Abstract
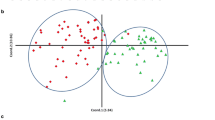
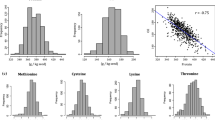
Association analysis studies can be used to test for associations between molecular markers and quantitative trait loci (QTL). In this study, a genome-wide scan was performed using 150 simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers to identify QTL associated with seed protein content in soybean. The initial mapping population consisted of two subpopulations of 48 germplasm accessions each, with high or low protein levels based on data from the USDA’s Germplasm Resources Information Network website. Intrachromosomal LD extended up to 50 cM with r 2 > 0.1 and 10 cM with r 2 > 0.2 across the accessions. An association map consisting of 150 markers was constructed on the basis of differences in allele frequency distributions between the two subpopulations. Eleven putative QTL were identified on the basis of highly significant markers. Nine of these are in regions where protein QTL have been mapped, but the genomic regions containing Satt431 on LG J and Satt551 on LG M have not been reported in previous linkage mapping studies. Furthermore, these new putative protein QTL do not map near any QTL known to affect maturity. Since biased population structure was known to exist in the original association analysis population, association analyses were also conducted on two similar but independent confirmation populations. Satt431 and Satt551 were also significant in those analyses. These results suggest that our association analysis approach could be a useful alternative to linkage mapping for the identification of unreported regions of the soybean genome containing putative QTL.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brummer EC, Graef GL, Orf J, Wilcox JR, Shoemaker RC (1997) Mapping QTL for seed protein and oil content in eight soybean populations. Crop Sci 37:370–378
Cardon LR, Bell JI (2001) Association study designs for complex diseases. Nat Rev Genet 2:91–99
Cardon LR, Palmer LJ (2003) Population stratification and spurious allelic association. The Lancet 361:598–604
Casanadi G, Vollmann J, Stift G, Lelly T (2001) Seed quality QTLs identified in a molecular map of early maturing soybean. Theor Appl Genet 103:912–919
Chung J, Babka HL, Graef GL, Staswick PE, Lee DJ, Cregan PB, Shoemaker RC, Specht JE (2003) The seed protein, oil, and yield QTL on soybean linkage group I. Crop Sci 43:1053–1067
Deu M, Glaszmann JC (2004) Linkage disequilibrium in sorghum. Paper presented at the Plant & animal genomes XII conference, Town & County Convention Center, San Diego, CA. W10, 10–14 Jan 2004
Diers BW, Keim P, Fehr WR, Shoemaker RC (1992) RFLP analysis of soybean seed protein and oil content. Theor Appl Genet 83:608–612
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JM (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 136:343–359
Flint-Garcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Buckler ES (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374
Gebhardt C, Ballvora A, Walkemeier B, Oberhagemann P, Schuler K (2004) Assessing genetic potential in germplasm collections of crop plants by marker-trait association: a case study for potatoes with quantitative variation of resistance to late blight and maturity type. Mol Breed 13:93–102
Goedde R, Sawcer S, Boehringer S, Miterski B, Sindern E, Haupts M, Schimrigk S, Compston A, Epplen JT (2002) A genome screen for linkage disequilibrium in HLA-DRB1*15-positive Germans with multiple sclerosis based on 4666 microsatellite markers. Hum Genet 111:270–277
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kulwal PL (2005) Linkage disequilibrium and association studies in higher plants: present status and future prospects. Plant Mol Biol 57:461–485
Hansen M, Kraft T, Ganestam S, Sall T, Nilsson N-O (2001) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of the bolting gene in sea beet using AFLP markers. Genet Res Camb 77:61–66
Hartwig EE (1990) Registration of soybean high-protein germplasm line D76–8070. Crop Sci 30:764–765
Hyten DL, Choi I-Y, Song Q, Shoemaker RC, Nelson RL, Costa JM, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2007) Highly variable patterns of linkage disequilibrium in multiple soybean populations. Genetics 175:1937–1944
Ivandic VC, Hackett A, Nevo E, Keith R, Thomas WTB, Foster BP (2002) Analysis of simple sequence repeat (SSRs) in wild barley from the Fertile Crescent: associations with ecology, geography, and flowering time. Plant Mol Biol 48:511–527
Jorde JB (2000) Linkage disequilibrium and the search for complex disease gene. Genome Res 10:1435–1444
Kraakman ATW, Niks RE, Van der Berg PMMM, Stam P, Van Eeuwijk FA (2004) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of yield and yield stability in modern spring barley cultivars. Genetics 168:435–446
Kruglyak L (1999) Prospects for whole-genome linkage disequilibrium mapping common disease genes. Nat Genet 22:139–144
Lee SH, Bailey MA, Mian MAR, Carter TE, Shipe ER, Ashley DA, Parrott WA, Hussey RS, Boerma HR (1996) RFLP loci associated with soybean seed protein and oil content across populations and locations. Theor Appl Genet 93:649–657
Leffel RC (1992) Registration of high protein soybean germplasm lines Barc-6, Barc-7, Barc-8, and Barc-9. Crop Sci 32:502
Lewis CM (2002) Genetic association studies: design, analysis and interpretation. Brief Bioinform 3:146–153
