Abstract
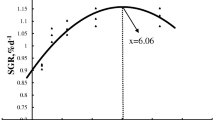
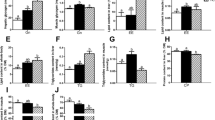
An 8-week feeding trial was conducted to evaluate the effects of dietary carbohydrate to lipid (CHO:L) ratios on growth performance, body composition, serum biochemical indexes, lipid metabolism, and gene expression of central appetite regulating factors in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi) (mean initial weight: 12.86 ± 0.10 g). Five isonitrogenous and isoenergetic diets (fish meal, casein as main protein sources) were formulated to contain different graded CHO:L ratio diets ranging from 0.12, 0.86, 1.71, 3.29, and 7.19. Each diet was assigned to triplicate groups of 18 experimental fish. Our results revealed that final body weight (FBW), weight gain rate (WGR), specific growth rate (SGR), and protein efficiency ratio (PER) increased with dietary CHO:L ratio from 0.12 to 1.71 and then decreased with further increases in dietary CHO:L ratio. A two-slope broken-line regression analysis based on WGR showed that the optimal dietary CHO:L level for maximum growth performance of fish was 1.60. Crude lipid and crude protein content in the liver and glycogen concentration in the muscle and liver were significantly influenced by the dietary CHO:L ratios (P < 0.05). The lowest crude lipid content in the liver was observed in fish fed the diet with a CHO:L ratio of 1.71(P < 0.05). Dietary CHO:L ratios significantly induced the glucose concentration of serum (P < 0.05). The relative expression levels of genes involved in lipid metabolism, such as srebp1 and fas in the liver, showed a trend of first decreased and then increased with the increase of dietary CHO:L ratio levels. Appropriate CHO:L ratio in the diet can effectively reduce the accumulation of liver fat. We observed in fish fed the 1.71 CHO:L ratio diet showed higher feed intake, up‐regulated mRNA expression of neuropeptide Y (npy) and agouti gene-related protein (agrp), and down‐regulated mRNA expression of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (cart) and pro‐opiomelanocorticoid (pomc) significantly as compared to control group. Thus, these results provide the theoretical basis for feed formulation to determine the appropriate CHO:L ratio requirement of Chinese perch.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available from the corresponding author by request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alexander C, Sahu NP, Pal AK, Akhtar MS (2011) Haemato-immunological and stress responses of Labeo rohita (Hamilton) fingerlings: effect of rearing temperature and dietary gelatinized carbohydrate. J Anim Physiol an N 95:653–663. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.01096.x
Brauge C, Corraze G, Médale FO (1995) Effects of dietary levels of carbohydrate and lipid on glucose oxidation and lipogenesis from glucose in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, reared in freshwater or in seawater. Comp Biochem Phys A 111:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-9629(95)98527-N
Basto-Silva C, Enes P, Oliva-Teles A, Balbuena-Pecino S, Navarro I, Capilla E, Guerreiro I (2021) Dietary protein source and protein/carbohydrate ratio affects appetite regulation-related genes expression in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata). Aquaculture 533:736142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736142
Blouet C, Schwartz GJ (2009) Hypothalamic nutrient sensing in the control of energy homeostasis. Behav Brain Res 209:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.12.024
Castro C, Corraze G, Pérez-Jiménez A, Larroquet L, Cluzeaud M, Panserat S, Oliva-Teles A (2015) Dietary carbohydrate and lipid source affect cholesterol metabolism of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) juveniles. Brit J Nutr 114:1143–1156. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114515002731
Castro C, Corraze G, Basto A, Larroquet L, Panserat S, Oliva-Teles A (2016) Dietary lipid and carbohydrate interactions: implications on lipid and glucose absorption, transport in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) juveniles. Lipids 51:743–755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4140-2
Conde-Sieira M, Soengas JL (2016) Nutrient sensing systems in fish: impact on food intake regulation and energy homeostasis. Front Neurosci-Switz 10:603. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00603
