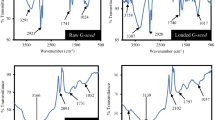
Abstract
The present study investigates the removal of glyphosate, glufosinate, aminomethylphosphonic acid and bialaphos herbicides from their 5 × 10–5 M aqueous solutions onto activated carbon cloth by adsorption and electrosorption. Analysis of these highly polar herbicides was achieved by UV–visible absorbance measurements, after derivatization with 9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl chloride. The limit of quantification values of glyphosate, glufosinate, aminomethylphosphonic acid and bialaphos were 1.06 × 10–6 mol L−1, 1.38 × 10–6 mol L−1, 1.32 × 10–6 mol L−1 and 1.08 × 10–6 mol L−1, respectively. Glyphosate, glufosinate, aminomethylphosphonic acid and bialaphos were removed from their aqueous solutions with higher efficiencies by means of electrosorption (78.2%, 94.9%, 82.3% and 97%, respectively) than of open-circuit adsorption (42.5%, 22%, 6.9% and 81.8%, respectively). Experimental kinetic data were fitted to pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic models. It was determined that pseudo-second order kinetic model represents experimental data better with satisfactory coefficient of determination, r2 (> 0.985) and normalized percent deviation, P (< 5.15) values. Adsorption isotherm data were treated according to Freundlich and Langmuir isotherm models. Based on the r2 (> 0.98) and P (< 5.9) values, it was found that experimental data well fitted to Freundlich isotherm model. Adsorption capacities of activated carbon cloth for glyphosate, glufosinate, aminomethylphosphonic acid and bialaphos, expressed in terms of Freundlich constant, were calculated as 20.31, 118.73, 239.33 and 30.68 mmol g−1, respectively. The results show that the studied ACC can be used in home/business water treatment systems as an adsorbent due to its high adsorption capacity.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Alalm, M. G., Tawfik, A., & Ookawara, S. (2015). Comparison of solar TiO2 photocatalysis and solar photo-Fenton for treatment of pesticides industry wastewater: Operational conditions, kinetics, and costs. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 8, 55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.09.007
Alves, A. A. A., Ruiz, G. L. O., Nonato, T. C. M., Müller, L. C., & Sens, M. L. (2019). Performance of the fixed-bed of granular activated carbon for the removal of pesticides from water supply. Environmental Technology, 40(15), 1977–1987. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1435731
Andrade, M., Santos, T. R. T., Silva, M. F., Vieira, M. F., Bergamasco, R., & Hamoudi, S. (2019). Graphene oxide impregnated with iron oxide nanoparticles for the removal of atrazine from the aqueous medium. Separation Science and Technology, 54(16), 2653–2670. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1549077
Ania, C. O., & Béguin, F. (2007). Mechanism of adsorption and electrosorption of bentazone on activated carbon cloth in aqueous solutions. Water Research, 41(15), 3372–3380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2007.03.031
Anirudhan, T. S., Shainy, F., Chithra Sekhar, V., & Athira, V. S. (2021). Highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of chlorpyrifos in aqueous solutions by nano hydroxyapatite modified CFGO/ZnO nanorod composite. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 418, 113333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2021.113333
Annett, R., Habibi, H. R., & Hontela, A. (2014). Impact of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on the freshwater environment. Journal of Applied Toxicology, 34, 458–479. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2997
Aparicio, V. C., De Gerónimo, E., Marino, D., Primost, J., Carriquiriborde, P., & Costa, J. L. (2013). Environmental fate of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters and soil of agricultural basins. Chemosphere, 93, 1866–1873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.06.041
