Abstract
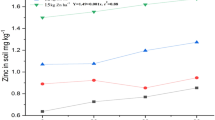
Field experiments were conducted during the wet seasons of 2005–2006 and 2006–2007 on an Aeric Endoaquept (pH 7.2) to study the relative performance of chelated zinc [Zn ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA)] and zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) on the growth and yield of rice (cv. IET 4094). The diethylene triamine penta-acetic acid (DTPA) extractable (available) Zn concentration in soil and total Zn content in dry matter of rice increased initially up to 28 days of crop growth when Zn was applied as a single basal source, being greater with chelated Zn compared with ZnSO4 application. The highest mean Zn uptake by rice grain and straw was found to be 209.2 and 133.8 g ha−1, respectively, in the treatment T7 (1 kg Zn ha−1 as Zn-EDTA at basal). The mean filled grain percentage, thousand grain weight and number of panicles m−2 were highest with 90.4%, 25.4 g and 452, respectively, in treatment T7 where 1 kg ha−1 Zn as Zn-EDTA was applied. The highest yield of grain and straw was 5.5 and 7.3 t ha−1, respectively, in treatment T7, resulting in a 37.5 and 43.1% increase in yield over that of the control during both the years.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez JM, Rico MI, Obrador A (1996) Lixiviation and extraction of zinc in a calcareous soil treated with zinc-chelated fertilizers. J Agric Food Chem 44:3383–3387
Alvarez JM, Novillo J, Obrador A, Valvidia LML (2001) Mobility and leachability of zinc in two soils treated with six organic zinc complexes. J Agric Food Chem 49:3833–3840
Brar MS, Sekhon GS (1976) Effect of Fe and Zn on the availability of micronutrients under flooded and unflooded condition. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 24:446–451
Chatterjee AK, Mandal LN (1985) Zinc sources for rice in soil at different moisture regimes and organic matter levels. Plant Soil 87:393–404
Das DK, Saha D (1999) In: Micronutrients research in soils and crops of West Bengal, Silver Jubilee Commemoration, Department of Agricultural Chemistry and Soil Science, Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Mohanpur, Nadia, West Bengal, India
Das DK, Karak T, Karmakar SK (2002) Efficiency of chelated Zn on the maintenance of Zn in soils in relation to yield and nutrition of rice. In: The 17th world congress of soil science, Thailand, 14–21 August 2002
Hazra GC, Mandal B, Mandal LN (1987) Distribution of zinc fractions and their transformation in submerged rice soils. Plant Soil 104:175–181
Jackson ML (1973) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice hall of India pvt. Ltd. New Delhi, India
Kabata-Pendias A (2000) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC, Boca Raton
Karak T, Singh UK, Das S, Das DK, Kuzyakov Y (2005) Comparative efficacy of ZnSO4 and Zn-EDTA application for fertilization of rice. Arch Agron Soil Sci 51:253–264
Kirk GJD, Bajita JB (1995) Root induced iron oxidation, pH changes and zinc solubilization in the rhizosphere of lowland rice. New Phytol 131:129–137
Klug A, Rhodes D (1987) ‘Zinc fingers’: a novel protein motif for nucleic acid recognition. Trends Biochem Sci 12:464–469
Lindsay WL, Norvell A (1978) Development of DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428
Maftoun M, Karimian N (1989) Relative efficiency of two zinc sources for maize in two calcareous soils from an arid area of Iran. Agronomie 9:771–775
Mandal B, Mandal LN, Ali MH (1993) Chemistry of zinc availability in submerged soils in relation to zinc nutrition of rice crop. In: Proceedings of the workshop on nicronutrients, Bhubaneswar, India, 22–23 January 1992, pp 240–253
Mandal B, Hazra GC, Mandal LN (2000) Soil management influences on zinc desorption for rice and maize nutrition. Soil Sci Soc Am J 64:1699–1705
Mehdi SM, Ranjaa AM, Hussain T (1990) Relative efficiency of various sources of zinc. Sarad J Agric 6:103–106
Mortvedt JJ (1979) Crop response to zinc sources applied alone or with suspensions. Fert Solutions 23:64–79
Norvell WA (1983) Equilibrio de los quelatos metalicos. In: Mortvedt JJ et al (eds) Micronutrients en agricultura. AGT Editor, Mexico, DF, pp 127–150
Ortiz EME, Garcia OA 1998. Process of sorption of zinc in three soils of Colombia cultivated with rice of the dry land variety Liano−5. In: Proceedings of the VIII congress of soil science, Santa Marta, Colombia. Suelos-Ecuatoriales 28, pp 112–117
Reddy CN, Patrick WH Jr (1977). Effect of redox potential on stability of zinc and copper chelates in flooded soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 41:729–732
Romheld V, Marschner H (1991) Function of micronutrients in plants. In: Mortvedt JJ et al (eds) Micronutrients in agriculture SSSA Book series 4, 2nd edn. SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 297–328
Singh MV, Abrol IP (1986) Transformation and availability of zinc in alkali soils. Fert News 37:17–27
Singh AK, Khan SK, Nongkynrih P (1999) Transformation of zinc in wetland rice soils in relation to nutrition of rice crop. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 47:248–253
Slaton NA, Wilson CE, Norman RJ, Boothe DL (2001) Evaluation of zinc seed treatments for rice. Agron J 93:152–157
Srivastava PC, Ghosh D, Singh VP (1999) Evaluation of different zinc sources for low land rice production. Biol Fertil Soils 30:168–172
Westfall DG, Anderson WB, Hodgens RJ (1971) Iron and zinc response of chlorotic rice growing on calcareous soil. Agron J 63:702–705
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, S.K., Das, D.K. Relative performance of chelated zinc and zinc sulphate for lowland rice (Oryza sativa L.). Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 81, 219–227 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9158-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-007-9158-7