Abstract
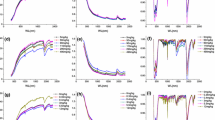
This study was aimed (i) to examine using diffuse reflectance spectra within VNIR region to estimate soil heavy metals concentrations at large scale, (ii) to compare the influence of different pre-processing models on predictive model accuracy, and (iii) to explore the best predictive models. A number of 325 topsoil samples were collected and their spectral data, pH, clay content, organic matter, Ni, and Cu concentrations were determined. To improve spectral data, various pre-processing methods including Savitzky-Golay smoothing filter, Savitzky-Golay smoothing filter with first and second derivatives, and standard normal variant (SNV) were used. Partial least squares regression (PLSR), principal component regression (PCR), and support vector machine regression (SVMR) models were employed to build calibration models for estimating soil heavy metals concentration followed by evaluation of provided predictive models. Results indicated that Cu had stronger correlation coefficients with spectral bands compared to Ni. Cu and Ni demonstrated strongest correlations at wavelengths 1925 and 1393 nm, respectively. Based on RMSE, R2, and RPD statistics, the PLSR model with Savitzky-Golay filter pretreatment provided the most accurate predictions for both Cu and Ni (R2 = 0.905, RMSE = 0.00123, RPD = 2.80 for Ni; R2 = 0.825, RMSE = 0.00467, RPD = 2.04 for Cu) where such prediction was much better for Ni than for Cu. Reasonable results with lower accuracy and stability were obtained for PCR (R2 = 0.742, RMSE = 0.00181, RPD = 1.91 for Ni; R2 = 0.731, RMSE = 0.00578, RPD = 1.65 for Cu) and SVMR (R2 = 0.643, RMSE = 0.00091, RPD = 3.80 for Ni; R2 = 0.505, RMSE = 0.00296, RPD = 3.22 for Cu). We concluded that reflectance spectroscopy technique could be applied as a reliable tool for detection and prediction of soil heavy metals.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Maliki, A., Owens, G., & Bruce, D. (2012). Capabilities of remote sensing hyperspectral images for the detection of lead contamination: a review. ISPRS annals of the photogrammetry, remote sensing and spatial information sciences, 25 august–01 September, Australia, Melbourne. Volume I-7. doi:https://doi.org/10.5194/isprsannals-I-7-55-2012.
Asadi Kapourchal, S., Asadi Kapourchal, S., Pazira, E., & Homaee, M. (2009). Assessing radish potential for phytoremediation of lead- polluted soils resulting from air pollution. Plant Soil and Environment., 55(5), 202–206.
Atafar, Z., Mesdaghinia, A. R., Nouri, J., Homaee, M., Yunesian, M., Ahmadimoghadam, M., & Mahvi, A. H. (2010). Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment., 160, 83–89.
Babaeian, E., Homaee, M., & Rahnemaei, R. (2016). Chelate-enhanced phytoextraction and phytostabilization of lead contaminated soils by carrot, Daucus Carrota. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 62(3), 339–358.
Bauycos, G. J. (1962). Hydrometer method improved for making particle size of soils. Agronomy Journal, 56, 464–465. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1962.00021962005400050028x.
Ben-Dor, E., Chabrillat, S., Demattê, J. A. M., Taylor, G. R., Hill, J., Whiting, M. L., & Sommer, S. (2009). Using imaging spectroscopy to study soil properties. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113, S38–S55.
Brown, D. J., Shepherd, K. D., Walsh, M. G., Mays, M. D., & Reinsch, T. G. (2006). Global soil characterization with VNIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma, 132, 273–290.
Chang, C. W., Laird, D. A., Mausbach, M. J., & Hurburgh, C. R. (2001). Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy-principal components regressionanalysis of soil properties. Soil Science Society of American Journal, 65, 480–490.
Davari, M., Homaee, M., & Rahnemaei, R. (2015a). An analytical deterministic model for simultaneous phytoremediation of Ni and Cd from contaminated soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 4609–4620.
Davari, M., Rahnemaei, R., & Homaee, M. (2015b). Competitive adsorption-desorption reactions of two hazardous heavy metals in contaminated soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 13024–13032.
Demmatê, J. A. M. (2002). Characterization and discrimination of soil by their reflected electromagnetic energy. Brazilian Journal of Agricultural Research, 37, 1445–1458.