Ayranci, E., & Bayram, E. (2005). Adsorption of phthalic acid and its esters onto high-area activated carbon-cloth studied by in situ UV-spectroscopy. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 122(1–2), 147–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.03.022
Ayranci, E., & Conway, B. E. (2001a). Removal of phenol, phenoxide and chlorophenols from waste-waters by adsorption and electrosorption at high-area carbon felt electrodes. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 513(2), 100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(01)00529-0
Ayranci, E., & Conway, B. E. (2001b). Adsorption and electrosorption of ethyl xanthate and thiocyanate anions at high-area carbon-cloth electrodes studied by in situ UV spectroscopy: Development of procedures for wastewater purification. Analytical Chemistry, 73(6), 1181–1189. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac000736e
Ayranci, E., & Conway, B. E. (2001c). Adsorption and electrosorption at high-area carbon-felt electrodes for waste-water purification: Systems evaluation with inorganic. S-Containing Anions. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 31(3), 257–266. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017528002713
Ayranci, E., & Hoda, N. (2004). Adsorption of bentazon and propanil from aqueous solutions at the high area activated carbon-cloth. Chemosphere, 57(8), 755–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.08.042
Battaglin, W. A., Kolpin, D. W., Scribner, E. A., Kuivila, K. M., & Sandstrom, M. W. (2005). Glyphosate, Others Herbicides, and Transformation Products in Midwestern Streams. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 41, 323–332. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2005.tb03738.x
Bayram, E., & Ayranci, E. (2010). Electrochemically enhanced removal of polycyclic aromatic basic dyes from dilute aqueous solutions by activated carbon cloth electrodes. Environmental Science and Technology, 44(16), 6331–6336. https://doi.org/10.1021/es101177k
Bayram, E., Hoda, N., & Ayranci, E. (2009). Adsorption/electrosorption of catechol and resorcinol onto high area activated carbon cloth. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 168(2–3), 1459–1466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.03.039
Beninca, C., Vargas, F. T., Martins, M. L., Gonçalves, F. F., Vargas, R. P., Freire, F. B., & Zanoelo, E. F. (2016). Removal of clomazone herbicide from a synthetic effluent by electrocoagulation. Water Science and Technology, 73(12), 2944–2952. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.133
Bradu, C., Magureanu, M., & Parvulescu, V. I. (2017). Degradation of the chlorophenoxyacetic herbicide 2,4-D by plasma-ozonation system. Journal of Hazardous Materials., 336, 52–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.04.050
Caceres-Jensen, L., Rodríguez-Becerra, J., Sierra-Rosales, P., Escudey, M., Valdebenito, J., Neira-Albornoz, A., Dominguez-Vera, V., & Villagra, C. A. (2019). Electrochemical method to study the environmental behavior of Glyphosate on volcanic soils: Proposal of adsorption-desorption and transport mechanisms. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 379, 120746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120746
Carneiro, R. T. A., Taketa, T. B., Gomes Neto, R. J., Oliveira, J. L., Campos, E. V. R., de Moraes, M. A., Silva, C. M. G., Beppu, M. M., & Fraceto, L. F. (2015). Removal of glyphosate herbicide from water using biopolymer membranes. Journal of Environmental Management, 151, 353–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.01.005
Cengiz, M. F., Basancelebi, O., & Kitis, Y. E. (2017). Glyphosate residues in drinking waters and adverse health effects. The Turkish Journal of Occupational/environmental Medicine and Safety, 2(1), 247–258.
Chamkasem, N., Morris, C., & Harmon, T. (2015). Direct determination of glyphosate, glufosinate and ampa in milk by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Regulatory Science, 02, 20–26.
Chamkasem, N., Morris, C., & Harmon, T. (2017). Determination of paraquat and diquat in potato by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometer. Journal of Regulatory Science, 05, 1–8.
