Abstract
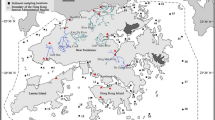
Hong Kong is an urbanized coastal city which experiences substantially different metal loads from anthropogenic activities. This study was aimed at analyzing the spatial distribution and pollution evaluation of ten selected heavy metals (As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, Hg, Ni, Zn, Fe, V) in the coastal sediments of Hong Kong. The distribution of heavy metal pollution in sediments has been analyzed using the geographic information system (GIS) technique, and their pollution degrees, corresponding potential ecological risks and source identifications, have been studied by applying the enrichment factor (EF) analysis, contamination factor (CF) analysis, potential ecological risk index (PEI), and integrated multivariate statistical methods, respectively. Firstly, the GIS technique was used to access the spatial distribution of the heavy metals; the result revealed that pollution trend of these metals was decreased from the inner to the outer coast sites of the studied area. Secondly, combining the EF analysis and CF analysis, we found that the pollution degree of heavy metals followed the order of Cu > Cr > Cd > Zn > Pb > Hg > Ni > Fe > As > V. Thirdly, the PERI calculations showed that Cd, Hg, and Cu were the most potential ecological risk factors compared to other metals. Finally, cluster analysis combined with principal component analysis showed that Cr, Cu, Hg, and Ni might originate from the industrial discharges and shipping activities. V, As, and Fe were mainly derived from the natural origin, whereas Cd, Pb, and Zn were identified from the municipal discharges and industrial wastewater. In conclusion, this work should be helpful in the establishment of strategies for contamination control and optimization of industrial structures in Hong Kong.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Ansari, T. M., Marr, I. L., & Tariq, N. (2004). Heavy metals in marine pollution perspective—a mini review. Journal of Applied Sciences, 4(1), 1–20.
American Public Health Association. (1995). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. Washington, DC.
American Society for Testing and Materials. (2001). American society of testing and materials standards. New York.
Archana, A., Li, L., Shuh-Ji, K., Thibodeau, B., & Baker, D. M. (2016). Variations in nitrate isotope composition of wastewater effluents by treatment type in Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 111(1–2), 143–152.
Badruzzaman, M., Voutchkov, N., Weinrich, L., & Jacangelo, J. G. (2019). Selection of pretreatment technologies for seawater reverse osmosis plants: a review. Desalination, 449, 78–91.
Belhaj, D., Jerbi, B., Medhioub, M., Zhou, J., Kallel, M., & Ayadi, H. (2016). Impact of treated urban wastewater for reuse in agriculture on crop response and soil ecotoxicity. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(16), 15877–15887.
Birmingham, B. C., & Colman, B. (1983). Potential phytotoxicity of diquat accumulated by aquatic plants and sediments. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 19, 123–131.
Bugenyi, F. W. B. (1982). Copper pollution studies in Lakes George and Edward, Uganda: the distribution of Cu, Cd and Fe in the water and sediments. Environmental Pollution Series B, Chemical and Physical, 3(2), 129–138.
Büttner, O., Becker, A., Kellner, S., Kuehn, B., Wendt-Potthoff, K., Zachmann, D. W., & Friese, K. (1998). Geostatistical analysis of surface sediments in an acidic mining lake. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 108, 297–316.
Camacho, J., Smilde, A. K., Saccenti, E., & Westerhuis, J. A. (2020). All sparse PCA models are wrong, but some are useful. Part I: computation of scores, residuals and explained variance. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 196, 103907.
Capelli, R., Contardi, V., Cosma, B., Minganti, V., & Zanicchi, G. (1983). A four-year study on the distribution of some heavy metals in five marine organisms of the Ligurian Sea. Marine Chemistry, 12(4), 281–293.
Chandrasekaran, A., Ravisankar, R., Harikrishnan, N., Satapathy, K. K., Prasad, M. V. R., & Kanagasabapathy, K. V. (2015). Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metal concentration in soils of Yelagiri Hills, Tamilnadu, India-Spectroscopical approach. Spectrochimica Acta, Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 137, 589–600.
Chapman, P. M. (1990). The sediment quality triad approach to determining pollution-induced degradation. Science of the Total Environment, 97, 815–825.
Cheung, K. C., Poon, B. H. T., Lan, C. Y., & Wong, M. H. (2003). Assessment of metal and nutrient concentrations in river water and sediment collected from the cities in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Chemosphere, 52(9), 1431–1440.
