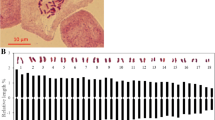
Abstract
Increased labor costs and reduced labor pools for hop production necessitate the development of strategies that improve efficiency and automation of hop production. One solution for reducing labor inputs is the use of “short-trellis” hop varieties. Unfortunately, little information exists on the genetic control of this trait in hop, and there are no known molecular markers available for selection. This preliminary study was enacted to identify QTLs associated with expression of short-stature growth phenotype using SNPs identified within genome-assembled scaffolds. A bi-parental mapping population of 87 offspring was obtained from the cross, “Pioneer × 25/95/15”. Genotyping-by-sequencing was performed on parents and offspring. SNPs were identified using TASSEL v3.0 with either ‘Teamaker’ reference genome or ‘Shinsuwase’ genome. The genetic map derived from ‘Teamaker’ SNPs was far superior and was used for all further analysis. QTL analysis identified eight QTLs linked to short stature with five showing strong statistical association based upon three different statistical analyses. All eight QTLs were found on linkage group one. Evaluation of scaffolds containing SNP markers located at or surrounding QTL regions (±1 cM) identified 67 putative genes—several of which are known structural genes. A genome-wide scan of SNP markers identified an additional marker found on a scaffold containing a putative gene (Aspartyl protease family protein) known to induce dwarf characteristics in other species. Further validation of significantly associated markers on different populations is necessary prior to implementation in marker-assisted selection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett LW, Fletcher S, Wilton SD (2012) Regulation of eukaryotic gene expression by the untranslated gene regions and other non-coding elements. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:3613–3634
Broman K, Wu H, Sen Ś, Churchill G (2003) R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19:889–890
Cartwright DA, Troggio M, Velasco R, Gutin A (2007) Genetic mapping in the presence of genotyping errors. Genetics 176(4):2521–2527
Darby P (1994) Dwarfness and resistance to aphids: two novel traits in hop breeding. In: European Brewery Convention Monograph XXII, Symposium on Hops, Zoeterwoude, Netherlands, 30 May–1 June 1994, pp 24–35
Darby P (2004) Hop growing in England in the twenty first century. J R Agric Soc Engl 165:84–90
Darby P (2008) Hop Breeding in 2020 in the UK. Proceedings of the International Hop Symposium, Wolnzach, Germany 5–6 May 2008. German Federal Ministry of Food, Agriculture and Consumer Protection, Bonn, pp 56–59
Davière J-M, Achard P (2013) Gibberellin signaling in plants. Development 140:1147–1151
Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Sun Q, Poland JA, Kawamoto K, et al. (2011) A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 6: e19379. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3087801&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
Glaubitz J, Casstevens T, Lu F, Harriman J, Elshire R, Sun Q, Buckler E (2014) TASSEL-GBS: a high capacity genotyping by sequencing analysis pipeline. PLoS ONE 9(2):e90346. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090346
Gnerre S, MacCallum I, Przybylski D, Ribeiro F, Burton J, Walker B, Sharpe T, Hall G, Shea T, Sykes S, Berlin A, Aird D, Costello M, Daza R, Williams L, Nicol R, Gnirke A, Nusbaum C, Lander ES, Jaffe DB (2011) High-quality draft assemblies of mammalian genomes from massively parallel sequence data. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 108:1513–1518
Henning JA (2006) The breeding of hop. In: Bamworth Charles (ed) Brewing: new technologies. Woodhead Publishing Limited, Cambridge
Henning JA, Haunold A, Townsend MS, Gent DH, Parker T (2008) Registration of ‘Teamaker’ Hop. Journal of Plant Registrations 2(1):13–14
Henning JA, Gent DH, Twomey MC, Townsend MS, Pitra NJ, Matthews PD (2015a) Genotyping-by-sequencing of a bi-parental mapping population segregating for downy mildew resistance in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 1–15
Henning JA, Gent DH, Twomey M, Townsend MS, Pitra N, Matthews P (2015b) Precision QTL mapping of downy mildew resistance in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 202:487–498
IUPAC-IUB Comm. on Biochem. Nomenclature (CBN) (1970) Abbreviations and symbols for nucleic acids, polynucleotides, and their constituents. Biochemistry 9(20):4022–4027. doi:10.1021/bi00822a023