Chandra, P. N., & Usha, K. (2021). Removal of atrazine herbicide from water by polyelectrolyte multilayer membranes. Materials Today: Proceedings, 41(3), 622–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.263
Coupe, R. H., Kalkhoff, S. J., Capel, P. D., & Gregoire, C. (2012). Fate and transport of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in surface waters of agricultural basins. Pest Management Science, 681, 16–30. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.2212
Cruz-Alcalde, A., Sans, C., & Esplugas, S. (2017). Priority pesticides abatement by advanced water technologies: The case of acetamiprid removal by ozonation. Science of the Total Environment, 599–600, 1454–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.065
Dehghani, M. H., Niasar, Z. S., Mehrnia, M. R., Shayeghi, M., Al-Ghouti, M. A., Heibati, B., McKay, G., & Yetilmezsoy, K. (2017). Optimizing the removal of organophosphorus pesticide malathion from water using multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 310(1), 22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.10.057
Dehghani, M. H., Kamalian, S., Shayeghi, M., Yousefi, M., Heidarinejad, Z., Agarwal, S., & Gupta, V. K. (2019). High-performance removal of diazinon pesticide from water using multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Microchemical Journal, 145, 486–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.10.053
Delmonico, E. L., Bertozzi, J., de Souza, N. E., & Oliveira, C. C. (2014). Determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid for assessing the quality tap water using SPE and HPLC. Acta Scientiarum - Technology, 36(3), 513–519. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascitechnol.v36i3.22406
Derylo-Marczewska, A., Blachnio, M., Marczewski, A. W., Swiatkowski, A., & Buczek, B. (2017). Adsorption of chlorophenoxy pesticides on activated carbon with gradually removed external particle layers. Chemical Engineering Journal, 308, 408–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.082
Diaw, P. A., Oturan, N., Seye, M. D. G., Coly, A., Tine, A., Aaron, J. J., & Oturan, M. A. (2017). Oxidative degradation and mineralization of the phenylurea herbicide fluometuron in aqueous media by the electro-Fenton process. Separation and Purification Technology, 186, 197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.06.005
Ding, C., Wang, X., Liu, H., Li, Y., Sun, Y., Lin, Y., Sun, W., Zhu, X., Dai, Y., & Luo, C. (2018). Glyphosate removal from water by functional three-dimensional graphene aerogels. Environmental Chemistry, 156, 325–335. https://doi.org/10.1071/EN18087
Druart, C., Millet, M., Scheifler, R., Delhomme, O., & Vaufleury, A. (2011). Glyphosate and glufosinate-based herbicides: Fate in soil, transfer to, and effects on land snails. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 11(8), 1373–1384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-011-0409-5
Duman, O., & Ayranci, E. (2010). Adsorptive removal of cationic surfactants from aqueous solutions onto high-area activated carbon cloth monitored by in situ UV spectroscopy. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174(1–3), 359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.058
Duman, O., Özcan, C., Gürkan Polat, T., & Tunç, S. (2019). Carbon nanotube-based magnetic and non-magnetic adsorbents for the high-efficiency removal of diquat dibromide herbicide from water: OMWCNT, OMWCNT-Fe3O4 and OMWCNT-Κ-carrageenan- Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Environmental Pollution., 244, 723–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.10.071
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2018). Label review manual, Chapter 7: Precautionary Statements. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-04/documents/chap-07-mar-2018.pdf
Geng, Y., Jiang, L., Zhang, D., Liu, B., Zhang, J., Cheng, H., Wang, L., Peng, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Xu, Y., & Liu, X. (2021). Glyphosate, aminomethylphosphonic acid, and glufosinate ammonium in agricultural groundwater and surface water in China from 2017 to 2018: Occurrence, main drivers, and environmental risk assessment. Science of The Total Environment, 769, 144396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144396
Gill, H. K., & Garg, H. (2014). Pesticides: Environmental Impacts and Management Strategies In Soloneski, S. (Ed). Pesticides - Toxic Aspects. (pp. 187–230). Intech. https://doi.org/10.5772/57399
