Abstract
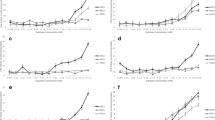
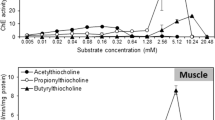
The characterization of cholinesterase activity in brain and muscle of gilthead seabream was carried out using four specific substrates and three selective inhibitors. In addition, K m and V max were calculated from the Michaelis–Menten equation for ASCh and BSCh substrates. Finally, the in vitro sensitivity of brain and muscle cholinesterases to three organophosphates (OPs) was also investigated by estimating inhibition kinetics. The results indicate that AChE is the enzyme present in the brain, whereas in muscle, a typical AChE form is present along with an atypical form of BChE. Very low ChE activity was found in plasma with all substrates used. The inhibitory potency of the studied OPs on brain and muscle AChEs based on bimolecular inhibition constants (k i ) was: omethoate < dichlorvos < azinphosmethyl-oxon. Furthermore, muscle BChE was found to be several orders of magnitude (from 2 to 4) more sensitive than brain and muscle AChE inhibition by dichlorvos and omethoate.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpuche-Gual L, Gold-Bouchot G (2008) Determination of esterase activity and characterization of cholinesterases in the reef fish Haemulon plumier. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 71:787–797. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.01.024
Arufe MI, Arellano JM, García L, Albendín G, Sarasquete C (2007) Cholinesterase activity in gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) larvae: characterization and sensitivity to the organophosphate azinphosmethyl. Aquat Toxicol 84:328–336. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.06.009
Assis CRD, Bezerra RS, Carvalho LB Jr (2011) Fish cholinesterases as biomarkers of organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides. In: Stoytcheva M (ed) Pesticides in the modern world - Pests control and pesticides exposure and toxicity assessment. InTech, pp 253–278. doi:10.5772/20777
Bradford MA (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carr RL, Chambers JE (1996) Kinetic analysis of the in vitro inhibition, aging, and reactivation of brain acetylcholinesterase from rat and channel catfish by paraoxon and chlorpyrifos-oxon. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 139:365–373. doi:10.1006/taap.1996.0177
Chuiko GM (2000) Comparative study of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in brain and serum of several freshwater fish: specific activities and in vitro inhibition by DDVP, and organophosphorus pesticide. Comp Biochem Physiol 127C:233–242. doi:10.1016/S0742-8413(00)00150-X
Chuiko GM, Podgornaya VA, Zhelnin YY (2003) Acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase activities in brain and plasma of freshwater teleosts: cross-species and cross-family differences. Comp Biochem Physiol 135B:55–61. doi:10.1016/S1096-4959(03)00048-4
De la Torre FR, Ferrari L, Salibián A (2002) Freshwater pollution biomarker: response of brain acetylcholinesterase activity in two fish species. Comp Biochem Physiol 131C:271–280. doi:10.1016/S1532-0456(02)00014-5
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, FeatherstoneI I, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colometric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Guilhermino L, Lopes MC, Carvalho AP, Soares AMVM (1996) Inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity as effect criterion in acute tests with juvenile Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 32:727–738. doi:10.1016/0045-6535(95)00360-6
Herzsprung P, Weil L, Niessner R (1992) Measurement of bimolecular rate constants k i of the cholinesterase inactivation reaction by 55 insecticides and of the influence of various pyridiniumoximes on k i . Int J Environ Anal Chem 47:181–200
Johnson JA, Wallace KB (1987) Species-related differences in the inhibition of brain acetylcholinesterase by paraoxon and malaoxon. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 88:234–241. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(87)90009-3
Jung JH, Addison RF, Shim WJ (2007) Characterization of cholinesterases in marbled sole, Limanda yokohamae, and their inhibition in vitro by the fungicide iprobenfos. Mar Environ Res 63:471–478. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2006.12.007
Kamrin MA (2000) Pesticides profiles. Toxicology, environmental impact, and fate. CRC Press LLC, CRC Press LLC
Kemp RJ, Wallace KB (1990) Molecular determinants of species-selective inhibition of brain acetylcholinesterase. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 104:246–258. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(90)90299-A