Iwata H, Ninomiya S (2006) AntMap: constructing genetic linkage maps using an ant colony optimization algorithm. Breed Sci 56(4):371–377. doi:10.1270/jsbbs.56.371
Jansen R (1993) Interval mapping of multiple quantitative trait loci. Genetics 135:205–211
Kawaoka A, Kaothien P, Yoshida K, Endo S, Yamada K, Ebinuma H (2000) Functional analysis of tobacco LIM protein Ntlim1 involved in lignin biosynthesis. Plant J 22:289–301
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Lu F, Lipka AE, Elshire RJ, Glaubitz JC, Cherney JH, Casler MD, Buckler ES, Costich DE (2013) Switchgrass genomic diversity, ploidy and evolution: novel insights from a network-based SNP discovery protocol. PLoS Genet 9(1):e1003215
Matthews PD, Coles MC, Pitra NJ (2013) Next generation sequencing for a plant of great tradition: application of NGS to SNP detection and validation in hops (Humulus lupulus L.)—hop special. Monatsschrift für Brauwissenschaft 66:185–191
Mayer AM, Staples RC (2002) Laccase: new functions for an old enzyme. Phytochemistry 60:551–565
Mehlenbacher S, Brown R, Nouhra E, Gokirmak T, Bassil N, Kubisiak T (2006) A genetic linkage map for hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) based on RAPD and SSR markers. Genome 49:122–133
Michael TP, Jackson S (2013) The First 50 Plant Genomes. The Plant Genome. doi:10.3835/plantgenome2013.03.0001in
Miles C, Wayne M (2008) Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis. Nat Educ 1(1):208 http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/quantitative-trait-locus-qtl-analysis-53904
Natsume S, Takagi H, Shiraishi A, Murata J, Toyonaga H, Patzak J, Takagi M, Yaegashi H, Uemura A, Mitsuoka C et al (2015) The draft genome of hop (Humulus lupulus), an essence for brewing. Plant Cell Physiol 56:428–441
Pepper A, Delaney T, Washburnt T, Poole D, Chory J (1994) DET1, a negative regulator of light-mediated development and gene expression in arabidopsis, encodes a novel nuclear-localized protein. Cell 78:109–116
Sanmartín M, Sauer M, Muñoz A, Rojo E (2012) MINIYO and transcriptional elongation: lifting the roadblock to differentiation. Transcription 3:25–28
Shuai B, Reynaga-Peña CG, Springer PS (2002) The lateral organ boundaries gene defines a novel, plant-specific gene family. Plant Physiol 129:747–761
Torii KU (2004) Leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases in plants: structure, function, and signal transduction pathways. In international review of cytology. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 1–46
Van Ooijen JW (2011) Multipoint maximum likelihood mapping in a full-sib family of an outbreeding species. Genet Res 93(5):343–349
Wagner TA, Kohorn BD (2001) Wall-associated kinases are expressed throughout plant development and are required for cell expansion. Plant Cell 13:303–318
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B (2012) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh. (http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm. Accessed 15 Sep 2015)
Wu Y, Bhat P, Close T and Lonardi S (2008) On the Accurate construction of consensus genetic maps CSB 2008—computational systems bioinformatics conference. Stanford. http://138.23.178.42/mgmap/. Accessed 18 Sep 2015
Xia Y, Suzuki H, Borevitz J, Blount J, Guo Z, Patel K, Dixon RA, Lamb C (2004) An extracellular aspartic protease functions in Arabidopsis disease resistance signaling. The EMBO J 23:980–988
Darby P (2001) Single gene traits in hop breeding. In: Proceedings of the scientific commission of the international hop growers Convention, Canterbury, UK. 2001. (Ed.) Seigner E 76–80
Zhang D, Pitra N, Coles M, Buckler ES, Matthews P (2016) Non-Mendelian inheritance of SNP markers reveals extensive chromosomal translocations in dioecious hops (Humulus lupulus L.). bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/069849
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Ms. Jamie Coggins, former Oregon State University student and now employee of Roy Farms Inc, Moxie, WA, for extracting DNA and preparing it for submission for sequencing as well as cataloging all samples associated with this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henning, J., Hill, S., Darby, P. et al. QTL examination of a bi-parental mapping population segregating for “short-stature” in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 213, 77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1848-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-017-1848-x