Dai YJ, Jiang GZ, Yuan XY, Liu WB (2018) High-fat-diet-induced inflammation depresses the appetite of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) through the transcriptional regulation of leptin/mammalian target of rapamycin. Brit J Nutr 120:1422–1431. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451800288X
Ding Z, Liu Y, Han J, Liu X, Zheng Y, Li W, Li Y (2020) Dietary lipid supplementation could significantly affect the growth, fatty acid profiles, and expression of PPARα, leptin, and adiponectin genes in juvenile genetically improved farmed tilapia. Eur J Lipid Sci Tech 123(1):2000207. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejlt.202000207
Dong LF, Tong T, Zhang Q, Wang QC, Xu MZ, Yu HR, Wang J (2018) Effects of dietary carbohydrate to lipid ratio on growth, feed utilization, body composition and digestive enzyme activities of golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Aquacult Nutr 24:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12565
Efeyan A, Comb WC, Sabatini DM (2015) Nutrient-sensing mechanisms and pathways. Nature 517:302–310. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14190
Egea M, Metón I, Córdoba M, Fernández F, Baanante IV (2008) Role of Sp1 and SREBP-1a in the insulin-mediated regulation of glucokinase transcription in the liver of gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Gen Comp Endocr 155:359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2007.06.018
Fao (2018) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018: Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals United Nations.
Fazio F (2019) Fish hematology analysis as an important tool of aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture 500:237–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2018.10.030
Ferré P, Foufelle F (2010) Hepatic steatosis: a role for de novo lipogenesis and the transcription factor SREBP-1c. Diabetes Obes Metab 12:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01275.x
Figueiredo-Silva AC, Saravanan S, Schrama JW, Panserat S, Kaushik S, Geurden I (2013) A comparative study of the metabolic response in rainbow trout and Nile tilapia to changes in dietary macronutrient composition. Brit J Nutr 109:816–826. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451200205X
Gao W, Liu YJ, Tian LX, Mai KS, Liang GY, Yang HJ, Huai MY, Luo WJ (2010) Effect of dietary carbohydrate-to-lipid ratios on growth performance, body composition, nutrient utilization and hepatic enzymes activities of herbivorous grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquacult Nutr 16:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2009.00668.x
Gao Y, Luo Y, Li X, Dong Y, Liao Y, Yao W, Jin Z, Wu X (2018) Effects of dietary carbohydrate/lipid ratios on growth, feed utilization, hematology parameters, and intestinal digestive enzyme activities of juvenile hybrid grouper (brown-marbled grouper Epinephelus fuscoguttatus♀×giant grouper E. lanceolatus♂). N Am J Aquacult 80:418–426. https://doi.org/10.1002/naaq.10057
Gong G, Xue M, Wang J, Wu X-F, Zheng Y-H, Han F, Liang X-F, Su X-O (2015) The regulation of gluconeogenesis in the Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii) affected later in life by a short-term high-glucose programming during early life. Aquaculture 436:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.10.044
Hemre GI, Mommsen TP, Krogdahl, (2002) Carbohydrates in fish nutrition: effects on growth, glucose metabolism and hepatic enzymes. Aquacult Nutr 8:175–194. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2095.2002.00200.x
Hirwitz W, Latimer G (1995) Official methods of analysis of AOAC International (16th edn). Trends Food Sci Tech 6:382–382
Honorato CA, Almeida LC, Nunes CDS, Carneiro DJ, Moraes G (2010) Effects of processing on physical characteristics of diets with distinct levels of carbohydrates and lipids: the outcomes on the growth of pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus). Aquacult Nutr 16:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2095.2008.00644.x
Ishak SD, Kamarudin MS, Ramezani-Fard E, Saad CR, Yusof YA (2016) Effects of varying dietary carbohydrate levels on growth performance, body composition and liver histology of Malaysian mahseer fingerlings (Tor tambroides). J Environ Biol 37:755–764
Jobling M (2012) National Research Council (NRC): Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. 20: 601–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-011-9480-6
