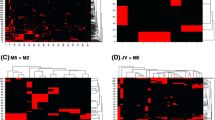
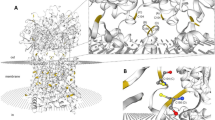
Abstract
The Na ( +)-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) is a member of the solute carrier family 10 (SLC10), which consists of 7 members (SLC10a1-SLC10a7). NTCP is a transporter localized to the basolateral membrane of hepatocytes and is primarily responsible for the absorption of bile acids. Although mammalian NTCP has been extensively studied, little is known about the lamprey NTCP (L-NTCP). Here we show that L-NTCP follows the biological evolutionary history of vertebrates, with conserved domain, motif, and similar tertiary structure to higher vertebrates. L-NTCP is localized to the cell surface of lamprey primary hepatocytes by immunofluorescence analysis. HepG2 cells overexpressing L-NTCP also showed the distribution of L-NTCP on the cell surface. The expression profile of L-NTCP showed that the expression of NTCP is highest in lamprey liver tissue. L-NTCP also has the ability to transport bile acids, consistent with its higher vertebrate orthologs. Finally, using a farnesoid X receptor (FXR) antagonist, RT-qPCR and flow cytometry results showed that L-NTCP is negatively regulated by the nuclear receptor FXR. This study is important for understanding the adaptive mechanisms of bile acid metabolism after lamprey biliary atresia based on understanding the origin, evolution, expression profile, biological function, and expression regulation of L-NTCP.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All authors make sure that all data and materials support published claims and comply with field standards.
References
Ananthanarayanan M, Ng OC, Boyer JL, Suchy FJ (1994) Characterization of cloned rat liver Na(+)-bile acid cotransporter using peptide and fusion protein antibodies. Am J Physiol 267:G637-643
Anwer MS, Hegner D (1978) Effect of Na on bile acid uptake by isolated rat hepatocytes. Evidence for a heterogeneous system. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem 359:181–192
Anwer MS, Stieger B (2014) Sodium-dependent bile salt transporters of the SLC10A transporter family: more than solute transporters. Pflugers Arch 466:77–89
Appelman MD, Wettengel JM, Protzer U, Oude Elferink RPJ, van de Graaf SFJ (2021) Molecular regulation of the hepatic bile acid uptake transporter and HBV entry receptor NTCP. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1866:158960
Cai SY, Boyer JL (2021) The role of bile acids in cholestatic liver injury. Ann Transl Med 9:737
Cai SY, Lionarons DA, Hagey L, Soroka CJ, Mennone A, Boyer JL (2013) Adult sea lamprey tolerates biliary atresia by altering bile salt composition and renal excretion. Hepatology 57:2418–2426
Chung-Davidson YW, Yeh CY, Li W (2015) The sea lamprey as an etiological model for biliary atresia. Biomed Res Int 2015:832943
Claro da Silva T, Polli JE, Swaan PW (2013) The solute carrier family 10 (SLC10) beyond bile acid transport. Mol Aspects Med 34:252–269
Claudel T, Zollner G, Wagner M, Trauner M (2011) Role of nuclear receptors for bile acid metabolism, bile secretion, cholestasis, and gallstone disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:867–878
Copple BL, Jaeschke H, Klaassen CD (2010) Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of cholestasis. Semin Liver Dis 30:195–204
Craddock AL, Love MW, Daniel RW, Kirby LC, Walters HC, Wong MH, Dawson PA (1998) Expression and transport properties of the human ileal and renal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. Am J Physiol 274:G157-169
Denson LA, Sturm E, Echevarria W, Zimmerman TL, Makishima M, Mangelsdorf DJ, Karpen SJ (2001) The orphan nuclear receptor, shp, mediates bile acid-induced inhibition of the rat bile acid transporter, ntcp. Gastroenterology 121:140–147
Di Ciaula A, Garruti G, Lunardi Baccetto R, Molina-Molina E, Bonfrate L, Wang DQ, Portincasa P (2017) Bile acid physiology. Ann Hepatol 16:s4–s14
Döring B, Lütteke T, Geyer J, Petzinger E (2012) The SLC10 carrier family: transport functions and molecular structure. Curr Top Membr 70:105–168
Drexler JF, Geipel A, König A, Corman VM, van Riel D, Leijten LM, Bremer CM, Rasche A, Cottontail VM, Maganga GD et al (2013) Bats carry pathogenic hepadnaviruses antigenically related to hepatitis B virus and capable of infecting human hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:16151–16156
Faber KN, Müller M, Jansen PL (2003) Drug transport proteins in the liver. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 55:107–124
Geier A, Martin IV, Dietrich CG, Balasubramaniyan N, Strauch S, Suchy FJ, Gartung C, Trautwein C, Ananthanarayanan M (2008) Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha is a central transactivator of the mouse Ntcp gene. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G226-233
Geyer J, Döring B, Meerkamp K, Ugele B, Bakhiya N, Fernandes CF, Godoy JR, Glatt H, Petzinger E (2007) Cloning and functional characterization of human sodium-dependent organic anion transporter (SLC10A6). J Biol Chem 282:19728–19741
Geyer J, Bakhaus K, Bernhardt R, Blaschka C, Dezhkam Y, Fietz D, Grosser G, Hartmann K, Hartmann MF, Neunzig J et al (2017) The role of sulfated steroid hormones in reproductive processes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 172:207–221
Grosser G, Müller SF, Kirstgen M, Döring B, Geyer J (2021) Substrate specificities and inhibition pattern of the solute carrier family 10 members NTCP, ASBT and SOAT. Front Mol Biosci 8:689757