Gholizadeh, A., Borůvka, L., Vašát, R., Saberioon, M. M., Klement, A., Kratina, J., Tejnecký, V., & Drábek, O. (2015). Estimation of potentially toxic elements contamination in anthropogenic soils on a brown coal mining dumpsite by reflectance spectroscopy: a case study. PLoS One, 10(2), 117–457. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117457.
Eskandari, M., Homaee, M., & Falamaki, A. (2016). Landfill site selection for municipal solid wastes in mountainous areas with landslide susceptibility. Environmental Science and Pollution Research., 23, 12423–12434.
Eskandari, M., Homaee, M., Mahmodi, S., Pazira, E., & van Genuchten, M. T. (2015). Optimizing landfill site selection by using land classification maps. Environmental Science and Pollution Research., 22, 7757–7765.
Eskandari, M., Homaee, M., & Mahmodi, S. (2012). An integrated multi criteria approach for landfill siting in a conflicting environmental, economical and socio-cultural area. Waste Management, 32(8), 1528–1538.
Farrokhian Firouzi, A., Homaee, M., Klumpp, E., Kasteel, R., & Tappe, W. (2015). Bacteria transport and retention in intact calcareous soil columns under saturated flow conditions. Journal of Hydrology and Hydromechanics, 62(2), 102–109.
Gras, J. P., Barthès, B. G., Mahaut, B., & Trupin, S. (2014). Best practices for obtaining and processing field visibleand near infrared (VNIR) spectra of topsoil. Geoderma, 215, 126–134.
Guerrero, C., ViscarraRossel, R. A., & Mouazen, A. M. (2010). Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy in soil science and land resource assessment. Geoderma, 158(1–2), 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.05.008.
Hansen, E., Lassen, C., Stuer-Lauridsen, F., & Kjølholt, F. (2002). Heavy Metals in Waste. European Commission DG ENV.E3, Project ENV.E.3,ETU/200/0058, Final Report.
Homaee, M., & Schmidhalter, U. (2008). Water integration by plants root under non-uniform soil salinity. Irrigation Science, 27, 83–95.
Jafarnejadi, A. R., Sayyad, G., Homaee, M., & Davamei, A. H. (2013). Spatial variability of soil total and DTPA-extractable cadmium caused by long-term application of phosphate fertilizers, crop rotation and soil characteristics. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment., 185, 4087–4096.
Jafarnejadi, A. R., Homaee, M., & Sayyad, G. (2011). Large scale spatial variability of accumulated cadmium in the wheat farm grains. Soil and Sediment Contamination Journal, 20(1), 93–99.
Ji, J. F., Balsam, W., Chen, J., & Liu, L. W. (2002). Rapid and quantitative measurement of hematite and goethite in the Chinese loess-paleosol sequence by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Clays and Clay Minerals, 50(2), 208–216.
Kabata-Pendias, A., & Mukherjee, A. B. (2007). Trace elements from soil to human (p. 561). Berlin Heidelberg New York (NY): Springer. https://doi.org/10.5860/choice.45-2048 Trace elements from soil to human.
Kemper, T., & Sommer, S. (2002). Estimate of heavy metal contamination in soils after a mining accident using reflectance spectroscopy. Environmental Science and Technology, 36(12), 2742–2747.
Khodaverdiloo, H., & Homaee, M. (2008). Modeling cadmium and lead phytoextraction from contaminated soils. Polish Journal of Soil Science, XLI(2), 149–162.
Kooistra, L., Wehren, R., Buydens, L. M. C., Leuven, R. S. E. W., & Nienhuis, P. H. (2001a). Possibilities of soil spectroscopy for the classification of contaminated areas in river floodplains. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 3(4), 337–344.
Kooistra, L., Wehrens, R., Leuven, R. S. E. W., & Buydens, L. M. C. (2001b). Possibilities of visible-near-infrared spectroscopy for the assessment of soil contamination in river flood plains. Analytica Chimica Acta, 446(1–2), 97–105.
Kooistra, L., Wanders, J., Eperma, G. F., Leuven, R. S. E. W., Wehrens, R., & Buydens, L. M. C. (2003). The potential of field spectroscopy for the assessment of sediment properties in river floodplains. Analytica Chimica Acta, 484(2), 189–200.
Liu, Y. L., Chen, H., Wu, G. F., & Xu, X. G. (2011). Feasibility of estimating heavy metal contaminations in floodplain soils using laboratory-based hyperspectral data—a case study along Le’an river, China. Geo-Spatial Information Science, 14(1), 10–16.