Christophoridis, C., Bourliva, A., Evgenakis, E., Papadopoulou, L., & Fytianos, K. (2019). Effects of anthropogenic activities on the levels of heavy metals in marine surface sediments of the Thessaloniki Bay, Northern Greece: Spatial distribution, sources and contamination assessment. Microchemical Journal, 149, 104001.
Cooper, J. A. (1980). Environmental impact of residential wood combustion emissions and its implications. Journal of the Air Pollution Control Association, 30(8), 855–861.
Daskalakis, K. D., & O’Connor, T. P. (1995). Normalization and elemental sediment contamination in the coastal United States. Environmental Science & Technology, 29(2), 470–477.
Duan, J., Han, J., Cheung, S. G., Chong, R. K. Y., Lo, C. M., Lee, F. W. F., Xu, J. L., Yang, Y., Tam, N. F., & Zhou, H. C. (2021). How mangrove plants affect microplastic distribution in sediments of coastal wetlands: Case study in Shenzhen Bay, South China. Science of the Total Environment, 767, 144695.
El-Shahawi, M. S., Hamza, A., Bashammakh, A. S., & Al-Saggaf, W. T. (2010). An overview on the accumulation, distribution, transformations, toxicity and analytical methods for the monitoring of persistent organic pollutants. Talanta, 80(5), 1587–1597.
Esen, E., Kucuksezgin, F., & Uluturhan, E. (2010). Assessment of trace metal pollution in surface sediments of Nemrut Bay, Aegean Sea. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160, 257–266.
Fang, W., Peng, Y., Muir, D., Lin, J., & Zhang, X. (2019). A critical review of synthetic chemicals in surface waters of the US, the EU and China. Environment International, 131, 104994.
Giger, W., Schaffner, C., & Wakeham, S. G. (1980). Aliphatic and olefinic hydrocarbons in recent sediments of Greifensee, Switzerland. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 44(1), 119–129.
Gu, Y. G., & Gao, Y. P. (2019). An unconstrained ordination-and GIS-based approach for identifying anthropogenic sources of heavy metal pollution in marine sediments. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 146, 100–105.
Gu, Y. G., Jiang, S. J., Jordan, R. W., Huang, H. H., & Wu, F. X. (2023). Nonmetric multidimensional scaling and probabilistic ecological risk assessment of trace metals in surface sediments of Daya Bay (China) using diffusive gradients in thin films. Science of The Total Environment, 161433.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A Sedimentological Approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001.
Han, F. I., Banin, A., Su, Y., Monts, D. I., Plodinec, J., Kingery, W. I., & Triplett, G. I. (2002). Industrial age anthropogenic inputs of heavy metals into the pedosphere. Naturwissenschaften, 89(11), 497–504.
Hasan, S., Shi, W., & Zhu, X. (2020). Impact of land use land cover changes on ecosystem service value–A case study of Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao in South China. PLoS One, 15(4), e0231259.
Helena, B., Pardo, R., Vega, M., Barrado, E., Fernandez, J. M., & Fernandez, L. (2000). Temporal evolution of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga River, Spain) by principal component analysis. Water Research, 34(3), 807–816.
Hiller, E., Jurkovič, Ľ, & Šutriepka, M. (2010). Metals in the surface sediments of selected water reservoirs, Slovakia. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 84(5), 635–640.
Holmes, P. R. (1996). Effluent control: The Hong Kong approach. Water and Environment Journal, 10(3), 199–204.
Huang, J. H., Huang, F., Evans, L., & Glasauer, S. (2015). Vanadium: Global (bio) geochemistry. Chemical Geology, 417, 68–89.
Jing, R., Liu, T., Tian, X., Rezaei, H., Yuan, C., Qian, J., & Zhang, Z. (2020). Sustainable strategy for municipal solid waste disposal in Hong Kong: Current practices and future perspectives. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(23), 28670–28678.
Lau, M. M. M., Rootham, R. C., & Bradley, G. C. (1993). A strategy for the management of contaminated dredged sediment in Hong Kong. Journal of Environmental Management, 38(2), 99–114.
Li, Q. G., Liu, G. H., Qi, L., Wang, H. C., Ye, Z. F., & Zhao, Q. L. (2022). Heavy metal-contained wastewater in China: discharge, management and treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 808, 152091.
Li, Q., Wu, Z., Chu, B., Zhang, N., Cai, S., & Fang, J. (2007). Heavy metals in coastal wetland sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environmental Pollution, 149(2), 158–164.
