Abstract
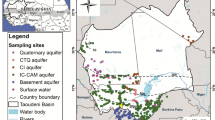
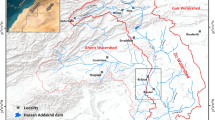
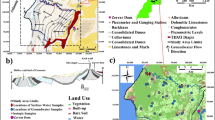
As many arid and semi-arid regions in the Mediterranean Basin, the Grombalia coastal aquifer (NE Tunisia) is affected by severe groundwater exploitation and contamination. Therefore, quality assessments are becoming increasingly important as the long-term protection of water resources is at stake. Multidisciplinary investigations, like the one presented in this paper, are particularly effective in identifying the different origins of mineralization within an aquifer and investigating the impact of anthropogenic activities on groundwater quality. An integrated assessment, focused on the combined use of geostatistical, geochemical and isotopic (δ18O, δ2H and 3H) tools, was performed in the Grombalia aquifer between February and March 2014. The overall goal was to study the main processes controlling aquifer salinization, with special focus to nitrate contamination. Results indicate a persisting deterioration of water quality over the whole basin except the south-eastern zone juxtaposing the recharge area of the aquifer. Nitrate contents exceed the drinking water standard (50 mg/l) in 70% of groundwater samples, mainly due to the excessive use of fertilizers and urban activities. Stable isotope measurements showed the contribution of modern rainwater to aquifer recharge and proved the presence of evaporation contributing to the salinity increase. Tritium values of groundwater samples suggested two hypotheses: the existence of mixture between old and recent water or/and the existence of two recharge periods of the aquifer, pre- and post-nuclear weapons test. Principal component analysis confirmed the geochemical interpretation, highlighting that water-rock interaction evaporation effect and intensive anthropogenic activities constitute the main processes controlling the regional groundwater mineralization.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid, K., Trabelsi, R., Zouari, K., & Abidi, I. (2009). Caractérisation hydrogéochimique de la nappe du Continental Intercalaire (sud tunisien)/Hydrogeochemical characterization of the Continental Intercalaire aquifer (southern Tunisia). Hydrological Sciences Journal, 54(3), 526–537. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.54.3.526
Baillargeon, S. (2005). Le krigeage : revue de la théorie et application à l’interpolation spatiale de données de précipitations. Maitrise en statistique pour l’obtention du grade de Maitre en sciences (pp. 20–21). Quebec: Faculté des études supérieures de l’Université Laval.
Ben Ayed, N. (1993). Evolution tectonique de l’avant-pays de la chaîne alpine de la Tunisie du début du Mésozoïque à l’Actuel. Thèse d’État Uni. Paris-11, Orsay, Publ. Office Nat. Mines Tunis.
Ben Hamouda, M. F., Tarhouni, J., Leduc, C., & Zouari, K. (2010). Understanding the origin of salinization of the Plio-quaternary eastern coastal aquifer of Cap Bon (Tunisia) using geochemical and isotope investigations. Environmental Earth Sciences, 63(5), 889–901.
Ben Moussa, A., & Zouari, K. (2011). Hydrochemical investigation of groundwater contamination in the Grombalia shallow aquifer, Cap Bon Peninsula, Tunisia: impact of irrigation with industrial waste water. INTECH Open Access Publisher, ISBN: 978-953-307-233-3, InTech.
Ben Salem, H. (1992). Contribution à la connaissance de la géologie du Cap Bon: stratigraphie, tectonique et sédimentologie. Thèse 3éme cycle, Géol. Univ. Tunis II.
Boettcher, J., Strebel, O., Voerkelius, S., & Schmidt, H. L. (1990). Using isotope fractionation of nitrate-nitrogen and nitrate-oxygen for evaluation of microbial denitrification in a sandy aquifer. Journal of Hydrology, 114(3–4), 413–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(90)90068-9
Castany, G. (1948). Les fossés d’effondrement de Tunisie, Géologie et hydrologie. Plaine de Grombalia et cuvettes de la Tunisie Orientale. 1er fasc. In: Ann. Mines. Géol. N°3, pp. 18–39.
Castany, G. (1968). Traité pratique des eaux souterraines. Ed Dunod, Paris, 2ème édition, p 471.
Charfi, S. (2015). Etude hydrogéologique, hydrochimique et isotopique du système aquifère de Grombalia, cap bon, Tunisie Nord-Orientale. Thèse d’état Uni. Sfax, Tunisie. p50.