Gomes, J., Roccamante, M., Contreras, S., Medina, F., Oller, I., & Martins, R. C. (2021). Scale-up impact over solar photocatalytic ozonation with benchmark-P25 and N-TiO2 for insecticides abatement in water. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(1), 104915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104915
Guo, L., Cao, Y., Jin, K., Han, L., Li, G., Liu, J., & Ma, S. (2018). Adsorption characteristics of glyphosate on cross-linked amino-starch. Journal of Chemistry Engineering Data., 63(2), 422–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.7b00842
Guo, H., Gao, Y., Guo, D., Liu, W., Wang, J., Zheng, J., Zhong, J., & Zhao, Q. (2019). Sensitive, rapid and non-derivatized determination of glyphosate, glufosinate, bialaphos and metabolites in surface water by LC–MS/MS. SN Applied Sciences, 1, 305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-0306-x
Hachami, F., Errami, M., Bazzi, L., Hilali, M., Salghi, R., Jodeh, S., Hammouti, B., & Hamed, O. A. (2015). A comparative study of electrochemical oxidation of methidation organophosphorous pesticide on SnO2 and boron-doped diamond anodes. Chemistry Central Journal, 9, 59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-015-0136-x
Hanke, I., Singer, H., & Hollender, J. (2008). Ultratrace-level determination of glyphosate, aminomethylphosphonic acid and glufosinate in natural waters by solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Performance tuning of derivatization, enrichment and detection. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 391, 2265–2276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2134-5
Herath, I., Kumarathilaka, P., Al-Wabel, M. I., Abduljabbar, A., Ahmad, M., Usman, A. R. A., & Vithanage, M. (2016). Mechanistic modeling of glyphosate interaction with rice husk derived engineered biochar. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 225, 280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.01.017
Huang, S., Chen, C., Tsai, H., Shaya, J., & Lu, C. (2018). Photocatalytic degradation of thiobencarb by a visible light-driven MoS2 photocatalyst. Separation and Purification Technology, 197, 147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2018.01.009
Kaczynski, P., & Tozowicka, B. (2015). Liquid chromatographic determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid residues in rapeseed with MS/MS detection or derivatization/fluorescence detection. Open Chemistry, 13, 1011–1019. https://doi.org/10.1515/chem-2015-0107
Karimi, H., Rahimpour, A., & Kebria, M. R. S. (2016). Pesticides removal from water using modified piperazine-based nanofiltration (NF) membranes. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(52), 24844–24854. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2016.1156580
Khenifi, A., Derriche, Z., Mousty, C., Prévot, V., & Forano, C. (2010). Adsorption of Glyphosate and Glufosinate by Ni2AlNO3 layered double hydroxide. Applied Clay Science, 47(3–4), 362–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.11.055
Konetzki, J., Nestola, M., Rothmeier, S., Becker, E., Hentschel, A., & Kirchhoff, E. (2020). Automated determination of glyphosate, AMPA and glufosinate in food by online ligand exchange SPE-LC-MS/MS. LC/MS Application Note, PAL System. Ingenious News. https://www.palsystem.com/fileadmin/public/docs/Downloads/Newsletter_Articles/Automated_determination_of_glyphosate_AMPA_and_glufosinate_in_food_by_online_ligand_exchange_SPE-LC-MSMS.pdf
Lan, H., He, W., Wang, A., Liu, R., Liu, H., Qu, J., & Huang, C. P. (2016). An activated carbon fiber cathode for the degradation of glyphosate in aqueous solutions by the Electro-Fenton mode: Optimal operational conditions and the deposition of iron on cathode on electrode reusability. Water Research, 105, 575–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.09.036
Le Fur, E., Colin, R., Charrêteur, C., Dufau, C., & Péron, J. J. (2000). Determination of glyphosate herbicide and aminomethylphosphonic acid in natural waters by liquid chromatography using pre-column fluorogenic labeling. Part I: Direct determination at the 0.1 mg/L level using FMOC. Analysis, 28, 813–818. https://doi.org/10.1051/analusis:2000148
Lebik-Elhadi, H., Frontistis, Z., Ait-Amar, H., Amrani, S., & Mantzavinos, D. (2018). Electrochemical oxidation of pesticide thiamethoxam on boron doped diamond anode: Role of operating parameters and matrix effect. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 116, 535–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.03.021
Lee, T., Ooi, C. H., Othman, R., & Yeoh, F. Y. (2014). Activated carbon fiber - The hybrid of carbon fiber and activated carbon. Reviews on Advanced Materials Science, 362, 118–136.
