Abstract
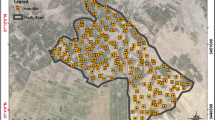
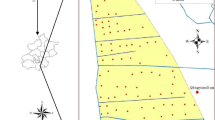
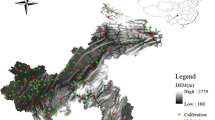
This study compared the performance of different interpolation methods for mapping soil salinity of three different agricultural fields having the same land use but different dataset characteristics. Four common spatial interpolation methods including global polynomial interpolation (GPI), inverse distance weighted (IDW), ordinary kriging (OK), and radial basis functions (RBF) were employed for mapping soil EC. The performance of interpolation methods in predicting soil EC was evaluated based on mean bias error, root mean square error, mean absolute percentage error, and coefficient of determinations criteria. Results showed that dataset characteristics, including central tendency and distribution, were significantly different among the studied fields. Experimental semivariogram and fitted model parameters indicated that three studied fields were also different in their spatial dependence strength. Considering all of the performance assessment measures used, the best interpolation method for fields A and C was OK and IDW for field B. The performance of interpolation methods was found to be affected by data characteristics of the studied fields, which were mostly ascribed to management practices. This study suggests in order to obtain accurate mapping of soil salinity in agricultural fields, it is essential to first find the best spatial interpolation method compatible with the characteristics of the collected data from the selected agricultural land.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EC:
-
electrical conductivity
- GPI:
-
global polynomial interpolation
- IDW:
-
inverse distance weighted
- MAPE:
-
mean absolute percentage error
- MBE:
-
mean bias error
- OK:
-
ordinary kriging
- R 2 :
-
coefficient of determination
- RBF:
-
radial basis functions
- RSS:
-
residual sum of squares
- TNV:
-
mean total neutralizing values
- κ:
-
Cohen’s kappa coefficient
References
Abuelgasim, A., & Ammad, R. (2018). Mapping soil salinity in arid and semi-arid regions using Landsat 8 OLI satellite data. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 13, 415–425.
Ahmed, H., Muhammad, T. S., Muhammad, I., & Fayyaz, H. (2017). Comparative study of interpolation methods for mapping soil pH in the apple orchards of Murree, Pakistan. Soil and Environment, 36, 70–76.
Allbed, A., Kumar, L., & Sinha, P. (2014). Mapping and modelling spatial variation in soil salinity in the Al Hassa oasis based on remote sensing indicators and regression techniques. Remote Sensing, 6, 1137–1157.
Buhmann, M. D. (2003). Radial basis functions: theory and implementations. Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press ISBN 978-0511040207.
Chiles, J. P., & Delfiner, P. (1999). Geostatistics: modeling spatial uncertainty. New York: Wiley.
Daliakopoulos, I. N., Tsanis, I. K., Koutroulis, A., Kourgialas, N. N., Varouchakis, A. E., Karatzas, G. P., & Ritsema, C. J. (2016). The threat of soil salinity: a European scale review. Science of the Total Environment, 573, 727–739.
Denton, O. A., Aduramigba-Modupe, V. O., Ojo, A. O., Adeoyolanu, O. D., Are, K. S., Adelana, A. O., Oyedele, A. O., Adetayo, A. O., & Oke, A. O. (2017). Assessment of spatial variability and mapping of soil properties for sustainable agricultural production using geographic information system techniques (GIS). Cogent Food & Agriculture, 3, 1279366.
Douaik, A., Meirvenne, M. V., & Toth, T. (2008). Stochastic approaches for space-time modeling and interpolation of soil salinity. In G. Metternicht & A. Zinck (Eds.), Remote sensing of soil salinization: impact on land management (pp. 273–290). CRC Press.
Gebbers, R., & de Bruin, S. (2010). Application of geostatistical simulation in precision agriculture. In M. A. Oliver (Ed.), Geostatistical applications for precision agriculture (pp. 269–303). Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
Goovaerts, P. (1997). Geostatistics for natural resources characterization. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Gorji, T., Tanik, A., & Sertel, E. (2015). Soil salinity prediction, monitoring and mapping using modern technologies. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 15, 507–512.
Isaaks, E. H., & Srivastava, R. M. (1989). Applied geostatistics. New York: Oxford University Press.
Jakobsson, S., Andersson, B., & Edelvik, F. (2009). Rational radial basis function interpolation with applications to antenna design. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 233, 889–904.
Joanes, D. N., & Gill, C. A. (1998). Comparing measures of sample skewness and kurtosis. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series D (The Statistician), 47, 183–189.
