Abstract
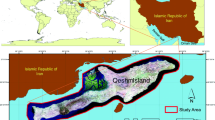
Land use change simulation is an important issue for its role in predicting future trends and providing implications for sustainable land management. Hybrid models have become a recognized strategy to inform decision-makers, but further attempts are needed to warrant the reliability of their projected results. In view of this, three hybrid models, including the cellular automata-Markov chain-artificial neural network, cellular automata-Markov chain-logistic regression, and Markov chain-artificial neural network, were applied to simulate land use change on the largest island in Iran, Qeshm Island. The Figure of Merit (FOM) was used to measure the modeling accuracy of the simulations, with the FOMs for the three models 6.7, 5.1, and 4.5, respectively. Consequently, the cellular automata-Markov chain-artificial neural network most precisely simulates land use change on Qeshm Island and is, thus, used to simulate land use change until 2026. The simulation shows that the incremental trend of the built-up class will continue in the coming years. Meanwhile, the areas of valuable ecosystems, such as mangroves, tend to decrease. Despite the protection plans for mangroves, these areas require more attention and conservation planning. This study demonstrates a referential example to select the proper land use models for informing planning and management in similar coastal zones.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aburas, M. M., Ho, Y. M., Ramli, M. F., & Ash’aari, Z. H. (2016). The simulation and prediction of spatio-temporal urban growth trends using cellular automata models: a review. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2016.07.007.
Alilou, H., Moghaddam Nia, A., Keshtkar, H. R., Han, D., & Bray, M. (2018). A cost-effective and efficient framework to determine water quality monitoring network locations. The Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.12.121.
Arsanjani, J. J., Helbich, M., Kainz, W., & Boloorani, A. D. (2013). Integration of logistic regression, Markov chain and cellular automata models to simulate urban expansion. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2011.12.014.
Benito, P. R., Cuevas, J. A., Bravo, R., Barrio, J. M. G. D., & Zavala, M. A. (2010). Land use change in a Mediterranean metropolitan region and its periphery: assessment of conservation policies through CORINE land cover data and Markov models. Forest Systems, 19, 315–328.
Bihamta Toosi, N., Soffianian, A., Fakheran, S., Pourmanafi, S., Ginzler, C., & Waser, L. (2019). Comparing different classification algorithms for monitoring mangrove cover changes in southern Iran. Global Ecology and Conservation, e00662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2019.e00662.
Chu, L., Sun, T., Wang, T., Li, Z., & Cai, C. (2018). Evolution and prediction of landscape pattern and habitat quality based on CA-Markov and InVEST model in Hubei section of three gorges reservoir area (TGRA). Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10113854.
De Rosa, M., Knudsen, M. T., & Hermansen, J. E. (2016). A comparison of land use change models: challenges and future developments. Journal of Cleaner Production. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.097.
Eastman, J. R. (2015). IDRISI TerrSet, guide to GIS and image processing, manual version 18.00. Worcester: Clark University.
Ebrahimi-Sirizi, Z., & Riyahi-Bakhtiyari, A. (2013). Petroleum pollution in mangrove forests sediments from Qeshm Island and Khamir Port—Persian Gulf, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2846-z.
Etemadi, H., Smoak, J., & Karami, J. (2018). Land use change assessment in coastal mangrove forests of Iran utilizing satellite imagery and CA–Markov algorithms to monitor and predict future change. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77, 208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7392-8.
Ghosh, P., Mukhopadhyay, A., Chanda, A., Mondal, P., Akhand, A., Mukherjee, S., Nayak, S. K., Ghosh, S., Mitra, D., Ghosh, T., & Hazra, S. (2017). Application of Cellular automata and Markov-chain model in geospatial environmental modeling- a review. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsase.2017.01.005.
Hamdy, O., Zhao, S., Osman, T., Salheen, M. A., & Eid, Y. Y. (2016). Applying a hybrid model of Markov chain and logistic regression to identify future urban sprawl in Abouelreesh, Aswan: a case study. Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences6040043.
Hu, X., & Weng, Q. (2009). Estimating impervious surfaces from medium spatial resolution imagery using the self-organizing map and multi-layer perceptron neural networks. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(10), 2089–2102.
Hu, X., Li, X., & Lu, L. (2018). Modeling the land use change in an arid oasis constrained by water resources and environmental policy change using cellular automata models. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10082878.
Hyandye, C., & Martz, L. W. (2017). A Markovian and cellular automata land use change predictive model of the Usangu Catchment. International Journal of Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1259675.