Li, Q., Sun, J., Ren, T., Guo, L., Yang, Z., Yang, Q., & Chen, H. (2018). Adsorption mechanism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid onto nitric-acid-modified activated carbon fiber. Environmental Technology., 39(7), 895–906. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1316318
Li, X., Zhang, R., Dong, F., Tang, Y., Xu, L., Sun, C., & Zhang, H. (2021). Exploring adsorption mechanism of glyphosate on pristine and elemental doped graphene. Chemical Physics Letters, 779, 138849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138849
Liu, R., Xie, Y., Cui, K., Xie, J., Zhang, Y., & Huang, Y. (2022). Adsorption behavior and adsorption mechanism of glyphosate in water by amino-MIL-101(Fe). Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 161, 110403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110403
Ma, L., Huang, L., Xu, Y., Liu, C., Wang, F., Xing, H., & Ma, S. (2021). Dynamics and Model Research on the Electrosorption by Activated Carbon Fiber Electrodes. Water, 13, 62. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13010062
Mahler, B. J., Van Metre, P. C., Burley, T. E., Loftin, K. A., Meyer, M. T., & Nowell, L. H. (2017). Similarities and differences in occurrence and temporal fluctuations in glyphosate and atrazine in small Midwestern streams (USA) during the 2013 growing season. Science of the Total Environment, 579, 149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.236
Mailler, R., Gasperi, J., Coquet, Y., Bulete, A., Vulliet, E., Deshayes, S., Zedek, S., Mirande-Bret, C., Eudes, V., Bressy, A., Caupos, E., Moilleron, R., Chebbo, G., & Rocher, V. (2016). Removal of a wide range of emerging pollutants from wastewater treatment plant discharges by micro-grain activated carbon in fluidized bed as tertiary treatment at large pilot scale. Science of the Total Environment, 542, 983–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.153
Marin, P., Bergamasco, R., Módenes, A. N., Paraiso, P. R., & Hamoudi, S. (2019). Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide functionalized with MnFe2O4 and supported on activated carbon for glyphosate adsorption in fixed bed column. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 123, 59–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.12.027
Masiol, M., Giannì, B., & Prete, M. (2018). Herbicides in river water across the northeastern Italy: Occurrence and spatial patterns of glyphosate, aminomethylphosphonic acid, and glufosinate ammonium. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25, 24368–24378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2511-3
Mata, K., Corazza, M. Z., Oliveira, F. M., Toffoli, A. L., Tarley, C. R. T., & Moreira, A. B. (2014). Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked molecularly imprinted polyacrylamide for the extraction/preconcentration of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid from water samples. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 83, 76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2014.07.004
McBeath, S. T., & Graham, N. J. D. (2021). Simultaneous electrochemical oxidation and ferrate generation for the treatment of atrazine: A novel process for water treatment applications. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 441, 125167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125167
Mukherjee, D., Bhattacharya, P., Jana, A., Bhattacharya, S., Sarkar, S., Ghosh, S., Majumdar, S., & Swarnakar, S. (2018). Synthesis of ceramic ultrafiltration membrane and application in membrane bioreactor process for pesticide remediation from wastewater. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 116, 22–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2018.01.010
Narayanan, N., Gupta, S., & Gajbhiye, V. T. (2020). Decontamination of pesticide industrial effluent by adsorption–coagulation–flocculation process using biopolymer-nanoorganoclay composite. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 17, 4775–4786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02785-y
Niu, J., & Conway, B. E. (2002). Development of techniques for purification of waste waters: Removal of pyridine from aqueous solution by adsorption at high-area C-cloth electrodes using in situ optical spectrometry. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 521(1–2), 16–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(02)00660-5
Nourouzi, M. M., Chuah, T. G., & Choong, T. S. Y. (2010). Adsorption of glyphosate onto activated carbon derived from waste newspaper. Desalination and Water Treatment, 24(1–3), 321–326. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2010.1461
Oliveira, B. R., Penetra, A., Cardoso, V. V., Benoliel, M. J., Barreto Crespo, M. T., Samson, R. A., & Pereira, V. J. (2015). Biodegradation of pesticides using fungi species found in the aquatic environment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 11781–11791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4472-0
Ouakouak, A., Youcef, L., Boulanouar, D., & Achour, S. (2017). Adsorptive removal of phosphate from groundwater using granular activated carbon. International Journal of Engineering Research in Africa, 32, 53–61. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JERA.32.53
Ozkara, A., Akyıl, D., & Konuk, M. (2016). Pesticides, Environmental Pollution, and Health. In Larramendy, M. L. and Soloneski, S. (Eds), Environmental Health Risk - Hazardous Factors to Living Species (pp. 3–27). Intech. https://doi.org/10.5772/63094.