Johnston, K., Ver Hoef, J., Krivoruchko, K., & Lucas, N. (2003). Using ArcGIS Geostatistical Analyst. Redlands: ESRI press.
Juan, P., Mateu, J., Jordan, M. M., Mataix-Solera, J., Meléndez-Pastor, I., & Navarro-Pedreño, J. (2011). Geostatistical methods to identify and map spatial variations of soil salinity. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 108, 62–72.
Kavianpoor, H., Esmali, Ouri, A., Jafarian Jeloudar, Z., & Kavian, A. (2012). Spatial variability of some chemical and physical soil properties in Nesho mountainous rangelands. American Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2(1), 34–44.
Kumari, N., Sakai, K., Kimura, S., Nakamura, S., Yuge, K., Gunarathna, M., Ranagalage, M., & Duminda, D. M. S. (2018). Interpolation methods for groundwater quality assessment in tank cascade landscape: a study of ulagalla cascade, Sri Lanka. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 16(5), 5359–5380.
Li, J., & Heap, A. D. (2011). A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in environmental sciences: performance and impact factors. Ecological Informatics, 6, 228–241.
Lin, G. F., & Chen, L. H. (2004). A spatial interpolation method based on radial basis function networks incorporating a semivariogram model. Journal of Hydrology, 288, 288–298.
McBratney, A. B., Mendonça Santos, M. L., & Minasny, B. (2003). On digital soil mapping. Geoderma, 117, 3–52.
McHugh, M. L. (2012). Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochemica Medica, 22(3), 276–282.
Rhoades, J. D. (1996). Salinity: electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids. In Methods of soil analysis part 3—chemical methods (pp. 417–435). Madison: Soil Science Society of America, American Society of Agronomy.
Setianto, A., & Triandini, T. (2013). Comparison of kriging and inverse distance weighted (IDW) interpolation methods in lineament extraction and analysis. Journal of Applied Geology, 5(1), 21–29.
Seyedmohammadi, J., Esmaeelnejad, L., & Shabanpour, M. (2016). Spatial variation modelling of groundwater electrical conductivity using geostatistics and GIS. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 2, 1–10.
Shi, J., Wang, H., Xu, J., Wu, J., Liu, X., Zhu, H., & Yu, C. (2007). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils: a case study of Changxing, China. Environmental Geology, 52, 1–10.
Simakova, M. S. (2011). Small-scale soil mapping. Eurasian Soil Science, 44, 1036.
Webster, R., & Oliver, M. (2001). Geostatistics for environmental scientists (Statistics in Practice). Wiley.
Xiao, Y., Gu, X., Yin, S., Shao, J., Cui, Y., Zhang, Q., & Niu, Y. (2016). Geostatistical interpolation model selection based on ArcGIS and spatio-temporal variability analysis of groundwater level in piedmont plains, northwest China. SpringerPlus, 5, 425.
Xie, Y., Chen, T. B., Lei, M., Yang, J., Guo, Q. J., Song, B., & Zhou, X. Y. (2011). Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere, 82, 468–476.
Yao, X., Fu, B., Lu, Y., Sun, F., Wang, S., & Liu, M. (2013). Comparison of four spatial interpolation methods for estimating soil moisture in a complex terrain catchment. PLoS One, 8(1), e54660.
Yao, L., Huo, Z., Feng, S., Mao, X., Kang, S., Chen, J., Xu, J., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2014). Evaluation of spatial interpolation methods for groundwater level in an arid inland oasis, northwest China. Environmental Earth Sciences Steenhuis, 71, 1911–1924.
Zewdu, S., Suryabhagavan, K. V., & Balakrishnan, M. (2017). Geo-spatial approach for soil salinity mapping in Sego Irrigation Farm, South Ethiopia. Journal of the Saudi Society of Agricultural Sciences, 16, 16–24.
Zhu, Q., & Lin, H. S. (2010). Comparing ordinary kriging and regression kriging for soil properties in contrasting landscapes. Pedosphere, 20, 594–606.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by ETKA organization, Iran. The authors thank Mr. Hossein Mahmoudi for field and laboratory assistance. The authors are also grateful to the anonymous reviewers who considerably improved the quality of this manuscript prior to publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fazeli Sangani, M., Namdar Khojasteh, D. & Owens, G. Dataset characteristics influence the performance of different interpolation methods for soil salinity spatial mapping. Environ Monit Assess 191, 684 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7844-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7844-y