Kitz R, Wilson IB (1962) Ester of methanesulfonic acid as irreversible inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem 237:3245–3249
Main AR, Iverson F (1966) Measurement of the affinity and phosphorylation constants governing irreversible inhibition of cholinesterases by di-isopropyl phosphofluoridate. Biochem J 100:525–531
Oliveira MM, Filho MVS, Bastos VLF, Fernandes FC, Bastos JC (2007) Brain acetylcholinesterase as a marine pesticide biomarker using brazilian fishes. Mar Environ Res 63:303–312. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2006.10.002
Quintaneiro C, Monteiro M, Pastorinho R, Soares AMVM, Noqueira AJA, Morgado F, Guilhermino L (2006) Environmental pollution and natural populations: a biomarkers case study from the Iberian Atlantic Coast. Mar Pollut Bull 52:1406–1413. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2006.04.002
Rendon Von Osten J, Ortíz-Arana A, Guilhermino L, Soares AMVM (2005) In vivo evaluation of three biomarkers in the mosquitofish (Gambusia yucatana) exposed to pesticides. Chemosphere 58:627–636. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.08.065
Rodríguez-Fuentes G, Gold-Bouchot G (2004) Characterization of cholinesterase activity from different tissues of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Mar Environ Res 58:505–509. doi:10.1016/j.marenvres.2004.03.037
Salles JB, Cunha Bastos VLF, Silva Filho MV, Machado OLT, Salles CMC, Giovanni de Simone S, Cunha Bastos J (2006) A novel butyrylcholinesterase from serum of Leporinus macrocephalus, a neotropical fish. Biochimie 88:59–68. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2005.06.017
Shaonan I, Xianchuan X, Guaonian Z, Yajun T (2004) Kinetic characters and resistance to inhibition of crude and purified brain acetylcholinesterase of three freshwater fishes by organophosphates. Aquat Toxicol 68:293–299. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.03.013
Silva Filho MVS, Oliveira MM, Salles JB, Cunha Bastos VLF, Cassano VPF, Cunha Bastos J (2004) Methyl-paraoxon comparative inhibition kinetics for acetylthiocholinesterases from brain of neotropical fishes. Toxicol Lett 153:247–254. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.04.026
Solè M, Vega S, Varò I (2012) Characterization of type “B” esterases and hepatic CYP450 isoenzimes in Senegalese sole for their further application in monitoring studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 78:72–79. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.11.013
Sturm A, da Silva de Assis HC, Hansen PD (1999) Cholinesterases of marine teleost fish: enzymological characterization and potential use in the monitoring of neurotoxic contamination. Mar Environ Res 47:389–398. Correction: Mar Environ Res 49(2000):95. doi:10.1016/S0141-1136(98)00127-5
Sturm A, Wogran J, Segner H, Liess M (2000) Different sensitivity to organophosphates of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase from three-spined stickeback (Gasterosteus aculeatus): application in biomonitoring. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:1607–1615. doi:10.1002/etc.5620190618
Tortelli V, Colares EP, Robaldo RB, Nery LEM, Pinho GLL, Bianchini A, Monserrat JM (2006) Importance of cholinesterase kinetic parameters in environmental monitoring using estuarine fish. Chemosphere 65:560–566. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.02.047
Varò I, Navarro JC, Nunes B, Guilhermino L (2007) Effects of dichlorvos aquaculture treatments on selected biomarkers of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) fingerlings. Aquaculture 266:87–96. doi:10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.02.045
Wang C, Murphy SD (1982) Kinetic analysis of species difference in acetylcholinesterase sensitivity to organophosphate insecticides. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 66:409–419. doi:10.1016/0041-008X(82)90307-6
Wilson BW (2010) Cholinesterases. Hayes’s handbook of pesticide toxicology. Academic Press, New York, pp 1457–1478
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Laboratory of Marine Culture at University of Cádiz for providing the experimental fish used in this study. This work was supported by Plan Nacional de I + D, Sciences and Technology Minister (Project: CTM2004-05718) and in part by Plan Andaluz de Investigación (PAI group: RNM-345).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albendín, G., Arellano, J.M., Mánuel-Vez, M.P. et al. Characterization and in vitro sensitivity of cholinesterases of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) to organophosphate pesticides. Fish Physiol Biochem 43, 455–464 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0299-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0299-y