Abstract
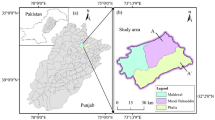
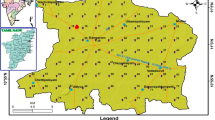
Groundwater qualities in Nashik District of Maharashtra were analyzed using hydro-geochemical characterization and geospatial techniques for sixty-one (n = 61) representative samples. GIS-based WQI was computed for planning and monitoring the groundwater qualities in the study region. Piper trilinear and Gibbs diagram were plotted to determine the variation in hydro-geochemical facies and to understand the functional sources of chemical constituents. The analytical results cleared that the nature of the groundwater is highly alkaline. Majority of the samples were within the desirable and maximum permissible limits as decided by Bureau of Indian Standards for each parameter. Piper diagram shows about 39.34% samples belong to Ca2+–Mg2+–Cl−–\({\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - }\) type, signifying permanent hardness and 57.37% samples belong to Ca2+–Mg2+–\({\text{HCO}}_{3}^{ - }\) type suggesting temporary hardness. Only 3.25% samples fall under Na+–K+–Cl−–\({\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - }\) type. Alkaline earth exceeds alkalis in 96.72% samples of the groundwater. The WQI suggests that 59% sites have excellent and good quality water; and about 41% sites characterized by poor quality water, which are unsuitable for drinking purposes. WQI values for TDS, TH, Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+, Cl−, K+, \({\text{NO}}_{3}^{ - }\) and \({\text{SO}}_{4}^{2 - }\) are more than the permissible limits. Hierarchical cluster analysis corroborates the spatial analysis results of WQI and proved statistically. The present investigation indicates significant dominance of agriculture and rock weathering that influence the groundwater chemistry in Nashik district.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adimalla, N. (2019a). Groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and potential health risks assessment: A case study from semi-arid region of South India. Exposure and Health, 11(2), 109–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0288-8.
Adimalla, N. (2019b). Controlling factors and mechanism of groundwater quality variation insemiarid region of South India: An approach of water quality index (WQI) and health risk assessment (HRA). Environmental Geochemistry and Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-019-00374-8.
Adimalla, N., Dhakate, R., Kasarla, A., & Taloor, A. K. (2020). Appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes in Central Telangana, India. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 10, 100334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100334.
Adimalla, N., Li, P., & Venkatayogi, S. (2018). Hydrogeochemical evaluation of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and integrated interpretation with water quality index studies. Environmental Process, 5(2), 363–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-018-0297-4.
Adimalla, N., & Qian, H. (2019). Groundwater quality evaluation using water quality index (WQI) for drinking purposes and human health risk (HHR) assessment in an agricultural region of Nanganur, South India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 176, 153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.066.
Anju, A., Ravi, S. P., & Bechan, S. (2010). Water pollution with special reference to pesticide contamination in India. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2(05), 432–448.
APHA. (1995). Standard method for the examination of water and waste water (14th ed.). Washington, DC: Public Health Association.
APHA. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (20th ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (1993). Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution (2nd ed., p. 536). Great Britain: Taylor and Francis.
Babiker, I. S., Mohamed, A. A. M., & Hiyama, T. (2007). Assessing groundwater quality using GIS. Water Resource Management, 21(4), 699–715.
Batabyal, A. K., & Chakraborty, S. (2015). Hydrogeochemistry and water quality index in the assessment of groundwater quality for drinking uses. Water Environment Research, 87(7), 607–617.
Benvenuti, T., Kieling-Rubio, M. A., Klauck, C. R., & Rodrigues, M. A. S. (2013). Evaluation of water quality at the source of streams of the Sinos River Basin, Southern Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 75(2), S98–S104.
Bhat, T. A. (2014). An Analysis of Demand and Supply of Water in India. Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 4(11), 67–72.
BIS. (1998). Specifications for drinking water. New Delhi: Bureau of Indian Standards.
BIS. (2003). Indian standard drinking water specifications. New Delhi: Bureau of Indian Standards.
Central Water Commission of India. (2016). On the spot study of water situation in drought affected areas of the. Delhi: Government of India.