Iran’s Population and Housing Census. (2016). from https://amar.sci.org.ir/index_e.aspx.
Kamusoko, C., Aniya, M., Adi, B., & Manjoro, M. (2009). Rural sustainability under threat in Zimbabwe – Simulation of future land use/cover changes in the Bindura district based on the Markov-cellular automata model. Applied Geography, 29, 435–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2008.10.002.
Karimi, H., Jafarnezhad, J., Khaledi, J., & Ahmadi, P. (2018). Monitoring and prediction of land use/land cover changes using CA-Markov model: a case study of Ravansar County in Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 592–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3940-5.
Kazemzadeh-Zow, A., Shahraki, S. Z., Salvati, L., & Samani, N. N. (2017). A spatial zoning approach to calibrate and validate urban growth models. International Journal of Geographical Information Science. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2016.1236927.
Keshtkar, H., & Voigt, W. (2016). A spatiotemporal analysis of landscape change using an integrated Markov chain and cellular automata models. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2, 2–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0068-4.
Khoorani, A., Bineiaz, M., & Amiri, H. R. (2015). Mangrove forest area changes due to climatic changes (case study: forest between the port and the Khamir island). Journal of Aquatic Ecology, 5(2), 100–111 (In Persian with English abstract).
Kokabi, M., Yousefzadi, M., Razaghi, M., & Feghhi, M. A. (2016). Zonation patterns, composition and diversity of macroalgal communities in the eastern coasts of Qeshm Island, Persian Gulf, Iran. Marine Biodiversity Records. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41200-016-0096-4.
Koomen, E., Stillwell, J., Bakema, A., & Scholten, H. J. (2007). Modelling land use change: progress and applications. GeoJournal. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-5648-2.
Kourosh Niya, A., Jinliang, H., Kazemzadeh-Zow, A., & Naimi, B. (2019). An adding/deleting approach to improve land change modeling: a case study in Qeshm Island, Iran. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4504-z.
Li, X., Chen, Y., Liu, X., Xu, X., & Chen, G. (2017). Experiences and issues of using cellular automata for assisting urban and regional planning in China. International Journal of Geographical Information Science. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2017.1301457.
Liu, D., Zheng, X., Zhang, C., & Wang, H. (2017). A new temporal–spatial dynamics method of simulating land use change. Ecological Modeling. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.02.005.
Mafi-Gholami, D., Zenner, E. K., Jaafari, A., & Ward, R. D. (2019). Modeling multi-decadal mangrove leaf area index in response to drought along the semi-arid southern coasts of Iran. The Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.462.
Memarian, H., Kumar Balasundram, S., Talib, J. B., Sung, C. T. B., Sood, A. M., & Abbaspour, K. (2012). Validation of CA-Markov for simulation of land use and cover change in the Langat Basin, Malaysia. Journal of Geographic Information System. https://doi.org/10.4236/jgis.2012.46059.
Mirza, R., Moeinaddini, M., Pourebrahim, S., & Zahed, M. A. (2019). Contamination, ecological risk and source identification of metals by multivariate analysis in surface sediments of the khouran Straits, the Persian Gulf. Marine Pollution Bullten. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.06.028.
Mitsova, D., Shuster, W., & Wang, X. (2011). A cellular automata model of land cover change to integrate urban growth with open space conservation. Landscape and Urban Planning. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.10.001.
Mustafa, Y. T. (2020). Multi-temporal satellite data for land use/cover (LULC) change detection in Zakho, Kurdistan Region-Iraq. In A. Al-Quraishi & A. Negm (Eds.), Environmental remote sensing and GIS in Iraq. Cham: Springer Water. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-21344-2_7.
Mustafa, A., Rienow, A., Saadi, I., Cools, M., & Teller, J. (2018). Comparing support vector machines with logistic regression for calibrating cellular automata land use change models. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 51, 391–401. https://doi.org/10.1080/22797254.2018.1442179.
Newman, G., Lee, J., & Berke, P. (2016). Using the land transformation model to forecast vacant land. Journal of Land Use Science. https://doi.org/10.1080/1747423X.2016.1162861.
Olmedo, M. T. C., Pontius Jr., R. G., Paegelow, M., & Mas, J. F. (2015). Comparison of simulation models in terms of quantity and allocation of land change. Environmental Modelling & Software. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.03.003.
Pickard, B., Gray, J., & Meentemeyer, R. (2017). Comparing quantity, allocation and configuration accuracy of multiple land change models. Land. https://doi.org/10.3390/land6030052.
