Abstract
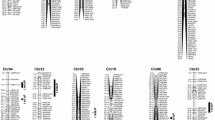
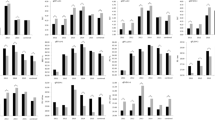
Fiber quality, as an important target trait in cotton breeding programs, is easily affected by the environment, and thus results in great complexity in breeding selection. In this study, we compared phenotypic variation in main fiber quality parameters (including fiber length, fiber strength and fiber micronaire) and dissected the molecular genetic basis using a recombinant inbred line population containing 282 individual lines grown at three locations in two major cotton-producing regions; i.e., the Yellow River Valley and the Yangtze River Valley in China, over two cotton planting seasons. We found that fibers produced from the Yangtze River Valley location appeared shorter, stronger and thicker relative to that from the Yellow River Valley location. A total of 27 Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) were identified for the main fiber quality parameters. Six QTLs were detected in more than five datasets, which explained 5.09–23.17 % of the phenotypic variance. One QTL (qFL16.1) was detected at the Yellow River Valley location over two planting seasons while three QTLs (qFL19.1, qFS03.1 and qFM19.1) were detected at the Yangtze River Valley location over the 2 years of planting seasons. Nine QTLs with significant additive × environment interactions (QEI) were also identified, and eight of these QTLs were detected at the Yangtze River Valley location. Moreover, four of twenty-three QTLs for boll weight and lint percentage were identified in more than five environments. These results may be beneficial for marker-assisted cotton breeding across different cotton-producing areas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burke JJ, Mahan JR, Hatfield JL (1988) Crop-specific thermal kinetic windows in relation to wheat and cotton biomass production. Agron J 80:553–556. doi:10.2134/agronj1988.00021962008000040001x
Chen J et al (2014) Effects of different planting dates and low light on cotton fibre length formation. Acta Physiol Plant 36:2581–2595. doi:10.1007/s11738-014-1629-2
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Dong H, Li W, Tang W, Li Z, Zhang D, Niu Y (2006) Yield, quality and leaf senescence of cotton grown at varying planting dates and plant densities in the Yellow River Valley of China. Field Crops Res 98:106–115. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2005.12.008
Fang DD, Jenkins JN, Deng DD, McCarty JC, Li P, Wu J (2014) Quantitative trait loci analysis of fiber quality traits using a random-mated recombinant inbred population in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). BMC Genomics 15:397. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-15-397
Gipson JR, Joham HE (1968) Influence of night temperature on growth and development of cotton (Gossypium birsutum L.). II fiber properties. Agron J 60:296–298. doi:10.2134/agronj1968.00021962006000030015x
Gipson JR, Joham HE (1969) Influence of night temperature on growth and development of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). III. Fiber elongation. Crop Sci 9:127–129. doi:10.2135/cropsci1969.0011183X000900020004x
Guo W et al (2007) A microsatellite-based, gene-rich linkage map reveals genome structure, function and evolution in Gossypium. Genetics 176:527–541. doi:10.1534/genetics.107.070375
Kim HJ, Triplett BA (2001) Cotton fiber growth in planta and in vitro. Models for plant cell elongation and cell wall biogenesis. Plant Physiol 127:1361–1366
Lacape J-M et al (2010) Meta-analysis of cotton fiber quality QTLs across diverse environments in a Gossypium hirsutum × G. barbadense RIL population. BMC Plant Biol 10:132
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(87)90010-3
Liakatas A, Roussopoulos D, Whittington WJ (1998) Controlled-temperature effects on cotton yield and fibre properties. J Agric Sci 130:463–471. doi:10.1017/s0021859698005413
Lokhande S, Reddy KR (2014) Quantifying temperature effects on cotton reproductive efficiency and fiber quality. Agron J 106:1275–1282. doi:10.2134/agronj13.0531
Ma F, Cao W, Li S, Zhu Y, Zhou Z, Zheng Z, Yang J (2005) Quantitative analysis on the relationships between cotton f iber quality and meteorological factors. Chin J Appl Ecol 16:2102–2107
Martin LK, Haigler C (2004) Cool temperature hinders flux from glucose to sucrose during cellulose synthesis in secondary wall stage cotton fibers. Cellulose 11:339–349. doi:10.1023/B:CELL.0000046420.10403.15
McCouch SR, Cho YG, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinosita T (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11
Paterson AH, Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1993) A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis. Plant Mol Biol Report 11:122–127. doi:10.1007/BF02670470
Paterson AH, Saranga Y, Menz M, Jiang CX, Wright R (2003) QTL analysis of genotype × environment interactions affecting cotton fiber quality. Theor Appl Genet 106:384–396. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1025-y
Pettigrew WT (2008) The effect of higher temperatures on cotton lint yield production and fiber quality. Crop Sci 48:278–285. doi:10.2135/cropsci2007.05.0261
