Abstract
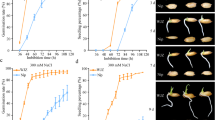
Using a recessive mutant with enhanced salt tolerance at seedling stage obtained from an indica rice cultivar R401 by gamma-ray irradiation, a novel gene controlling salt tolerance in rice was previously mapped to a 406-kb region on chromosome 6. We named the gene Seedling Salt Tolerance (SST). In this study, with a large F2 population derived from a cross between mutant sst and a japonica cultivar Nipponbare (salt sensitive), SST was further fine mapped to a 17-kb interval between InDel markers ID27101 and ID27118, in which only one gene (OsSPL10) was predicted. Sequencing analysis indicated that the 232nd base of the coding sequence of OsSPL10 was deleted in the sst allele, resulting in a frameshift mutation. The result strongly suggested that OsSPL10 should be the candidate of SST. OsSPL10 is a member of the SBP-box gene family. This is the first time that the SBP-box gene family is found to be probably involved in the regulation of seedling salt tolerance in plant.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardon GH, Höhmann S, Nettesheim K, Saedler H, Huijser P (1997) Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana SBP-box gene SPL3: a novel gene involved in the floral transition. Plant J 12:367–377
Du H, Liu LH, You L, Yang M, He YB, Li XH, Xiong LZ (2011) Characterization of an inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5/6-kinase gene that is essential for drought and salt stress responses in rice. Plant Mol Biol 77:547–563
Flowers TJ, Koyama ML, Flowers SA, Sudhakar C, Singh KP, Yeo AR (2000) QTL: their place in engineering tolerance of rice to salinity. J Exp Bot 51:99–106
Ghomi K, Rabiei B, Sabouri H, Sabouri A (2013) Mapping QTLs for traits related to salinity tolerance at seedling stage of rice (Oryza sativa L.): an agrigenomics study of an Iranian rice population. OMICS 17:242–251
Gong JM, He P, Qian Q, Shen LS, Zhu LH, Chen SY (1998) QTL mapping of rice for salt tolerance. Chin Sci Bull 43:1847–1850
Gou JY, Felippes FF, Liu CJ, Weigel D, Wang JW (2011) Negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis by a miR156-Targeted SPL transcription factor. Plant Cell 23:1512–1522
Gu XY, Mei MT, Yan XL, Zhen SL, Lu YG (2000) Preliminary detection of quantitative trait loci for salt tolerance in rice. Chin J Rice Sci 14:65–70
Hou HM, Li J, Gao M, Singer SD, Wang H, Mao LY, Fei ZJ, Wang XP (2013) Genomic organization, phylogenetic comparison and differential expression of the SBP-box family genes in grape. PLoS ONE 8:1–15
Hu S, Tao H, Qian Q, Guo L (2012) Genetics and molecular breeding for salt-tolerance in rice. Rice Genomics Genet 3:39–49
Huang XY, Chao DY, Gao JP, Zhu MZ, Shi M, Lin HX (2009) A previously unknown zinc finger protein, DST, regulates drought and salt tolerance in rice via stomatal aperture control. Gene Dev 23:1805–1817
Jung JH, Ju Y, Seo PJ, Lee JH, Park CM (2012) The SOC1-SPL module integrates photoperiod and gibberellic acid signals to control flowering time in Arabidopsis. Plant J 69:577–588
Klein J, Saedler H, Huijser P (1996) A new family of DNA binding proteins includes putative transcriptional regulators of the Antirrhinum majus floral meristem identity gene SQUAMOS. Mol Gen Genet 250:7–16
Koyama ML, Levesley A, Koebner RMD, Flowers TJ, Yeo AR (2001) Quantitative trait loci for component physiological traits determining salt tolerance in rice. Plant Physiol 125:406–422
Lan T, Liang KJ, Chen ZW, Duan YL, Wang JL, Ye N, Wu WR (2007) Genetic analysis and gene mapping of cold-induced seedling chlorosis in rice. Hereditas (Beijing) 29:1121–1125
Lee SY, Ahn JH, Cha YS, Yun DW, Lee MC, Ko JC, Lee KS, Eun MY (2007) Mapping QTLs related to salinity tolerance of rice at the young seedling stage. Plant Breed 126:43–46
Li J, Hou H, Li X, Xiang J, Yin X, Gao H, Zheng Y, Bassett CL, Wang X (2013) Genome-wide identification and analysis of the SBP-box family genes in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.). Plant Physiol Biochem 70:100–114
Lin HX, Zhu MZ, Yano M, Gao JP, Liang ZW, Su WA, Hu XH, Ren ZH, Chao DY (2004) QTLs for Na+ and K+ uptake of the shoots and roots controlling rice salt tolerance. Theor Appl Genet 108:253–260
Lincoln S, Daly M, Lander E (1992) Constructing genetics maps with MAPMAKER/EXP 3.0. Whitehead Institute Technical Report, Cambridge
Manning K, Tör M, Poole M, Hong YG, Thompson AJ, King GJ, Giovannoni JJ, Seymour GB (2006) A naturally occurring epigenetic mutation in a gene encoding an SBP-box transcription factor inhibits tomato fruit ripening. Nat Genet 38:948–952
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Pandit A, Rai V, Bal S, Sinha S, Kumar V, Chauhan M, Gautam RK, Singh R, Sharma PC, Singh AK, Gaikwad K, Sharma TR, Mohapatra T, Singh NK (2010) Combining QTL mapping and transcriptome profiling of bulked RILs for identification of functional polymorphism for salt tolerance genes in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Genet Genomics 284:121–136