Charfi, S., Zouari, K., Feki, S., & Mami, E. (2013). Study of variation in groundwater quality in a coastal aquifer in north-eastern Tunisia using multivariate factor analysis. Quaternary International, 302, 199–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2012.11.002
Chatfield, C., & Collins, A. J. (1980). Introduction to multivariate analysis (256 p). London: Chapman and Hall. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-3184-9
Chenini, I., Zghibi, A., & Kouzana, L. (2015). Hydrogeological investigations and groundwater vulnerability assessment and mapping for groundwater resource protection and management: state of the art and a case study. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 109, 11–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.05.008
Clark, I., & Fritz, P. (1997). Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. CRC Press, p. 328.
CRDA (2016) Commissariat Régional du Développement Agricole, carte d’occupation du sol de la plaine de Grombalia.
DGRE (1990–2015). General Direction of Water Ressources, annuaires d’exploitation des nappes phréatiques en Tunisie.
Dulinski, M., Rozanski, K., Kania, J., Karlikowska, J., Korczynski-Jackowicz, M., Witczak, S., Mochalski, P., Opoka, M., Sliwka, I., & Zuber, A. (2003). Groundwater dating with sulfur hexafluoride: methodology and field comparison with tritium and hydrodynamic methods. International symposium, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria, IAEA-CN-104/8.
Edmunds, W. M. (2009). Palaeoclimate and groundwater evolution in Africa-implications for adaptation and management. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 54(4), 781–792. https://doi.org/10.1623/hysj.54.4.781
Ennabli, M. (1980). Etude hydrogéologique des aquifères du Nord-Est de la Tunisie pour une gestion intégrée des ressources en eau. Thèse de Doctorat d’Etat. Nice, 570 p.
Fisher, R. S., & Mullican, W. F. (1997). Hydrochemical evolution of sodium-sulfate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the northern Chihuahuan Desert, Trans-Pecos, Texas, USA. Hydrogeology Journal, 5(2), 4–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100400050102
Gaaloul, N., Candela, L., Chebil, A., Soussi, A., & Tamoh, K. (2014). Groundwater flow simulation at the Grombalia phreatic aquifer (Cap Bon, Northeastern Tunisia). Desalination and Water Treatment, 52(10-12), 1997–2008. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.821026
Garcia, G. M., Hidalgo, M. D. V., & Blesa, M. A. (2001). Geochemistry of groundwater in the alluvial plain of Tucuman province, Argentina. Hydrogeology Journal, 9(6), 597–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-001-0166-4
Giordano, M. (2009). Global groundwater? Issues and solutions. Annual Review of Environment and Resources, 34(1), 153–178. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.environ.030308.100251
GWP. (2012). Global water partnership. Water demand. Management: The Mediterranean experience. Technical focus paper ISBN: 978–91–85321-88-9.
Hadj Sassi, M., Zouari, H., & Jallouli, C. (2006). Contribution de la gravimétrie et de la sismique réflexion pour une nouvelle interprétation géodynamique des fossés d’effondrement en Tunisie: exemple du fossé de Grombalia. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 338(11), 751–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2006.07.005
Hamza, M. H., Maâlej A., Ajmi, M., Added, A. (2010). Validity of the vulnerability methods DRASTIC and SI applied by GIS technique to the study of diffuse agricultural pollution in two phreatic aquifers of a semi-arid region (Northeast of Tunisia). AQUAmundi-Am01009, 57-64.
Journel, A., & Huijbregts, C. J. (1978). Mining geostatistics. New York: Academic Press.
Khan, R., & Jhariya, D. C. (2017). Groundwater quality assessment for drinking purpose in Raipur city, Chhattisgarh using water quality index and geographic information system. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 90(1), 69–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0665-0
Kihumba, A. M., Longo, J. N., & Vanclooster, M. (2016). Modelling nitrate pollution pressure using a multivariate statistical approach: the case of Kinshasa groundwater body, Democratic Republic of Congo. Hydrogeology Journal, 24(2), 425–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-015-1337-z
Koutsoyiannis, D., Kundzewicz, Z. W., Watkins, F., & Gardner, C. (2010). Something old, something new, something red, something blue. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 55(1), 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626660903525294
Machiwal, D., & Jha, M. K. (2015). Identifying sources of groundwater contamination in a hard-rock aquifer system using multivariate statistical analyses and GIS-based geostatistical modeling techniques. Journal of Hydrology: Regional Studies, 4, 80–110.