Pan, S., Chen, X., Li, X., & Jin, M. (2019). Nonderivatization method for determination of glyphosate, glufosinate, bialaphos, and their main metabolites in environmental waters based on magnetic metal-organic framework pretreatment. Journal of Separation Science, 42(5), 1045–1050. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201800957
Papadakis, E. N., Vryzas, Z., Kotopoulou, A., Kintzikoglou, K., Makris, K. C., & Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, E. (2015). A pesticide monitoring survey in rivers and lakes of northern Greece and its human and ecotoxicological risk assessment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 116, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.02.033
Paul, M., Hossain, S., Rahman, M., Khaliq, Q. A., & Rahman, S. (2016). Chemodynamics of cypermethrin insecticide in summer country bean ecosystem in Bangladesh. Research Journal of Environmental Toxicology, 10(1), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.3923/rjet.2016.50.59
Perez-Lucas, G., Vela, N., El Aatik, A., Navarro, S. (2018). Environmental risk of groundwater pollution by pesticide leaching through the soil profile. In Larramendy, M., Soloneski, S. (Eds), Pesticides - Use and Misuse and Their Impact in the Environment. InTech, (pp. 1–27). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.82418
Rojano-Delgado, A. M., Priego-Capote, F., De Prado, R., & De Castro, M. D. L. (2014). Qualitative/quantitative strategy for the determination of glufosinate and metabolites in plants. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 406(2), 611–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7484-y
Rosenbom, A., Brüsch, W., Juhler, R., Ernstsen, V., Gudmundsson, L., Plauborg, F., Grant, R., & Olsen, P. (2010). The Danish pesticide leaching assessment programme. Monitoring Results May 1999–June 2009, Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland (p. 102). Copenhagen, Denmark. http://pesticidvarsling.dk/wp-content/uploads/Rapporter/2009/Monitoring-results-May-1999%E2%80%93June-2009.pdf
Sanchís, J., Kantiani, L., Llorca, M., Rubio, F., Ginebreda, A., Fraile, J., Garrido, T., & Farré, M. (2012). Determination of glyphosate in groundwater samples using an ultrasensitive immunoassay and confirmation by on-line solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 402, 2335–2345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5541-y
Sarika K., Sneha K., Shivani M., Shefali B., & Sangami S. (2021). Removal of 2,4-D herbicide from water by electrocoagulation using copper electrodes. In Narasimhan M. C., George V., Udayakumar G., Kumar A. (Eds). Trends in Civil Engineering and Challenges for Sustainability. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, 99. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-6828-2_41
Sen, K., Datta, J. K., & Mondal, N. K. (2021). Box-Behnken optimization of glyphosate adsorption on to biofabricated calcium hydroxyapatite: Kinetic, isotherm, thermodynamic studies. Applied Nanoscience, 11, 687–697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01612-7
Shadmehr, J., Mirsoleimani-azizi, S. M., Zeinali, S., & Setoodeh, P. (2019). Electrocoagulation process for propiconazole elimination from wastewater: Experimental design for correlative modeling and optimization. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16, 5409–5420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1891-8
Sharma, D. K., Kumar, N., Chaudhary, A., et al. (2020). Differential Pulse Polarographic Investigations on Glyphosate and Glufosinate Herbicides in Relation to Their Environmental Analysis. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 105, 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02901-1
Sidoli, P., Baran, N., & Angulo-Jaramillo, R. (2016). Glyphosate and AMPA adsorption in soils: Laboratory experiments and pedotransfer rules. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 5733–5742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5796-5
Skeff, W., Recknagel, C., Düwel, Y., & Schulz-Bull, D. E. (2018). Adsorption behaviors of glyphosate, glufosinate, aminomethylphosphonic acid, and 2-aminoethylphosphonic acid on three typical Baltic Sea sediments. Marine Chemistry, 198, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2017.11.008
Su, X., & Hatton, T. A. (2016). Electrosorption. John Wiley & Sons, Inc (Ed.). Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, https://doi.org/10.1002/0471238961.koe00022
Tongur, T., & Ayranci, E. (2021). Adsorption and electrosorption of paraquat, diquat and difenzoquat from aqueous solutions onto activated carbon cloth as monitored by in-situ uv–visible spectroscopy. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(4), 105566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105566