Liu, L., Wang, Z., Ju, F., & Zhang, T. (2015). Co-occurrence correlations of heavy metals in sediments revealed using network analysis. Chemosphere, 119, 1305–1313.
Liu, X., & Yu, S. (2022). Anthropogenic metal loads in nearshore sediment along the coast of China mainland interacting with provincial socioeconomics in the period 1980–2020. Science of the Total Environment, 839, 156286.
Mantovan, P., Vitturi, L. M., Pavoni, B., & Rabitti, S. (1985). Sediments and pollution in the Northern Adriatic Sea: a statistical analysis. Continental Shelf Research, 4(3), 321–340.
McGeer, J. C., Brix, K. V., Skeaff, J. M., DeForest, D. K., Brigham, S. I., Adams, W. J., & Green, A. (2003). Inverse relationship between bioconcentration factor and exposure concentration for metals: implications for hazard assessment of metals in the aquatic environment. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry: An International Journal, 22(5), 1017–1037.
Moturi, M. C. Z., Rawat, M., & Subramanian, V. J. E. M. (2004). Distribution and fractionation of heavy metals in solid waste from selected sites in the industrial belt of Delhi, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 95, 183–199.
Mrema, E. J., Rubino, F. M., Brambilla, G., Moretto, A., Tsatsakis, A. M., & Colosio, C. (2013). Persistent organochlorinated pesticides and mechanisms of their toxicity. Toxicology, 307, 74–88.
Namieśnik, J., & Rabajczyk, A. (2010). The speciation and physico-chemical forms of metals in surface waters and sediments. Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability, 22(1), 1–24.
Nicholson, S., Hui, Y. H., & Lam, P. K. S. (2011). Pollution in the coastal waters of Hong Kong: case studies of the urban Victoria and Tolo Harbours. Water and Environment Journal, 25(3), 387–399.
Nour, H. E., Helal, S. A., & Wahab, M. A. (2022). Contamination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in beach sediments of Red Sea and Gulf of Aqaba, Egypt. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 177, 113517.
Nriagu, J. O., & Coker, R. D. (1980). Trace metals in humic and fulvic acids from Lake Ontario sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 14(4), 443–446.
Passarella, S., Guerriero, E., Quici, L., Ianiri, G., Cerasa, M., Notardonato, I., Protano, C., Vitali, M., Russo, M., Cristofaro, A., & Avino, P. (2022). PAHs presence and source apportionment in honey samples: fingerprint identification of rural and urban contamination by means of chemometric approach. Food Chemistry, 382, 132361.
Pavoni, B., Marcomini, A., Sfriso, A., & Orio, A. A. (1988). Multivariate analysis of heavy metal concentrations in sediments of the lagoon of Venice. Science of the Total Environment, 77(2–3), 189–202.
Pejman, A., Bidhendi, G. N., Ardestani, M., Saeedi, M., & Baghvand, A. (2015). A new index for assessing heavy metals contamination in sediments: a case study. Ecological Indicators, 58, 365–373.
Peshut, P. J., Morrison, R. J., & Brooks, B. A. (2008). Arsenic speciation in marine fish and shellfish from American Samoa. Chemosphere, 71(3), 484–492.
Preisner, M. (2020). Surface water pollution by untreated municipal wastewater discharge due to a sewer failure. Environmental Processes, 7(3), 767–780.
Pruter, A. T. (1987). Sources, quantities and distribution of persistent plastics in the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 18(6), 305–310.
Renberg, I., Persson, M. W., & Emteryd, O. (1994). Pre-industrial atmospheric lead contamination detected in Swedish lake sediments. Nature, 368(6469), 323–326.
Rios, L. M., Moore, C., & Jones, P. R. (2007). Persistent organic pollutants carried by synthetic polymers in the ocean environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54(8), 1230–1237.
Rong, S., Wu, J., Cao, X., & Sun, Y. (2022). Comprehensive ecological risk assessment of heavy metals based on species sensitivity distribution in aquatic of coastal areas in Hong Kong. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(20), 13376.
Ruan, Y., Wu, R., Lam, J. C., Zhang, K., & Lam, P. K. (2019). Seasonal occurrence and fate of chiral pharmaceuticals in different sewage treatment systems in Hong Kong: Mass balance, enantiomeric profiling, and risk assessment. Water Research, 149, 607–616.