Malley, D. F., & Williams, P. C. (1997). Use of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy in prediction of heavy metals in freshwater sediment by their association with organic matter. Environmental Science and Technology, 31(12), 3461–3467.
Martens, H., & Martens, M. (2000). Modified jack-knife estimation of parameter uncertainty in bilinear modeling by partial least squares regression (PLSR). Food Quality and Preference, 11(1–2), 5–16.
Mohammadi, S., Homaee, M., & Sadeghi, S. H. (2018). Runoff and sediment behavior from soil plots contaminated with kerosene and gasoil. Soil & Tillage Resarch, 182, 1–9.
Noshadi, E., & Homaee, M. (2018). Herbicides degradation kinetics in soil under different herbigation systems at field scale. Soil & Tillage Resarch, 184, 37–44.
Nouri, M., Homaee, M., & Bybordi, M. (2014). Quantitative assessment of LNAPLs retention in soil porous media. Soil and Sediment Contamination., 23, 801–819.
Pandit, M., Filippelli, M., & Li, L. (2010). Estimation of heavy metal contamination in soil using reflectance spectroscopy and partial least-squares regression. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 31(15), 4111–4123.
Plaza, A., Martínez, P., Pérez, R., & Plaza, J. (2002). Spatial/spectral endmember extraction by multidimensional morphological operations. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remot Sensing, 40(9), 2025–2041. https://doi.org/10.1109/tgrs.2002.802494.
Rhoades, J. D. (1996). Methods of soil analysis: chemical methods: electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids (pp. 417–436). Wisconsin: ASA/SSSA Madison.
Rossel, R. A. V., Cattle, S. R., Ortega, A., & Fouad, Y. (2009). In situ measurements of soil colour, mineral composition and clay content by vis-NIR spectroscopy. Geoderma, 150(3–4), 253–266.
Rowell, D. L. (1994). Soil science: methods and applications (p. 345). Harlow: Longman Group.
Savitzky, A., & Golay, M. J. E. (1964). Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Analytical Chemistry, 36(8), 1627–1639.
Shi, T., Chen, Y., Yaolin, L., & Wu, G. (2014). Visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy—an alternative for monitoring soil contamination by heavy metals. Journal of Hazardous Material, 265, 166–176.
Sposito, G., Lund, L. J., & Chang, A. C. (1982). Trace metal chemistry in arid-zone field soils amended with sewage sludge: I. Fractionation of Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb in solid phases. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 46, 260–264.
Thomas, G. W. (1996). Methods of soil analysis: chemical methods: soil pH and soil acidity (pp 475–490). Wisconsin: ASA/SSSA Madison.
Udelhoven, T., Emmerling, C., & Jarmer, T. (2003). Quantitative analysis of soil chemical properties with diffuse reflectance spectrometry and partial least-square regression: a feasibility study. Plant and Soil, 251(2), 319–329.
Viscarra Rossel, R. A. V. (2008). ParLeS: Software for chemometric analysis of spectroscopic data. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 90(1), 72–83.
Wang, J., Huang, C. P., Allen, H. E., Poesponegoro, I., Poesponegoro, H., & Takiyama, L. R. (1999). Effects of dissolved organic matter and pH on heavy metal uptake by sludge particulates exemplified by copper (II) and nickel (II): three-variable model. Water Environment Research, 71, 139–147.
Wang, J., Cui, L., Gao, W., Shi, T., Chen, Y., & Gao, Y. (2014). Prediction of low heavy metal concentrations in agricultural soils using visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma, 216, 1–9.
Winkelmann, K. H. (2005). On the applicability of imaging spectrometry for the detection and investigation of contaminated sites with particular consideration given to the detection of fuel hydrocarbon contaminants in soil. Dissertation, Brandenburg university of technology.
Wu, Y., Chen, J., Wu, X., Tian, Q., Ji, J., & Qin, Z. (2005). Possibilities of reflectance spectroscopy for assessment of contamination element in suburban soil. Applied Geochemistry, 20(6), 1051–1059.
Zhang, Z., Wen, J., & Zhao, D. (2010). Band selection method for retrieving soil lead content with hyperspectral remote sensing data. Proceeding (SPIE), earth resources and environmental remote sensing/GIS applications. Toulouse, France. p. 78311K-78311K-7.
Acknowledgements
This research was granted by Tarbiat Modares University, Grant Number IG-39713.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yousefi, G., Homaee, M. & Norouzi, A.A. Estimating soil heavy metals concentration at large scale using visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Environ Monit Assess 190, 513 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6898-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6898-6