Traas, T. P., & Smit, C. E. (2003). Environmental risk limits for aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA). RIVM Report 601501018. The Netherlands: National Institute of Public Health and the Environment (RIVM). https://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/601501018.pdf
Tripathi, N. K., Singh, V. V., Sathe, M., Thakare, V. B., & Singh, B. (2018). Activated carbon fabric: An adsorbent material for chemical protective clothing. Defence Science Journal, 68(1), 83–90. https://doi.org/10.14429/dsj.68.11734
Vu, C. T., Le, P. T., Chu, D. B., Bui, V. H., Phung, T. L. A., Le, H. Y. N., Labanowski, J., Mondamert, L., Herrmann, M., & Behra, P. (2021). One-step purification/extraction method to access glyphosate, glufosinate, and their metabolites in natural waters. Journal of Chromatography A, 1649, 462188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462188
Waiman, C. V., Avena, M. J., Garrido, M., Fernández Band, B., & Zanini, G. P. (2012). A simple and rapid spectrophotometric method to quantify the herbicide glyphosate in aqueous media. Application to adsorption isotherms on soils and goethite. Geoderma, 170, 154–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.11.027
Wang, S., Liu, B., Yuan, D., & Ma, J. (2016). A simple method for the determination of glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid in seawater matrix with high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. Talanta, 161, 700–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.09.023
Wang, Y., Wang, S., Xie, T., & Cao, J. (2020). Activated carbon derived from waste tangerine seed for the high-performance adsorption of carbamate pesticides from water and plant. Bioresource Technology, 316, 123929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123929
Wang, Y., Lin, C., Liu, X., Ren, W., Huang, X., He, M., & Ouyang, W. (2021). Efficient removal of acetochlor pesticide from water using magnetic activated carbon: Adsorption performance, mechanism, and regeneration exploration. Science of the Total Environment, 778, 146353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146353
World Health Organization (WHO) (2005). Glyphosate and AMPA in drinking-water. Background document for development of WHO guidelines for drinking-water quality. WHO/SDE/SWH/03.04/97. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/glyphosate-2003.pdf?sfvrsn=c93027cd_3
Wolterink, G., Mahieu, C. M., & Davies, L. (2012). Glufosinate-ammonium - Pesticide residues in food. Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues. Evaluations 2012 Part-II Toxicological (pp. 547–652). https://www.inchem.org/documents/jmpr/jmpmono/v2012pr01.pdf
Xu, J., Gu, X., Guo, Y., Tong, F., & Chen, L. (2016). Adsorption behavior and mechanism of glufosinate onto goethite. Science of the Total Environment, 560–561, 123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.03.239
Yamaguchi, N. U., Bergamasco, R., & Hamoudi, S. (2016). Magnetic MnFe2O4-graphene hybrid composite for efficient removal of glyphosate from water. Chemical Engineering Journal, 295, 391–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.03.051
Zacharia, J.T. (2011). Identity, physical and chemical properties of pesticides. In: M. Stoytcheva (Ed.), Pesticides in the Modern World - Trends in Pesticides Analysis, InTech, Rijeka (pp. 1–18). https://doi.org/10.5772/17513
Zhang, C., Zhang, R. Z., Ma, Y. Q., Guan, W. B., Wu, X. L., Liu, X., Li, H., Du, Y. L., & Pan, C. P. (2015). Preparation of cellulose/graphene composite and ıts applications for triazine pesticides adsorption from water. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 3(3), 396–405. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc500738k
Zhu, X., Li, B., Yang, J., Li, Y., Zhao, W., Shi, J., & Gu, J. (2015). Effective adsorption and enhanced removal of organophosphorus pesticides from aqueous solution by Zr-based MOFs of UiO-67. ACS Publications., 7(1), 223–231. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5059074
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Akdeniz University for financial support.
Funding
This research is financially supported by Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Akdeniz University with project number FDK-2017–2919.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Timur TONGUR: Methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing-original draft, visualization. Erol AYRANCI: Conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing-review & editing, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on "Ethical responsibilities of Authors" as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tongur, T., Ayranci, E. Investigation of the performance of activated carbon cloth to remove glyphosate, glufosinate, aminomethylphosphonic acid and bialaphos from aqueous solutions by adsorption/electrosorption. Environ Monit Assess 195, 814 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11395-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11395-3