Hagenbuch B, Dawson P (2004) The sodium bile salt cotransport family SLC10. Pflugers Arch 447:566–570
Hartley JL, Davenport M, Kelly DA (2009) Biliary atresia. Lancet 374:1704–1713
Janvier P (2006) Palaeontology: modern look for ancient lamprey. Nature 443:921–924
Jones H, Alpini G, Francis H (2015) Bile acid signaling and biliary functions. Acta Pharm Sin B 5:123–128
Jung D, Kullak-Ublick GA (2003) Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha: a key mediator of the effect of bile acids on gene expression. Hepatology 37:622–631
Mathai PP, Byappanahalli MN, Johnson NS, Sadowsky MJ (2021) gut microbiota associated with different sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus) life stages. Front Microbiol 12:706683
Ortiz-Perez A, Donnelly B, Temple H, Tiao G, Bansal R, Mohanty SK (2020) Innate immunity and pathogenesis of biliary atresia. Front Immunol 11:329
Perino A, Demagny H, Velazquez-Villegas L, Schoonjans K (2021) Molecular physiology of bile acid signaling in health, disease, and aging. Physiol Rev 101:683–731
Shneider BL, Dawson PA, Christie DM, Hardikar W, Wong MH, Suchy FJ (1995) Cloning and molecular characterization of the ontogeny of a rat ileal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter. J Clin Invest 95:745–754
Sidon EW, Youson JH (1983) Morphological changes in the liver of the sea lamprey, Petromyzon marinus L., during metamorphosis. II. Canalicular degeneration and transformation of the hepatocytes. J Morphol 178:225–246
Stieger B, Hagenbuch B, Landmann L, Höchli M, Schroeder A, Meier PJ (1994) In situ localization of the hepatocytic Na+/Taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide in rat liver. Gastroenterology 107:1781–1787
Vij M, Rela M (2020) Biliary atresia: pathology, etiology and pathogenesis. Future Sci OA 6:Fso466
Wang B, Cai SR, Gao C, Sladek FM, Ponder KP (2001) Lipopolysaccharide results in a marked decrease in hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha in rat liver. Hepatology 34:979–989
Yan H, Zhong G, Xu G, He W, Jing Z, Gao Z, Huang Y, Qi Y, Peng B, Wang H et al (2012) Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife 1:e00049
Yeh CY, Chung-Davidson YW, Wang H, Li K, Li W (2012) Intestinal synthesis and secretion of bile salts as an adaptation to developmental biliary atresia in the sea lamprey. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:11419–11424
Youson JH, Sidon EW (1978) Lamprey biliary atresia: first model system for the human condition? Experientia 34:1084–1086
Youson JH, Sidon EW, Peek WD, Shivers RR (1985) Ultrastructure of the hepatocytes in a vertebrate liver without bile ducts. J Anat 140(Pt 1):143–158
Yu D, Zhang H, Lionarons DA, Boyer JL, Cai SY (2017) Na(+)-taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP/SLC10A1) ortholog in the marine skate Leucoraja erinacea is not a physiological bile salt transporter. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 312:R477-r484
Zakrzewicz D, Geyer J (2022) Multitasking Na(+)/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) as a drug target for HBV infection: from protein engineering to drug discovery. Biomedicines 10: 196–216
Zollner G, Wagner M, Fickert P, Geier A, Fuchsbichler A, Silbert D, Gumhold J, Zatloukal K, Kaser A, Tilg H et al (2005) Role of nuclear receptors and hepatocyte-enriched transcription factors for Ntcp repression in biliary obstruction in mouse liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289:G798-805
Funding
This work was funded by the Education Department of Liaoning Province (No. LF2020005, JYTMS20231058), Liaoning Province Natural Science and Technology Plan Guidance Project (No. 2019-ZD-0301), and Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Liaoning Normal University (BS2020L002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yan Chi contributed to the study conception and design. Yingying Zhu prepared Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. Qipeng Zhang prepared Figs. 6, 7. Primary cell isolation was performed by Jilong Pan and Jindi Liu. Molecular docking was performed by Lei Qian. Material preparation were performed by Tiesong Li and Hao Wang. Ting Zhu helped us analyze the phylogenetic trees. Yue Pang and Qingwei Li provided the lab conditions. The manuscript was written by Yan Chi and Qipeng Zhang. Yan Chi will revise the manuscript. All of the authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The animal experiments were performed in accordance with the regulations of the Animal Welfare and Research Ethics Committee of the Institute of Dalian Medical University’s Animal Care protocol (Permit Number: SCXK2008-0002).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10695_2024_1324_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary file4 Supplementary Figure 1. Multiple sequence alignments of SLC10a1 in the indicated species. The red arrows represent conserved amino acid sites that are involved in bile acid transport between L-NTCP and other higher vertebrate orthologs. (TIF 16137 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Zhang, Q., Pan, J. et al. Evolutionary analysis of SLC10 family members and insights into function and expression regulation of lamprey NTCP. Fish Physiol Biochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-024-01324-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-024-01324-7