CWC. (2016). On the spot study of water situation in drought affected areas of the country. Central Water Commission, Government of India. https://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/file/ON_THE_SPOT_STUDY_DROUGHT_2015-16.pdf.
Chaurasia, N. K., & Tiwari, R. K. (2011). Effect of industrial effluents and wastes on physico-chemical parameters of river Rapti. Advances in Applied Science Research, 2(5), 207–211.
Das, S. (2019). Comparison among influencing factor, frequency ratio, and analytical hierarchy process techniques for groundwater potential zonation in Vaitarna basin, Maharashtra, India. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 8, 617–629.
Das, S., Gupta, A., & Ghosh, S. (2017). Exploring Groundwater potential zones using MIF technique in semi-arid region: A case study of Hingoli district, Maharashtra. Spatial Information Research, 25(6), 749–756.
Deshmukh, K. K., & Aher, S. P. (2016). Assessment of the impact of municipal solid waste on groundwater quality near the Sangamner city using GIS approach. Water Resource Management, 30(7), 2425–2443.
Dinka, M. O., Loiskandl, W., & Ndambuki, J. M. (2015). Hydrochemical characterization of various surface water and groundwater resources available in Matahara areas, FantalleWoreda of Oromiya region. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 3, 444–456.
Dohare, D., Deshpande, S., & Kotiya, A. (2014). Analysis of ground water quality parameters: A review. Research Journal of Engineering Sciences, 3(5), 26–31.
FAO, & WHO (2008) Viruses in food: Scientific advice to support risk management activities. Microbiological risk assessment series (13) Rome, Italy http://www.fao.org/tempref/docrep/fao/011/i0451e/i0451e00.pdf.
Farhat, B., BenMammou, A., Kouzana, L., Chenini, I., Podda, F., & De Giudici, G. (2010). Groundwater chemistry of the Mornag aquifer system in NE Tunisia. Resource Geology, 60(4), 377–388.
¦, S., Gaikwad, S., Meshram, D., Wagh, V., Kandekar, A., & Kadam, A. (2019). Geochemical mobility of ions in groundwater from the tropical western coast of Maharashtra, India: Implication to groundwater quality. Environment, Development and Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00312-9.
Gaikwad, H., Shaikh, H., & Umrikar, B. (2018). Evaluation of groundwater quality for domestic and irrigation suitability from Upper Bhima Basin Western India: A hydro-geochemical perspective. Hydrospatial Analysis, 2(2), 113–123. https://doi.org/10.21523/gcj3.18020204.
Gibbs, R. J. (1970). Mechanism controlling world water chemistry. Science, 170(3962), 795–840.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (Vol 2254). Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey Water-Supply.
Ishaku, J. M., Ahmed, A. S., & Abubakar, M. A. (2012). Assessment of groundwater quality using water quality index and GIS in Jada, northeastern Nigeria. International Research Journal of Geology and Mining, 2(3), 54–61.
Kadave, P. T., Bhor, M. B., Bhor, A. B., & Bhosale, M. S. (2012). Physicochemical analysis of open well water Samples near Industrial Area of Niphad, Nashik District, (Maharashtra), India. Journal of Environmental Science, Toxicology and Food Technology, 1(4), 01–04.
Kale, S., & Pawar, N. J. (2017). Fluoride accumulation in groundwater from semi-arid part of Deccan Volcanic Province India: A cause of urolithiasis outbreak. Hydrospatial Analysis, 2(1), 7–17. https://doi.org/10.21523/gcj3.17010102.
Kanade, S.B. (2010). Groundwater quality monitoring of Nashik and Niphad taluka Nashik District Maharashtra. Published Ph. D thesis submitted to Savitribai Phule Pune University Pune. http://hdl.net/10603/126036.
Kanwar, J. S. (1961). Quality of irrigation waters as an index of its suitability for irrigation purposes. Potash Rev, 18, 1–13.
Ketata-Rokbani, M., Gueddari, M., & Bouhlila, R. (2011). Use of geographical information system and water quality index to assess groundwater quality in El Khairat Deep Aquifer (Enfidha, Tunisian Sahel). Iranica Journal of Energy and Environment, 2(2), 133–144.
Khan, R., & Jhariya, D. C. (2018). Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment for drinking and irrigation purpose of Raipur City, Chhattisgarh. Journal Geological Society of India, 91, 475–482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-0881-2.