Ryan, J. D., & Windom, H. L. (1988). A geochemical and statistical approach for assessing metal pollution in coastal sediments. Metals in coastal environments of Latin America, 47–58.
Schlesinger, W. H., Klein, E. M., & Vengosh, A. (2017). Global biogeochemical cycle of vanadium. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 114(52), E11092–E11100.
Selbig, W. R., Bannerman, R., & Corsi, S. R. (2013). From streets to streams: assessing the toxicity potential of urban sediment by particle size. Science of the Total Environment, 444, 381–391.
Tian, L., Wai, O. W., Chen, X., Liu, Y., Feng, L., Li, J., & Huang, J. (2014). Assessment of total suspended sediment distribution under varying tidal conditions in deep bay: initial results from HJ-1A/1B satellite CCD images. Remote Sensing, 6(10), 9911–9929.
Tkalin, A. V., Presley, B. J., & Boothe, P. N. (1996). Spatial and temporal variations of trace metals in bottom sediments of Peter the Great Bay, the Sea of Japan. Environmental Pollution, 92(1), 73–78.
Wang, H., Liu, Z., Sathiamurthy, E., Colin, C., Li, J., & Zhao, Y. (2011). Chemical weathering in Malay Peninsula and North Borneo: clay mineralogy and element geochemistry of river surface sediments. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(2), 272–282.
Wang, J. J., & Cheng, M. C. (2010). From a hub port city to a global supply chain management center: a case study of Hong Kong. Journal of Transport Geography, 18(1), 104–115.
Wang, S. L., Xu, X. R., Sun, Y. X., Liu, J. L., & Li, H. B. (2013). Heavy metal pollution in coastal areas of South China: a review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 76(1–2), 7–15.
Wang, T., & Khim, J. S. (2020). Accumulation and ecological risk of heavy metals in soils along the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea: a comparative study of China and South Korea. Environment International, 137, 105519.
Wong, K. W., Yap, C. K., Nulit, R., Hamzah, M. S., Chen, S. K., Cheng, W. H., Karami, A., & Al-Shami, S. A. (2017). Effects of anthropogenic activities on the heavy metal levels in the clams and sediments in a tropical river. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(1), 116–134.
Wong, Y. S., Tam, N. F. Y., Lau, P. S., & Xue, X. Z. (1995). The toxicity of marine sediments in Victoria Harbour, Hong Kong. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 31(4–12), 464–470.
Wu, W., Qu, S., Nel, W., & Ji, J. (2020). The impact of natural weathering and mining on heavy metal accumulation in the karst areas of the Pearl River Basin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 734, 139480.
Xiao, H., Shahab, A., Ye, F., Wei, G., Li, J., & Deng, L. (2022). Source-specific ecological risk assessment and quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Pearl River Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 179, 113726.
Xu, J., Lee, J. H., Yin, K., Liu, H., & Harrison, P. J. (2011). Environmental response to sewage treatment strategies: Hong Kong’s experience in long term water quality monitoring. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62(11), 2275–2287.
Zandbergen, P. A. (1998). Urban watershed ecological risk assessment using GIS: a case study of the Brunette River watershed in British Columbia, Canada. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 61(1–3), 163–173.
Zhang, M., He, P., Qiao, G., Huang, J., Yuan, X., & Li, Q. (2019). Heavy metal contamination assessment of surface sediments of the Subei Shoal, China: Spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk. Chemosphere, 223, 211–222.
Zhang, Q., Ren, F., Xiong, X., Gao, H., Wang, Y., Sun, W., Leng, P., Li, Z., & Bai, Y. (2021). Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metal pollution of sediments in coastal reclamation areas: a case study in Shenzhen Bay, China. Environmental Sciences Europe, 33, 1–11.
Zhang, X., Man, X., & Jiang, H. (2015). Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metals in the marine sediments of Hong Kong. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 1–12.
Zhang, Y., Guo, F., Meng, W., & Wang, X. Q. (2009). Water quality assessment and source identification of Daliao river basin using multivariate statistical methods. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 152, 105–121.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department for providing the monitoring data of marine sediments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the study: Chen Chen, Fengwen Huang; analyzed the data: Chen Chen, Fengwen Huang; drafted the manuscript: Chen Chen, Fengwen Huang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors”.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, F., Chen, C. GIS-based approach and multivariate statistical analysis for identifying sources of heavy metals in marine sediments from the coast of Hong Kong. Environ Monit Assess 195, 518 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11152-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11152-6