Kamalam BS, Medale F, Panserat S (2016) Utilisation of dietary carbohydrates in farmed fishes: new insights on influencing factors, biological limitations and future strategies. Aquaculture 467:3–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.02.007
Kuipers RS, Luxwolda MF, Sango WS, Kwesigabo G, Velzing-Aarts FV, DaJ D-B, FaJ M (2011) Postpartum changes in maternal and infant erythrocyte fatty acids are likely to be driven by restoring insulin sensitivity and DHA status. Med Hypotheses 76:794–801
Kumar S, Sahu NP, Pal AK, Choudhury D, Yengkokpam S, Mukherjee SC (2005) Effect of dietary carbohydrate on haematology, respiratory burst activity and histological changes in L. rohita juveniles. Fish Shellfish Immunol 19:331–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2011.02.020
Li AX, Yuan XC, Liang X-F, Liu LW, Li J, Li B, Fang JG, Li J, He S, Xue M, Wang J, Tao Y-X (2016) Adaptations of lipid metabolism and food intake in response to low and high fat diets in juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus). Aquaculture 457:43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.01.014
Li H, Xu W, Jin J, Zhu X, Yang Y, Han D, Liu H, Xie S (2019a) Effects of dietary carbohydrate and lipid concentrations on growth performance, feed utilization, glucose, and lipid metabolism in two strains of gibel carp. Front Vet Sci 6:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2019.00165
Li L, Fang J, Liang XF, Alam MS, Liu L, Yuan X (2019b) Effect of feeding stimulants on growth performance, feed intake and appetite regulation of mandarin fish, Siniperca chuatsi. Aquac Res 50:3684–3691. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14327
Li S, Yin J, Zhang H, Liu Z, Chen N (2019c) Effects of dietary carbohydrate and lipid levels on growth performance, feed utilization, body composition and non-specific immunity of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Aquacult Nutr 25(5):995–1005. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12917
Li S, Sang C, Wang A, Zhang J, Chen N (2019d) Effects of dietary carbohydrate sources on growth performance, glycogen accumulation, insulin signaling pathway and hepatic glucose metabolism in largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Aquaculture 513:734391–734391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734391
Li XF, Liu WB, Lu KL, Xu WN, Ying W (2012) Dietary carbohydrate/lipid ratios affect stress, oxidative status and non-specific immune responses of fingerling blunt snout bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. Fish Shellfish Immunol 33:316–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2012.05.007
Liang XF, Oku H, Ogata H, Liu J, He X (2001) Weaning Chinese perch Siniperca chuatsi (Basilewsky) onto artificial diets based upon its specific sensory modality in feeding. Aquac Res 32:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1355-557x.2001.00006.x
Liang X, Liu J, Huang B, Liang X, Liu J, Huang B (2010) The role of sense organs in the feeding behaviour of Chinese perch. J Fish Biol 52:1058–1067. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1998.tb00603.x
Lin SM, Shi CM, Mu MM, Chen YJ, Luo L (2018) Effect of high dietary starch levels on growth, hepatic glucose metabolism, oxidative status and immune response of juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. Fish Shellfish Immunol 78:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.04.046
Liu D, Guo B, Han D, Deng K, Gu Z, Yang M, Xu W, Zhang W, and Mai K (2018) Comparatively study on the insulin-regulated glucose homeostasis through brain-gut peptides in Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus after intraperitoneal and oral administration of glucose. Gen Comp Endocr 9-20https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.02.013
Liu L, Fang J, Liang XF, He S (2020) Nucleotide promotes feed intake and protein utilization via regulating the gene expression of feeding and nitrogen metabolism in juvenile Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Aquacult Nutr 26:1702–1712. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.13121
Lu KL, Xu WN, Li JY, Li XF, Huang GQ, Liu WB (2013) Alterations of liver histology and blood biochemistry in blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala fed high-fat diets. Fisheries Sci 79:661–671. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-013-0635-4