Krishna Kumar, S., Logeshkumaran, A., Magesh, N. S., Godson, P. S., & Chandrasekar, N. (2015). Hydro-geochemistry and application of water quality index (WQI) for groundwater quality assessment, Anna Nagar, part of Chennai City, Tamil Nadu, India. Applied Water Science, 5(4), 335–343.
Ledesma-Ruiz, R., Pastén-Zapata, E., Parra, R., Harter, T., & Mahlknecht, J. (2015). Investigation of the geochemical evolution of groundwater under agricultural land: A case study in northeastern Mexico. Journal of Hydrology, 521, 410–423.
Machiwal, D., & Jha, M. K. (2015). GIS-based water balance modeling for estimating regional specific yield and distributed recharge in data-scarce hard-rock regions. Journal of Hydro-environment Research, 9(4), 554–568.
Magesh, N. S., Krishnakumar, S., Chandrasekar, N., & Soundranayagam, J. P. (2012). Groundwater quality assessment using WQI and GIS techniques, Dindigul district, Tamil Nadu, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6(11), 4179–4189.
Majumdar, D., & Gupta, N. (2000). Nitrate pollution of groundwater and associated human health disorders Indian. Journal of Environmental Health, 42(1), 28–39.
Malik, D. S., Kumar, P., & Bharti, U. (2009). A study on ground water quality of industrial area at Gajraula (UP), India. Journal of Applied and Natural Science, 1, 275–279.
Milovanovic, M. (2007). Water quality assessment and determination of pollution sources along the Axios/Vardar River, Southeastern Europe. Desalination, 213, 159–173.
Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. (2016). Swachhta status report, 2016. Government of India, New Delhi.
Murty, M.N., & Kumar, S. (2011). Water pollution in India. India Infrastructure Report, pp 285–298. http://www.idfc.com/pdf/report/2011/Chp-19-Water-Pollution-in-India-An-Economic-Appraisal.pdf.
Nawlakhe, W. G., & Bulusu, K. R. (1989). Nalgonda technique-a process for removal of fluoride from drinking water. Water Quality Bull, 14, 218–220.
Nguyen, T. T., Kawamura, A., Tong, T. N., Nakagawa, N., Amaguchi, H., & Gilbuena, R. (2014). Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater from the two main aquifers in the Red River Delta, Vietnam. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 93, 180–192.
Park, S. C., Yun, S. T., Chae, G. T., Yoo, I. S., Shin, K. S., Heo, C. H., et al. (2005). Regional hydrochemical study on salinization of coastal aquifers, western coastal area of South Korea. Journal of Hydrology, 313(3–4), 182–194.
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Transactions of the American Geophysical Union, 25, 914–928.
Ramakrishnaiah, C. R., Sadashivaiah, C., & Ranganna, G. (2009). Assessment of water quality index for the groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. E-Journal of Chemistry, 6(2), 523–530.
Reza, R., & Singh, G. (2010). Assessment of ground water quality status by using water quality index method in Orissa, India. World Applied Sciences Journal, 9(12), 1392–1397.
Sadat-Noori, S. M., Ebrahimi, K., & Liaghat, A. M. (2013). Groundwater quality assessment using the water quality index and GIS in Saveh-Nobaran aquifer. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(9), 3827–3843.
Selvakumar, S., Chandrasekar, N., & Kumar, G. (2017). Hydrogeochemical characteristics and groundwater contamination in the rapid urban development areas of Coimbatore, India. Water Resources and Industry, 17, 26–33.
Singh, S., & Hussian, A. (2016). Water quality index development for groundwater quality assessment of Greater Noida sub-basin, Uttar Pradesh, India. Cogent Engineering, 3, 1–17.
Singh, S., Raju, N. J., & Ramakrishna, C. (2015). Evaluation of groundwater quality and its suitability for domestic and irrigation use in parts of the Chandauli-Varanasi region, Uttar Pradesh, India. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 7(7), 572–587.
Srinivasamoorthy, K., Gopinath, M., Chidambaram, S., Vasanthavigar, M., & Sarma, V. S. (2014). Hydrochemical characterization and quality appraisal of groundwater from Pungar sub basin, Tamilnadu. India Journal of King Saud University—Science, 26, 37–52.