Reddy KR, Davidonis GH, Johnson AS, Vinyard BT (1999) Temperature regime and carbon dioxide enrichment alter cotton boll development and fiber properties. Agron J 91:851–858. doi:10.2134/agronj1999.915851x
Roberts EM, Rao NR, Huang JY, Trolinder NL, Haigler CH (1992) Effects of cycling temperatures on fiber metabolism in cultured cotton ovules. Plant Physiol 100:979–986
Said JI, Lin Z, Zhang X, Song M, Zhang J (2013) A comprehensive meta QTL analysis for fiber quality, yield, yield related and morphological traits, drought tolerance, and disease resistance in tetraploid cotton. BMC Genomics 14:776. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-776
Said JI, Knapka JA, Song M, Zhang J (2015a) Cotton QTLdb: a cotton QTL database for QTL analysis, visualization, and comparison between Gossypium hirsutum and G. hirsutum x G. barbadense populations. Mol Genet Genomics MGG 290:1615–1625. doi:10.1007/s00438-015-1021-y
Said JI, Song M, Wang H, Lin Z, Zhang X, Fang DD, Zhang J (2015b) A comparative meta-analysis of QTL between intraspecific Gossypium hirsutum and interspecific G. hirsutum × G. barbadense populations. Mol Genet Genomics MGG 290:1003–1025. doi:10.1007/s00438-014-0963-9
Shao Q et al (2014) Identifying QTL for fiber quality traits with three upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) populations. Euphytica 198:43–58. doi:10.1007/s10681-014-1082-8
Sun F-D et al (2012) QTL mapping for fiber quality traits across multiple generations and environments in upland cotton. Mol Breed 30:569–582. doi:10.1007/s11032-011-9645-z
Tian J, Hu X, Gou L, Luo H, Zhang Y, Zhang W (2014) Growing degree days is the dominant factor associated with cellulose deposition in cotton fiber. Cellulose 21:813–822. doi:10.1007/s10570-013-0152-8
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng Z-B (2006) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm
Wang F, Gong Y, Zhang C, Liu G, Wang L, Xu Z, Zhang J (2011) Genetic effects of introgression genomic components from Sea Island cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) on fiber related traits in upland cotton (G. hirsutum L.). Euphytica 181:41–53. doi:10.1007/s10681-011-0378-1
Wang P et al (2012) Inheritance of long staple fiber quality traits of Gossypium barbadense in G. hirsutum background using CSILs. Theor Appl Genet 124:1415–1428. doi:10.1007/s00122-012-1797-7
Wang F et al (2013) Genetic dissection of the introgressive genomic components from Gossypium barbadense L. that contribute to improved fiber quality in Gossypium hirsutum L. Mol Breed 32:547–562. doi:10.1007/s11032-013-9888-y
Xiong Z, Wang X, Gu S, Zhang L, Zhou Z (2014) Correlation between meteorological factors and cotton fiber quality in major cotton producing regions of China cotton. Science 26:95–104
Yang J, Hu C, Hu H, Yu R, Xia Z, Ye X, Zhu J (2008) QTLNetwork: mapping and visualizing genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 24:721–723. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm494
Yang X et al (2015) Mapping QTL for cotton fiber quality traits using simple sequence repeat markers, conserved intron-scanning primers, and transcript-derived fragments. Euphytica 201:215–230. doi:10.1007/s10681-014-1194-1
Yeates SJ, Constable GA, McCumstie T (2010) Irrigated cotton in the tropical dry season. III: impact of temperature, cultivar and sowing date on fibre quality. Field Crops Res 116:300–307. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2010.01.006
Yu J et al (2013) Mapping quantitative trait loci for lint yield and fiber quality across environments in a Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense backcross inbred line population. Theor Appl Genet 126:275–287. doi:10.1007/s00122-012-1980-x
Zhang J, Guo W, Zhang T (2002) Molecular linkage map of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. × Gossypium barbadense L.) with a haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 105:1166–1174. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-1100-4
Zhang T et al (2015) Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat Biotech 33:531–537. doi:10.1038/nbt.3207, http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v33/n5/abs/nbt.3207.html#supplementary-information
Acknowledgments
We thank the local meteorological stations at Linqing, Anyang and Lishui for kindly providing the meteorological data. This work was financially supported in part by Grants from the National Science Foundation in China (31171598), National Project of Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System in China (CARS-18-10), National Major Project on Transgenic Breeding in China (2014ZX08005-00501B) and Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong Province (No. ts201511070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10681_2016_1728_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
ESM-1. QTLs for boll weight and lint percentage detected using WinQTLcart2.5 based on composite interval mappingSupplementary material 1 (PDF 32 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Zhang, C., Liu, G. et al. Phenotypic variation analysis and QTL mapping for cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) fiber quality grown in different cotton-producing regions. Euphytica 211, 169–183 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1728-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1728-9