Lu K-L, Xu W-N, Wang L-N, Zhang D-D, Zhang C-N, Liu W-B (2014) Hepatic β-oxidation and regulation of carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT) I in blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala fed a high fat diet. PLoS One 9:93135. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0093135
Lu X, Peng D, Chen X, Wu F, Jiang M, Tian J, Liu W, Yu L, Wen H, Wei K (2020) Effects of dietary protein levels on growth, muscle composition, digestive enzymes activities, hemolymph biochemical indices and ovary development of pre-adult red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquacult Rep 18:100542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100542
Misra S, Sahu NP, Pal AK, Xavier B, Kumar S, Mukherjee SC (2005) Pre- and post-challenge immuno-haematological changes in Labeo rohita juveniles fed gelatinised or non-gelatinised carbohydrate with n-3 PUFA. Fish Shellfish Immunol 21:346–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2005.12.010
Mobbs CV, Isoda F, Makimura H, Mastaitis J, Mizuno T, Shu I-W, Yen K, Yang X-J (2005) Impaired glucose signaling as a cause of obesity and the metabolic syndrome: the glucoadipostatic hypothesis. Physiol Behav 85:3–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.04.005
Montoya-Camacho N, Marquez-Ríos E, Castillo-Yáñez FJ, López JLC, López-Elías JA, Ruíz-Cruz S, Jiménez-Ruíz EI, Rivas-Vega ME, Ocaño-Higuera VM (2019) Advances in the use of alternative protein sources for tilapia feeding. Rev Aquacult 11:515–526. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12243
Ortinau LC, Hoertel HA, Douglas SM, Leidy HJ (2014) Effects of high-protein vs. high-fat snacks on appetite control, satiety, and eating initiation in healthy women. Nutr J 13:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-13-97
Otero-Rodiño C, Velasco C, Álvarez-Otero R, López-Patiño MA, Míguez JM, Soengas JL (2016) In vitro evidence supports the presence of glucokinase-independent glucosensing mechanisms in hypothalamus and hindbrain of rainbow trout. J Exp Biol 219:1750–1759. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.137737
Rasmussen RS, Ostenfeld TH, Rønsholdt B, and Mclean E (2000) Manipulation of end‐product quality of rainbow trout with finishing diets. Aquacult Nutr 6https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2095.2000.00119.x
Ren MC, Ai QH, Mai KS, Ma HM, Wang XJ (2011) Effect of dietary carbohydrate level on growth performance, body composition, apparent digestibility coefficient and digestive enzyme activities of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum L. Aquac Res 42:1467–1475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2109.2010.02739.x
Shearer GC, Savinova OV, Harris WS (2012) Fish oil – how does it reduce plasma triglycerides? Bba-Rev Cancer 1821:843–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.10.011
SitjÀ-Bobadilla A, PÉrez-SÁnchez J (1999) Short communication diet related changes in non-specific immune response of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol 9:637–640. https://doi.org/10.1006/fsim.1999.0219
Tantot F, Parkes SL, Marchand AR, Boitard C, Naneix F, Laye S, Trifilieff P, Coutureau E, Ferreira G (2017) The effect of high-fat diet consumption on appetitive instrumental behavior in rats. Appetite 108:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2016.10.001
Taj S, Irm M, Jin M, Yuan Y, Andriamialinirina HJT, Zhou Q (2020) Effects of dietary carbohydrate to lipid ratios on growth performance, muscle fatty acid composition, and intermediary metabolism in juvenile black seabream (Acanthopagrus schlegelii). Front Physiol 11:507. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2020.00507
Turchini GM, Torstensen BE, Ng WK (2009) Fish oil replacement in finfish nutrition. Rev Aquacult 1:10–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-5131.2008.01001.x
Volkoff H, Canosa LF, Unniappan S, Cerdá-Reverter JM, Bernier NJ, Kelly SP, Peter RE (2004) Neuropeptides and the control of food intake in fish. Gen Comp Endocr 142:3–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2004.11.001
Wang BK, Liu WB, Xu C, Cao XF, Zhong XQ, Shi HJ, Li XF (2017) Dietary carbohydrate levels and lipid sources modulate the growth performance, fatty acid profiles and intermediary metabolism of blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala in an interactive pattern. Aquaculture 481:140–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2017.08.034