Maduabuchi, C., Faye, S., & Maloszewski, P. (2006). Isotope evidence of paleorecharge and paleoclimate in the deep confined aquifers of the Chad basin, NE Nigeria. Science of the Total Environment, 370(2-3), 467–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.08.015
Mann, W. B., Unterweger, M. P., & Coursey, B. M. (1982). Comments on the NBS tritiated-water standards and their use. The International Journal of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 33(5), 383–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-708X(82)90153-3
McLean, W., Jankowski, J., & Lavitt, N. (2000). Groundwater quality and sustainability in an alluvial aquifer, Australia. Groundwater, past achievements and future challenges (pp. 567–573). Rotterdam: A Balkema.
Mengis, M., Schif, S. L., Harris, M., English, M. C., Aravena, R., Elgood, R. J., & Maclean, A. (1999). Multiple geochemical and isotopic approaches for assessing ground water NO3 elimination in a riparian zone. Groundwater, 37(3), 448–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1999.tb01124.x
Ouhamdouch, S., Bahir, M., Carreira, P., Chkir, N., & Goumih, A. (2016). Climate change impact on Hauterivian aquifer of Essaouira basin (Morocco). Larhyss Journal ISSN, 1112-3680(25), 269–283.
Paniconi, C., Khlaifi, I., Lecca, G., Agiacomelli, A., Tarhouni, J. (2001). Modeling and analysis of seawater intrusion in the coastal aquifer of eastern cap-bon, Tunisia. Transport in Porous Media 43:3–28. Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands.
Penna, D., Stenni, B., Wrede, S., Bogaard, T. A., Gobbi, A., Borga, M., Fischer, B. M. C., Bonazza, M., & Charova, Z. (2010). On the reproducibility and repeatability of laser absorption spectroscopy measurements for [delta] 2H and [delta] 18O isotopic analysis. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 14(8), 1551–1566. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-14-1551-2010
Piper, A. M. (1944). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Transactions, American Geophysical Union, 25(6), 914–923. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR025i006p00914
Re, V. (2015). Incorporating the social dimension into hydrogeochemical investigations for rural development: the Bir Al-Nas approach for socio-hydrogeology. Hydrogeology Journal, 23(7), 1293–1304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-015-1284-8
Re, V., Sacchi, E., Kammoun, S., Tringali, C., Trabelsi, R., Zouari, K., & Daniele, S. (2017). Integrated socio-hydrogeological approach to tackle nitrate contamination in groundwater resources. The case of Grombalia Basin (Tunisia). Science of the Total Environment, 593–594(2017), 664–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.151
Re, V., Sacchi, E., Mas-Pla, J., Menció, A., & El Amrani, N. (2014). Identifying the effects of human pressure on groundwater quality to support water management strategies in coastal regions: a multi-tracer and statistical approach (Bou-Areg region, Morocco). Science of the Total Environment, 500, 211–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.115
Re, V., & Zuppi, G. M. (2011). Influence of precipitation and deep saline groundwater on the hydrological systems of Mediterranean coastal plains: a general overview. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 56(6), 966–980. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2011.597355
Rozanski, K., Araguás-Araguás, L., & Gonfiantini, R. (1993). Isotopic patterns inmodern global precipitation. Geophysical Monograph, 78, 1–36.
Schoeller, H. (1939). Le quaternaire du Golfe ancien de Grombalia. Tunisie Actes Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux, 91, 14–30.
Sebei, A., Chaabani, F., Souissi, F., & Abdeljaoued, S. (2004). Hydrologie et qualité des eaux de la nappe de Grombalia (Tunisie nord-orientale). Sécheresse, 15(2), 159–166.
