Abstract
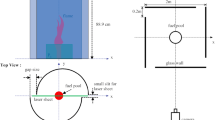
Fire whirls are often reported to occur in wildland and urban fires due to the effect of ambient wind. This paper presents an experimental study on the fire whirls over a line fire with cross wind, focusing on the occurrence frequency of fire whirls. The experimental observations indicated that the fire whirls induced by a line fire may spread beyond the line fire region with the effect of wind. For the effect of cross wind, it is indicated that the cross wind basically increases the occurrence frequency, while the velocity components parallel or perpendicular to the line fire have competitive effects. A scaling law is presented for the critical wind speed inducing fire whirls based on the experimental data in this work and literature. A method is proposed to estimate the magnitude of the fire whirl height under the critical wind speed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soma S, Saito K (1991) Reconstruction of fire whirls using scale models. Combust Flame 86(3):269–284. doi:10.1016/0010-2180(91)90107-M
Shinohara M, Matsushima S (2012) Formation of fire whirls: Experimental verification that a counter-rotating vortex pair is a possible origin of fire whirls. Fire Safety J 54(0):144–153. doi:10.1016/j.firesaf.2012.03.009
Zhou K, Liu N, Zhang L, Satoh K (2014) Thermal radiation from fire whirls: revised solid flame model. Fire Technol 50(6):1573–1587. doi:10.1007/s10694-013-0360-7
Wang P, Liu N, Zhang L, Bai Y, Satoh K (2014) Fire whirl experimental facility with no enclosure of solid walls: design and validation. Fire Technol 1–19. doi:10.1007/s10694-014-0435-0
Dessens J (1962) Man-made tornadoes. Nature 193(4810):14–15. doi:10.1038/193013a0
Dupuy J-L, Maréchal J, Portier D, Valette J-C (2011) The effects of slope and fuel bed width on laboratory fire behaviour. Int J Wildland Fire 20(2):272–288. doi:10.1071/WF09075
Silvani X, Morandini F, Dupuy J-L (2012) Effects of slope on fire spread observed through video images and multiple-point thermal measurements. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 41(0):99–111. doi:10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2012.03.021
Emori R, Saito K (1982) Model experiment of hazardous forest fire whirl. Fire Technol 18(4):319–327. doi:10.1007/BF02473115
Kuwana K, Sekimoto K, Saito K, Williams FA (2008) Scaling fire whirls. Fire Safety J 43(4):252–257. doi:10.1016/j.firesaf.2007.10.006
Liu N, Liu Q, Deng Z, Kohyu S, Zhu J (2007) Burn-out time data analysis on interaction effects among multiple fires in fire arrays. Proc the Combust Inst 31(2):2589–2597. doi:10.1016/j.proci.2006.08.110
Kuwana K, Sekimoto K, Akafuah NK, Chuah KH, Lei J, Saito K, Williams FA (2011) The moving-type fire whirl observed during a recent Brazil bush fire. Paper presented at the 7th US National Technical Meeting of the Combustion Institute, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA
Kuwana K, Sekimoto K, Minami T, Tashiro T, Saito K (2013) Scale-model experiments of moving fire whirl over a line fire. Proc Combust Inst 34(2):2625–2631. doi:10.1016/j.proci.2012.06.092
Zhou K, Liu N, Yin P, Yuan X, Jiang J (2014) Fire whirl due to interaction between line fire and cross wind. Paper presented at the Fire Safety Science—Proceedings of the Eleventh International Symposium, Canterbury, New Zealand
Yuan LM, Cox G (1996) An experimental study of some line fires. Fire Safety J 27(2):123–139. doi:10.1016/S0379-7112(96)00047-1
Zhou K, Liu N, Lozano JS, Shan Y, Yao B, Satoh K (2013) Effect of flow circulation on combustion dynamics of fire whirl. Proc Combust Inst 34(2):2617–2624. doi:10.1016/j.proci.2012.06.053
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant (51476156 and 51120165001), International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (No. 2014DFG72300), and the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB719702). Naian Liu was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. WK 2320000020). Kuibin Zhou was supported by the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Fire Science (No. HZ2013-KF09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, K., Liu, N. & Yuan, X. Effect of Wind on Fire Whirl Over a Line Fire. Fire Technol 52, 865–875 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-015-0507-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-015-0507-9