Qian YL, Wang H, Chen MY, Zhang LK, Chen BS, Cui JT, Liu HY, Zhu LH, Shi YY, Gao YM, Li ZK (2009) Detection of salt-tolerant QTL using BC2F3 yield selected introgression lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Plant Breed 7:224–232
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S, Lin HX (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet 37:1141–1146
Riese M, Zobell O, Saedler H, Huijser P (2008) SBP-domain transcription factors as possible effectors of cryptochrome-mediated blue light signalling in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Planta 227:505–515
Salinas M, Xing S, Höhmann S, Berndtgen R, Huijser P (2012) Genomic organization, phylogenetic comparison and differential expression of the SBP-box family of transcription factors in tomato. Planta 235:1171–1184
Schwarz S, Grande AV, Bujdoso N, Saedler H, Huijser P (2008) The microRNA regulated SBP-box genes SPL9 and SPL15 control shoot maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 67:183–195
Shen B, Jiang J, Yu WD, Fan YY, Zhuang JY (2009) QTL analysis of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters in rice seedlings under salt stress. Chin J Rice Sci 23:319–322
Shikata M, Koyama T, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M (2009) Arabidopsis SBP-Box Genes SPL10, SPL11 and SPL2 control morphological change in association with shoot maturation in the reproductive phase. Plant Cell Physiol 50:2133–2145
Stone JM, Liang XW, Nekl ER, Stiers JJ (2005) Arabidopsis AtSPL14, a plant-specific SBP-domain transcription factor, participates in plant development and sensitivity to fumonisin B1. Plant J 41:744–754
Sun Y, Zang JP, Wang Y, Zhu LH, Mohammadhosein F, Xu JL, Li ZK (2007) Mining favorable salt-tolerant QTL from rice germplasm using a backcrossing introgression line population. Acta Agron Sin 33:1611–1617
Takehisa H, Shimodate T, Fukuta Y, Ueda T, Yano M, Yamaya T, Kameya T, Sato T (2004) Identification of quantitative trait loci for plant growth of rice in paddy field flooded with salt water. Field Crops Res 89:85–95
Temnykh S, Declerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Toda Y, Tanaka M, Ogawa D, Kurata K, Kurotani KI, Habu Y, Ando T, Sugimoto K, Mitsuda N, Katoh E, Abe K, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Hattori T, Takeda S (2013) RICE SALT SENSITIVE3 Forms a ternary complex with JAZ and class-C bHLH factors and regulates jasmonate-induced gene expression and root cell elongation. Plant Cell 25:1709–1725
Unte US, Sorensen AM, Pesaresi P, Gandikota M, Leister D, Saedler H, Huijser P (2003) SPL8, an SBP-box gene that affects pollen sac development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:1009–1019
Wang B, Lan T, Wu WR (2007) Mapping of QTLs for Na+ content in rice seedlings under salt stress. Chin J Rice Sci 21:585–590
Wang JW, Schwab R, Czech B, Mica E, Weigel D (2008) Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 20:1231–1243
Wang ZF, Cheng JP, Chen ZW, Huang J, Bao YM, Wang JF, Zhang HS (2012) Identification of QTLs with main, epistatic and QTL × environment interaction effects for salt tolerance in rice seedlings under different salinity conditions. Theor Appl Genet 125:807–815
Wang B, Liu TT, Zhang SJ, Lan T, Guan HZ, Zhou YC, Wu WR (2013) Genetic analysis and gene mapping for a salt tolerant mutant at seedling stage in rice. Hereditas (Beijing) 35:1101–1105
Xie KB, Wu CQ, Xiong LZ (2006) Genomic organization, differential expression, and interaction of SQUAMOSA promoter-binding-like transcription factors and microRNA156 in rice. Plant Physiol 142:280–293
Xing SP, Salinas M, Höhmann S, Berndtgen R, Huijsera P (2010) miR156-targeted and nontargeted SBP-box transcription factors act in concert to secure male fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:3935–3950
Yu N, Cai WJ, Wang SC, Shan CM, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2010) Temporal control of trichome distribution by MicroRNA156-targeted SPL genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 22:2322–2335
Zang JP, Sun Y, Wang Y, Yang J, Li F, Zhou YL, Zhu LH, Jessica R, Mohammadhosein F, Xu JL, Li ZK (2008) Dissection of genetic overlap of salt tolerance QTLs at the seedling and tillering stages using backcross introgression lines in rice. Sci China Life Sci 51:583–591
Zhang L, Wu B, Zhao D, Li C, Shao F, Lu S (2013) Genome-wide analysis and molecular dissection of the SPL gene family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J Integr Plant Biol. doi:10.1111/jipb.12111
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31071399), Fujian Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2011J01078), and Fujian Science and Technology Project (Grant No. JK2012014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Tao Lan and Shujun Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, T., Zhang, S., Liu, T. et al. Fine mapping and candidate identification of SST, a gene controlling seedling salt tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 205, 269–274 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1453-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1453-9