Wang LN, Liu WB, Lu KL, Xu WN, Cai DS, Zhang CN, Qian Y (2014) Effects of dietary carbohydrate/lipid ratios on non-specific immune responses, oxidative status and liver histology of juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco. Aquaculture 426–427:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.01.022
Wang J, Liang XF, He S, Li J, Huang K, Zhang YP, Huang D (2018) Lipid deposition pattern and adaptive strategy in response to dietary fat in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Nutr Metab 15(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12986-018-0315-6
Wiegertjes GF, Stet RM, Parmentier HK, Muiswinkel WBV (1996) Immunogenetics of disease resistance in fish: a comparative approach. Dev Comp Immunol 20:365–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0145-305X(96)00032-8
Wilson RP (1994) Utilization of dietary carbohydrate by fish. Aquaculture 124:67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/0044-8486(94)90363-8
Xu H, Han T, Li X, Wang J, Zheng P, Yin F, and Wang C (2020) Effects of dietary lipid levels on survival, growth performance, and antioxidant ability of the early juvenile Scylla paramamosain. Aquaculture 528https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735559
Yokobori E, Azuma M, Nishiguchi R, Kang KS, Kamijo M, Uchiyama M, Matsuda K (2012) Neuropeptide Y stimulates food intake in the Zebrafish, Danio rerio. J Neuroendocrinol 24:766–773. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02281.x
Yuan XC, Liang X-F, Liu LW, Fang JG, Li J, Li AX, Cai WJ, Xue M, Wang J, Wang QC (2016) Fat deposition pattern and mechanism in response to dietary lipid levels in grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idellus. Fish Physiol Biochem 42:1557–1569. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0240-4
Zhang L, Liu W-B, Brown PB, Xu C, Shi H-J, Zheng X-C, Zhang L, He C, Huang Y-Y, Li X-F (2020) Utilization of raw and gelatinized starch by blunt snout bream Megalobrama amblycephala as evidenced by the glycolipid metabolism, glucose tolerance and mitochondrial function. Aquaculture 529:735603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735603
Zhao H, Cao J, Chen X, Wang G, Hu J, Chen B (2020) Effects of dietary lipid-to-carbohydrate ratio on growth and carbohydrate metabolism in juvenile cobia(Rachycentron canadum). Anim Nutr 6:80–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aninu.2019.11.010
Zhou C, Liu B, Ge X, Xie J, Xu P (2013) Effect of dietary carbohydrate on the growth performance, immune response, hepatic antioxidant abilities and heat shock protein 70 expression of Wuchang bream, Megalobrama amblycephala. J Appl Ichthyol 29:1348–1356. https://doi.org/10.1111/jai.12264
Zhou PP, Wang MQ, Xie FJ, Deng D-F, Zhou QC (2016) Effects of dietary carbohydrate to lipid ratios on growth performance, digestive enzyme and hepatic carbohydrate metabolic enzyme activities of large yellow croaker (Larmichthys crocea). Aquaculture 452:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.10.010
Zhou YL, Guo JL, Tang RJ, Ma HJ, Lin SM (2020) High dietary lipid level alters the growth, hepatic metabolism enzyme, and anti-oxidative capacity in juvenile largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. Fish Physiol Biochem 46:125–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-019-00705-7
Funding
This work was financially supported by China Agriculture Research System (CARS-46), the National Key R & D Program of China (2019YFD0900500) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972809).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.P. and X-F L.: designed the experiments and draft the manuscript. D.P., F-R C., and H–X F.: performed the experiments. J. L., S-L T., K. L., and Q-W Z.: revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All experiments and animal-handling procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Institute of Laboratory Animal Centre, Huazhong Agriculture University (Ethical code: HZAUFI-2020–0004).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors review and approve the manuscript for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, D., Liang, XF., Chai, F. et al. Effects of dietary carbohydrate to lipid ratios on growth, biochemical indicators, lipid metabolism, and appetite in Chinese perch (Siniperca chuatsi). Fish Physiol Biochem 48, 101–116 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-01043-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-021-01043-3