Stigter, T. Y., Van Ooijen, S. P. J., Post, V. E. A., Appelo, C. A. J., & Carvalho Dill, A. M. M. (1998). A hydrogeological and hydrochemical explanation of the groundwater composition under irrigated land in a Mediterranean environment, Algarve, Portugal. Journal of Hydrology, 208(3–4), 262–279.
Tarki, M., Ben Hammadi, M., El Mejri, H., & Dassi, L. (2016). Assessment of hydrochemical processes and groundwater hydrodynamics in a multilayer aquifer system under long-term irrigation condition: A case study of Nefzaoua basin, southern Tunisia. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 110(5–6), 138–149.
Thambavani, S. D., & Mageswari, U. T. S. (2013). Metal pollution assessment in ground water bulletin of environment. Pharmacol Life Science, 2, 122–129.
Tiwari, T. N., & Mishra, M. (1985). A preliminary assignment of water quality index of major Indian rivers. Indian Journal of Environment Protection, 5(4), 276–279.
Tiwari, A. K., Singh, A. K., & Mahato, M. K. (2017). Assessment of groundwater quality of Pratapgarh district in India for suitability of drinking purpose using water quality index (WQI) and GIS technique. Sustainable Water Resource Management. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0144-1.
Todmal, R. S., Korade, M. S., Dhorde, A. G., & Zolekar, R. B. (2018). Hydro-meteorological and agricultural trends in water-scarce Karha Basin, western India: Current and future scenario. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3655-7.
Vasanthavigar, M., Srinivasamoorthy, K., Vijayaragavan, K., Ganthi, R., Chidambaram, S., Anandhan, P., et al. (2010). Application of water quality index for groundwater quality assessment: Thirumanimuttar sub-basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 171(1–4), 595–609.
Wagh, V., Panaskar, D., Aamalawar, M., Lolage, Y., Mukate, S., & Adimalla, N. (2018). Hydrochemical characterisation and groundwater suitability for drinking and irrigation uses in Semiarid Region of Nashik Maharashtra India. Hydrospatial Analysis, 2(1), 43–60. https://doi.org/10.21523/gcj3.18020104.
Wanda, E. M. M., Gulula, L. C., & Phiri, G. (2012). Hydrochemical assessment of groundwater used for irrigation in Rumphi and Karonga districts, Northern Malawi. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 50(52), 92–97.
Ward, J. H. (1963). Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 58(301), 236–244.
WHO. (1997). Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Health Organization, Geneva, 1, 1–4.
Wick, K., Heumesser, C., & Schmid, E. (2012). Groundwater nitrate contamination: Factors and indicators. Journal of Environment Management, 111(3), 178–186.
Zolekar, R. B. (2018). Integrative approach of RS and GIS in characterization of land suitability for agriculture: A case study of Darna catchment. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-4148-4.
Zolekar, R. B., & Bhagat, V. S. (2014). Use of IRS P6 LISS-IV data for land suitability analysis for cashew plantation in hilly zone. Asian Journal of Geoinformatics, 14(3), 23–35.
Zolekar, R. B., & Bhagat, V. S. (2015). Multi-criteria land suitability analysis for agriculture in hilly zone: Remote sensing and GIS approach. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 118-C, 300–321.
Zolekar, R. B., & Bhagat, V. S. (2018). Multi-criteria land suitability analysis for plantation in Upper Mula and Pravara basin: Remote sensing and GIS approach. Journal of Geographical Studies, 2(1), 12–20.
Acknowledgements
The first author would like to express his sincere gratitude toward The Indian Council of Social Science Research, New Delhi, for funding and supporting the present major research project under IMPRESS (IMPRESS/P783/2018-19/ICSSR] for research grants. The authors would also like to thank the editors and anonymous reviewers for their meticulous comments and suggestions which greatly helped us to improve this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zolekar, R.B., Todmal, R.S., Bhagat, V.S. et al. Hydro-chemical characterization and geospatial analysis of groundwater for drinking and agricultural usage in Nashik district in Maharashtra, India. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 4433–4452 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00782-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-00782-2