Pontius Jr., R. G., & Schneider, L. C. (2001). Land-cover change model validation by an roc method for the Ipswich watershed, Massachusetts, USA. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 85(1), 239–248.
Pontius Jr., R. G., & Millones, M. (2011). Death to kappa: birth of quantity disagreement and allocation disagreement for accuracy assessment. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 32(15), 4407-4429. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2011.552923.
Pourahmad, A., Hosseini, A., Pourahmad, A., Zoghi, M., & Sadat, M. (2018). Tourist value assessment of Geotourism and environmental capabilities in Qeshm Island-Iran. Geoheritage., 10, 687–706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12371-017-0273-9.
Rimal, B., Zhang, L., Keshtkar, H. R., Haack, B., Rijal, S., & Zhang, P. (2018). Land use/land cover dynamics and modeling of urban land expansion by the integration of cellular automata and Markov chain. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7040154.
Sang, L., Zhang, C., Yang, J., Zhu, D., & Yun, W. (2011). Simulation of land use spatial pattern of towns and villages based on CA-Markov model. Mathematical and Computer Modelling. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcm.2010.11.019.
Shadman-Roodposhti, M., Aryal, J., & Bryan, B. A. (2019). A novel algorithm for calculating transition potential in cellular automata models of land use/cover change. Environmental Modelling & Software. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2018.10.006.
Shafizadeh-Moghadam, H., Asghari, A., Taleai, M., Helbich, M., & Tayyebi, A. (2017). Sensitivity analysis and accuracy assessment of the land transformation model using cellular automata. GIScience & Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1080/15481603.2017.1309125.
Silva, H. J. F., Gonçalves, W. A., & Bezerra, B. G. (2019). Comparative analyzes and use of evapotranspiration obtained through remote sensing to identify deforested areas in the Amazon. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2019.01.015.
Sun, B., & Robinson, D. T. (2018). Comparisons of statistical approaches for Modelling land use change. Land. https://doi.org/10.3390/land7040144.
Tajbakhsh, S. M., Memarian, H., Moradi, K., & Afshar, A. H. A. (2018). Performance comparison of land change modeling techniques for land use projection of arid watersheds. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management. https://doi.org/10.22034/gjesm.2018.03.002.
Varga, O. G., Pontius Jr., R. G., Singh, S. K., & Szabó, S. (2019). Intensity analysis and the Figure of Merit’s components for assessment of a cellular automata – Markov simulation model. Ecological Indicators. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.01.057.
Verburg, P., Schot, P., Dijst, M., & Veldkamp, A. (2004). Land use change modeling: current practice and research priorities. GeoJournal., 61, 309–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-004-4946-y.
Xu, T., Gao, J., & Coco, G. (2019). Simulation of urban expansion via integrating artificial neural network with Markov chain – cellular automata. International Journal of Geographical Information Science. https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2019.1600701.
Yan, R., Cai, Y., Li, C., Wang, X., & Liu, Q. (2019). Hydrological responses to climate and land use changes in a watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11051443.
Yang, X., Zheng, X. Q., & Lv, L. N. (2012). A spatiotemporal model of land use change based on ant colony optimization, Markov chain and cellular automata. Ecological Modelling. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2012.03.011.
Yao, Y., Li, J., Zhang, X., Duan, P., Li, S., & Xu, Q. (2017). Investigation on the expansion of urban construction land use based on the CART-CA model. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 6(5), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi6050149.
Yazdi, A., & Dabiri, R. (2018). Investigating the Geotourism phenomena in eroded land of Iran, Qeshm Island; Revista Publicando. 5 No 16. (2). 2018, 35–94. ISSN 1390-9304.
Yirsaw, E., Wu, W., Shi, X., Temesgen, H., & Bekele, B. (2017). Land use/land cover change modeling and the prediction of subsequent changes in ecosystem service values in a coastal area of China, the Su-Xi-Chang Region. Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071204.
Yuan, H., Van Der Wiele, C. F., & Khorram, S. (2009). An automated artificial neural network system for land use/land cover classification from Landsat TM imagery. Remote Sensing, 1, 243–265.
Acknowledgments
Anonymous reviewers supplied constructive feedback that helped to improve this manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Chinese Government Marine Scholarship (Grant No. 2016SOA016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kourosh Niya, A., Huang, J., Kazemzadeh-Zow, A. et al. Comparison of three hybrid models to simulate land use changes: a case study in Qeshm Island, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 192, 302 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08274-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08274-6