Ma H, Bernstein L, Ross RK, Ursin G (2006) Hormone-related risk factors for breast cancer in women under age 50 years by estrogen and progesterone receptor status: results from a case-control and case-case comparison. Breast Cancer Res 8:R39
Maccaferri M, Sanguineti MC, Noli E, Tuberosa R (2005) Population structure and long-range linkage disequilibrium in a durum wheat elite collection. Mol Breed 15:271–289
Malysheva-Otto LV, Ganal MW, Röder MS (2006) Analysis of molecular diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in a worldwide survey of cultivated barley germplasm (Hordum vulgrae L.). BMC Genet 7:6
Meuwissen THE, Goddard ME (2000) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci using linkage disequilibria with closely linked marker loci. Genetics 155:421–430
Nordborg M, Borevitz JO, Bergelson J, Berry CC, Chory J, Hagenblad J, Kreitman M, Maloof JN, Noyes T, Oefner P, Stahl EA, Weigel D (2002) The extent of linkage disequilibrium in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 30:190–193
Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Mansur LM, Cregan PB, Alder FR, Lark KG (1999) Genetics of soybean agronomic traits: I. Comparison of three related recombinant inbred populations. Crop Sci 39:1642–1651
Ostrowski MF, David A, Santoni S, Mckhann H, Reboud X, Corre VL, Camilleri C, Brunel D, Bouchez D, Faure B, Bataillon T (2006) Evidence for a large-scale population structure among accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana: possible causes and consequences for the distribution of linkage disequilibrium. Mol Ecol 15:1507–1517
Palaisa K, Morgante M, Williams M, Rafalski A (2004) Long-range patterns of diversity and linkage disequilibrium surrounding the maize Y1 gene are indicative of an asymmetric selective sweep. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9885–9890
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GenAIEx 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Potoski BA, Adams J, Clarke L, Shutt K, Linden PK, Baxter C, Pasculle AW, Capitano B, Peleg AY, Szabo D, Paterson DL (2006) Epidemiological profile of linezolid-resistant coagulase–negative staphylococci. Clin Infect Dis 43:165–171
Pritchard JK, Przeworski M (2001) Linkage disequilibrium in humans: models and data. Am J Hum Genet 69:1–14
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000a) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Rosenberg NA, Donnelly P (2000b) Association mapping in structured populations. Am J Hum Genet 67:170–181
Reich D, Cargill M, Bolk S, Ireland J, Sabetl PC, Richter DJ, Lavery T, Kouyoumjian R, Farhadian SF, Ward R, Lander ES (2001) Linkage disequilibrium in the human genome. Nature 411:199–204
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler ES (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic association in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11479–11484
Risch N, Merikangas K (1996) The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science 273:1516–1517
Robert J, Bismuth R, Lemaitre N, Jarlier V (2006) Gentamicin-susceptible or gentamicin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a case-case study. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 27:879–883
Sebolt AM, Shoemaker RC, Diers BW (2000) Analysis of a quantitative trait locus allele from wild soybean that increase seed protein concentration in soybean. Crop Sci 40:1438–1444
Shure M, Wessler S, Fedoreff N (1983) Molecular identification and isolation of the waxy locus in maize. Cell 35:225–233
Song QJ, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Concibido VC, Delannay X, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2004) A new integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109:122–128
Stella A, Boettcher PJ (2004) Optimal designs for linkage disequilibrium mapping and candidate gene association test in livestock populations. Genetics 166:341–350
Terwilliger JD, Weiss KM (1998) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of complex disease: fantasy or reality? Curr Opin Biotechnol 9:578–594
Twells RCJ, Mein CA, Payne F, Veijola R, Gilbey M, Bright M, Timms A, Nakagawa Y, Snook H, Nutland S, Rance HE, Carr P, Dudbridge F, Cordell HJ, Cooper J, Tuomilehto-Wolf E, Tuomilehto J, Phillips M, Metzker M, Hess JF, Todd JA (2003) Linkage and association mapping of the LRP5 locus on chromosome 11q13 in type 1 diabetes. Hum Genet 113:99–105
Weiss KM, Clark AG (2002) Linkage disequilibrium and the mapping of complex human traits. Trends Genet 18:19–24
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by a grant (code no. CG3121) from the Crop Functional Genomics Center of the 21st Century Frontier Research Program, funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) of the Republic of Korea. We also thank the National Instrumentation Center for Environmental Management at Seoul National University in Korea. We express our thanks to Dr. H. Roger Boerma (University of Georgia, USA) for his critical comments of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jun, TH., Van, K., Kim, M.Y. et al. Association analysis using SSR markers to find QTL for seed protein content in soybean. Euphytica 162, 179–191 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9491-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9491-6