamugafata P, Nyamadzawo G, Giller KE (2003) Nitrate-N dynamics following improved fallows and maize root development in a Zimbabwean sandy clay loam. Agrofor Syst 59:187–195. doi:10.1023/B:AGFO.0000005219.07409.a0
Croker J, Poss R, Hartmann C, Bhuthorndharaj S (2004) Effects of recycled bentonite addition on soil properties, plant growth and nutrient uptake in a tropical sandy soil. Plant Soil 267:155–163. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-4641-x
Di HJ, Cameron KC (2002) Nitrate leaching in temperate agroecosystems: source, factors and mitigating strategies. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 64:237–256. doi:10.1023/A:1021471531188
Dinnes DL, Karlen DL, Jaynes DB, Kasper TC, Hatfield JL, Colvin TS, Cambardella CA (2002) Nitrogen management strategies to reduce nitrate leaching in tile-drained Midwestern soils. Agron J 94:153–171
Djodjic F, Börling K, Bergström L (2004) Phosphorus leaching in relation to soil type and soil phosphorus content. J Environ Qual 33:678–684
Edmeades DC, Thorrold BS, Roberts AHC (2005) The diagnosis and correction of sulfur deficiency and the management of sulfur requirements in New Zealand pastures: a review. Aust J Exp Agric 45:1205–1223. doi:10.1071/EA01173
Eghball B, Binford GD, Baltensperger DD (1996) Phosphorus movement and adsorbtion in a soil receiving long-term manure and fertilizer application. J Environ Qual 25:1339–1343
Elliott HA, O’Connor GA, Brinton S (2002) Phosphorus leaching from biosolids-amended sandy soil. J Environ Qual 31:681–689
Eriksen J, Askegaard M (2000) Sulphate leaching in an organic crop rotation on sandy soil in Denmark. Agric Ecosyst Environ 78:107–114. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(99)00117-6
Eswaran H, Vearasilp T, Reich P, Beinroth F (2007) Sandy soils of Asia: a new frontier for agricultural development? In: Management of tropical sandy soils for sustainable development. Proceedings of the International Conference on the Management of tropical sandy soils, Khon Kaen, Nov. 2005. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok, pp 22–30
Francis GS, Haynes RJ, Speir TW, Williams PH (1995) The effects of a nitrification inhibitor on leaching losses and recovery of mineralized nitrogen by a wheat crop after ploughing in temporary leguminous pastures. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 41:33–39
Gehl RJ, Schmidt JP, Maddux LD, Gordon WB (2005) Corn yield response to nitrogen rate and timing in sandy irrigated soils. Agron J 97:1230–1238. doi:10.2134/agronj2004.0303
Hartemink AE, Huting J (2007) Sandy soils in southern and eastern Africa: extent, properties and management. In: Management of tropical sandy soils for sustainable development. Proceedings of the International Conference on the Management of tropical sandy soils, Khon Kaen, Nov. 2005. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok, pp 54–59
Irigoyen I, Muro J, Azpilikueta M, Aparicio-Tejo P, Lamsfus C (2003) Ammonium oxidation kinetics in the presence of nitrification inhibitors CDC and DMPP at various temperatures. Aust J Soil Res 41(6):1177–1183. doi:10.1071/SR02144
Jalali M, Merrikhpour H (2008) Effects of poor quality irrigation waters on the nutrient leaching and groundwater quality from sandy soil. Environ Geol 53:1289–1298. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0735-5
Johnston AE, Goulding KWT, Mercer E (1993) Potassium leaching from a sandy soil. International Potash Institute. Subject 12 No. 4
Jokela WE, Randall GW (1997) Fate of fertilizer nitrogen as affected by time and rate of application to corn. Soil Sci Soc Am J 61:1695–1703
Kamukondiwa W, Bergstrom L (1994) Nitrate leaching in field lysimeters at an agricultural site in Zimbabwe. Soil Use Manage 10:118–124. doi:10.1111/j.1475-2743.1994.tb00471.x
Kayser M, Isselstein J (2005) Potassium cycling and losses in grassland system: a review. Grass Forage Sci 60:213–224. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2494.2005.00478.x
Liedgens M, Soldati A, Stamp P, Richner W (2000) Root development of maize (Zea may L.) as observed with minirhizotrons in lysimeters. Crop Sci 40:1665–1672
Mandal B, De DK (1993) Depthwise distribution of extractable boron in some acidic Inceptisols of India. Soil Sci 155:256–262. doi:10.1097/00010694-199304000-00004
Meteorological Department (2002) Climatological data of Thailand for 30 year period 1971–2000. Thai Meteorological Department, Thailand