Selek, Z., & Yetis, A. D. (2017). Assessment of nitrate contamination in a transnational groundwater basin: a case study in the Ceylanpinar Plain, Turkey. Environment and Earth Science, 76(20), 698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7044-4
Siebert, S., Burke, J., Faures, J. M., Frenken, K., Hoogeveen, P. D., Döll, P., & Portmann, F. T. (2010). Groundwater use for irrigation—a global inventory. Hydrology and Earth System Science, 14(10), 1863–1880. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-14-1863-2010
Spalding, R. F., & Exner, M. E. (1993). Occurrence of nitrate in groundwaterea review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 22(3), 392–402. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1993.00472425002200030002x
Spruill, T. B., Showers, W. J., & Howe, S. S. (2002). Application of classification-tree methods to identify nitrate sources in ground water. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31(5), 1538–1549. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2002.1538
Stigter, T. Y., Dill, A. C., Ribeiro, L., & Reis, E. (2006). Impact of the shift from groundwater to surface water irrigation on aquifer dynamics and hydrochemistry in a semi-arid region in the south of Portugal. Agricultural Water Management, 85(1), 121–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2006.04.004
Subramani, T., Elango, L., & Damodarasamy, S. R. (2005). Groundwater quality and its suitability for drinking and agricultural use in Chithar River Basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Environmental Geology, 47(8), 1099–1110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-1243-0
Suthar, S., Bishnoi, P., Singh, S., Mutiyar, P. K., Nema, A. K., & Patil, N. S. (2009). Nitrate contamination in groundwater of some rural areas of Rajasthan, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171(1), 189–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.111
Taylor, C.B. (1977). Tritium enrichment of environmental waters by electrolysis: development of cathodes exhibiting high isotopic separation and precise measurements and Applications. High Tatras, Czechoslovakia, October 1975, Bratislava, 133–140 pp.
Tlili-Zrelli, B., Hamzaoui-Azaza, F., Gueddari, M., & Bouhlila, R. (2013). Geochemistry and quality assessment of groundwater using graphical and multivariate statistical methods. A case study: Grombalia phreatic aquifer (northeastern Tunisia). Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6(9), 3545–3561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-012-0617-3
Tringali, C., Re, V., Siciliano, G., Chkir, N., Tuci, C., Zouari, K. (2017). Insights and participatory actions driven by a socio-hydrogeological approach for groundwater management: the Grombalia Basin case study (Tunisia). Hydrogeology Journal. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1542-z).
UNESCO-ISARM. (2004). United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization -Internationally Shared Aquifer Resources Management Managing shared aquifer resources in Africa. In: B. Appelgren (Ed.) Paris: UNESCO IHP-VI, Series in Groundwater no 8.
Van der Gun, J. (2012). Groundwater and global change: Trends, Opportunities and Challenges. UNESCO Side Publication Series 01. ISBN 978-92-3-001049-2.
WHO. (2011). World Health Organization, Guidelines for drinking-water quality, fourth edition. 564p. ISBN: 978 92 4 154815 1.
Yuan, L., Zonghe, P., & Tianming, H. (2012). Integrated assessment on groundwater nitrate by unsaturated zone probing and aquifer sampling with environmental tracers. Environmental Pollution, 171, 226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.07.027
Zghibi, A., Tarhouni, J., & Zouhri, L. (2013). Assessment of seawater intrusion and nitrate contamination on the groundwater quality in the Korba coastal plain of Cap-Bon (North-east of Tunisia). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 87, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2013.07.009
Zouari, K., Aranyossy, J.F., Mamou, A., & Fontes, J.Ch. (1985). Etude isotopique et géochimique des mouvements et de l’évolution des solutions de la zone aérée des sols sous climat semi-aride (Sud tunisien). In: Stable and radiactive isotopes in the study of the unsaturated soil zone (pp.121–144). IAEA-TECDOC-357, Vienna.
Zouari, K., Re, V., Sacchi, E., Trabelsi, R., & Kammoun, S. (2015). The use of nitrate isotopes to assess agricultural and domestic impacts on groundwater quality in rural zones. The example of Grombalia basin (Tunisia). Vienna: International Symposium on Isotope Hydrology: Revisiting Foundations and Exploring Frontiers.
Zuppi, G. M. (2008). The groundwater challenge. In C. Clini, I. Musu, & M. L. Gullino (Eds.), Sustainable development and environmental management Experience and case studies. DORDRECHT: Springer.
Acknowledgements
This research is partially supported by a Marie Curie Fellowship awarded to Dr. Viviana Re within the EU 7th FP for Research and Technological Development (FP7-PEOPLE-2012-IOF n.327287). The authors gratefully acknowledge the contribution of the staff members of the Regional Commissariat for Agricultural Development (CRDA) of Nabeul for their help during fieldwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kammoun, S., Trabelsi, R., Re, V. et al. Groundwater quality assessment in semi-arid regions using integrated approaches: the case of Grombalia aquifer (NE Tunisia). Environ Monit Assess 190, 87 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6469-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6469-x