Milroy SP, Asseng S, Poole ML (2008) Systems analysis of wheat production on low water-holding soils in a Mediterranean-type environment II. Drainage and nitrate leaching. Field Crops Res 107:211–220. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2008.02.008
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Nyamangara J, Bergstrom LF, Pila MI, Giller KE (2003) Fertilizer use efficiency and nitrate leaching in a tropical sandy soil. J Environ Qual 32:599–606
Office of Agricultural Economics (2005) Agricultural Statistics of Thailand 2004. Center for Agricultural Statistics, Office of Agricultural Economics, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, Bangkok
Powell T, Gaines ST (1994) Soil texture effect on nitrate leaching in soil percolates. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 25:2561–2570. doi:10.1080/00103629409369207
Randall GW, Vetsch JA, Huffman JR (2003) Corn production on a subsurface-drained mollisol as affected by time of nitrogen application and nitrapyrin. Agron J 95:1213–1219
Richie SW, Hanway JJ (1993) How a corn plant develops. Rev. ed. Iowa state Univ. of Sci. and Techno. Coop Ext. Serv. Spec. Rep. 48
Sainz Rozas HR, Echeverria HE, Barbieri PA (2004) Nitrogen balance as affected by application time and nitrogen fertilizer rate in irrigated no-tillage maize. Agron J 96:1622–1631
Sarkar D, Mandal B, Kundu MC (2007) Increasing use efficiency of boron fertilisers by rescheduling the time and methods of application for crops in India. Plant Soil 301:77–85. doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9423-1
Scholefield D, Tyson KC, Garwood EA, Armstrong AC, Hawkins J, Stone AC (1993) Nitrate leaching from grassland lysimeters: effects of fertilizer input, field drainage, age of sward and pattern of weather. J Soil Sci 44:601–613. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.1993.tb02325.x
Seng V, Bell RW, White PF, Schonecht N, Hin S, Vance W (2007) Sandy soils of Cambodia. In: Management of tropical sandy soils for sustainable development. Proceedings of the International Conference on the Management of tropical sandy soils, Khon Kaen, Nov. 2005. FAO Regional Office for Asia and the Pacific, Bangkok, pp 42–48
Serna MD, Bañuls J, Quiñones A, Primo-Millo E, Legaz F (2004) Evaluation of 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate as a nitrification inhibitor in a Citrus-cultivated soil. Biol Fertil Soils 32:41–46. doi:10.1007/s003740000211
Shan YH, Yang LZ, Yan TM, Wang JG (2005) Downward movement of phosphorus in paddy soil installed in large-scale monolith lysimeters. Agric Ecosyst Environ 111:270–278. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2005.05.011
Shepherd MA, Withers PJ (2001) Phosphorus leaching from liquid digested sewage sludge applied to sandy soil. J Agric Sci Camb 136:433–441
Sims JT, Sinnard RR, Joern BC (1998) Phosphorus loss in agricultural drainage: historical perspective and current research. J Environ Qual 27:277–293
Thomsen IK, Chistensen BT (1998) Cropping system and residue management effect on nitrate leaching and crop yields. Agric Ecosyst Environ 68:73–84. doi:10.1016/S0167-8809(97)00134-5
Timmons DR (1984) Nitrate leaching as influenced by water application level and nitrification inhibitors. J Environ Qual 13:305–309
van Es HM, Sogbedji JM, Schindelbeck RR (2006) Effect of manure application timing, crop, and soil type on nitrate leaching. J Environ Qual 35:670–679. doi:10.2134/jeq2005.0143
Vibulsukh N, Somnus P, Boonyon B, Paisalcharoen C, Wongwiwatchai C, Rungrarattanakasin W, Yoshioka S (1987) Nutrient movement in a sandy soil. In: Yoshida S (ed) Compilation report on soil fertility in Northeast Thailand. Agricultural Department Research Center in Northeast Thailand, Khon Kaen, pp 37–47
Zotarelli L, Scholberg JM, Dukes MD, Muňoz-Carpene R (2007) Monitoring of nitrate leaching in sandy soils: comparison of three methods. J Environ Qual 36:953–962. doi:10.2134/jeq2006.0292
Acknowledgment
The research reported here was funded by the Thailand Research Fund through the Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sitthaphanit, S., Limpinuntana, V., Toomsan, B. et al. Fertiliser strategies for improved nutrient use efficiency on sandy soils in high rainfall regimes. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 85, 123–139 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-009-9253-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-009-9253-z