Abstract
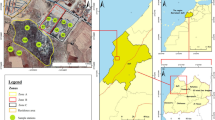
The present study was conducted in one of the most densely cultivated area of Al-Qassim region in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia to (i) monitor trace metal (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn) contents in surface and subsurface soils, (ii) assess the pollution and potential ecological risk levels of trace metals, and (iii) identify trace metal sources using enrichment factor (EF), correlation matrix, and principal component analysis (PCA). The pollution levels of the analyzed trace metals calculated by the geoaccumulation index (I geo) and contamination factor (C f) suggested that the soils were highly contaminated with Cd and moderately contaminated with Pb. Based on the average values of EF, soil samples were found to present extremely high enrichment for Cd, significant enrichment for Pb, moderate enrichment for Zn, and deficient to minimal enrichment for other trace metals. Among the analyzed trace metals, a very high ecological risk was observed only in the case of Cd at some sampling sites. Meanwhile, other investigated trace metals had a low ecological risk. The results of PCA combined with correlation matrix suggested that Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, Cr Ni, Cu, and Co represent natural abundance in soil, but Cd, Pb, and Cu are of anthropogenic inputs, mainly due to agrochemical and fertilizer applications. It could be generally concluded that the obtained results can be useful for assessing and conducting a future program for trace metal monitoring in agricultural areas of Saudi Arabia.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaslou, H., Martin, F., Abtahi, A., & Moore, F. (2014). Trace element concentrations and background values in the arid soils of Hormozgan Province of southern Iran. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 60, 1125–1143.
Almasoud, F. I., Usman, A. R., & Al-Farraj, A. S. (2015). Heavy metals in the soils of the Arabian Gulf coast affected by industrial activities: analysis and assessment using enrichment factor and multivariate analysis. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 8, 1691–1703.
Al-Salamah, I. S., & Nassar, I. N. (2009). Trends in drinking water quality for some wells in Qassim, Saudi Arabia, 1997–2009. Journal of Applied Sciences, 9, 3555–3561.
Al-Wabel, M. I., El-Saeid, M. H., Al-Rurki, A. M., & Abdel-Nasser, G. (2011). Monitoring of pesticide residues in Saudi Arabia agricultural soils. Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 5, 269–278.
Al-Wabel, M., El-Saeid, M. H., El-Naggar, A. H., Al-Romian, A., Osman, K., Elnazi, K., & Sallam, A. S. (2016). Spatial distribution of pesticide residues in the groundwater of a condensed agricultural area. Arabian Journal of Geosciences. doi:10.1007/s12517-015-2122-y.
Atafar, Z., Mesdaghinia, A., Nouri, J., Homaee, M., Yunesian, M., Ahmadimoghaddam, M., & Mahvi, A. H. (2010). Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal concentration. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160, 83–89.
Azeez, J. O., Mesele, S. A., Sarumi, B. O., Ogundele, J. A., Uponi, A. O., & Hassan, A. O. (2014). Soil metal pollution as a function of traffic density and distance from road in emerging cities: a case study of Abeokuta, southwestern Nigeria. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 60, 275–295.
Bai, J., Xiao, R., Cui, B., Zhang, K., Wang, Q., Liu, X., Gao, H., & Huang, L. (2011a). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from the young and old reclaimed regions in the Pearl River estuary, South China. Environmental Pollution, 159, 817–824.
Bai, J., Xiao, R., Gong, A., Gao, H., & Huang, L. (2011b). Assessment of heavy metal contamination of surface soils from typical paddy terrace wetlands on the Yunnan Plateau of China. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 36, 447–450.
Bai, J., Yang, Z., Cui, B., Gao, H., & Ding, Q. (2010). Some heavy metals distribution in wetland soils under different land use types along a typical plateau lake, China. Soil & Tillage Research, 106, 344–348.
Bai, J., Zhao, Q., Lu, Q., Wanga, J., & Reddy, K. R. (2015). Effects of freshwater input on trace element pollution in salt marsh soils of a typical coastal estuary, China. Journal of Hydrology, 520, 186–192.
Balkhair, K. S., & Ashraf, M. A. (2016). Field accumulation risks of heavy metals in soil and vegetable crop irrigated with sewage water in western region of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 23, S32–S44.
Bao, Z., Wu, W., Liu, H., Chen, H., & Yin, S. (2014). Impact of long-term irrigation with sewage on heavy metals in soils, crops, and groundwater—a case study in Beijing. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 23, 309–318.
Bortey-Sam, N., Nakayama, S. M. M., Akoto, O., Ikenaka, Y., Baidoo, E., Mizukawa, H., & Ishizuka, M. (2015). Ecological risk of heavy metals and a metalloid in agricultural soils in Tarkwa, Ghana. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12, 11448–11465.
Effendi, H., Kawaroe, M., Mursalin, & Lestari, D. F. (2016). Ecological risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface sediment of Mahakam Delta, East Kalimantan. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 33, 574–582.
El-Mergawi, R. A., & Al-Redhaiman, K. (2010). Effect of organic and conventional production practices on antioxidant activity, antioxidant constituents and nutritional value of tomatoes and carrots in Saudi Arabia markets. Journal of Food, Agriculture and Environment, 8, 253–258.
Gan, J. L., Jia, X. P., Lin, Q., Li, C. H., Wang, Z. H., Zhou, G. J., Wang, X. P., Cai, W. G., & Lu, X. Y. (2000). A primary study on ecological risk caused by the heavy metals in coastal sediments. Journal of Fisheries of China, 24, 533–538.
Gee, G.W., & Bauder, J.W. (1994). Particle-size analysis. In A. Klute (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 1, 3rd edition. Physical and mineralogical methods. Madison: SSSA and ASA.
Gupta, N., Khan, D. K., & Santra, S. C. (2008). An assessment of heavy metal contamination in vegetables grown in wastewater-irrigated areas of Titagarh, West Bengal, India. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80, 115–118.
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14, 975–1001.
He, Q. B., & Singh, B. R. (1994a). Crop uptake of cadmium from phosphorus fertilizers: II. Relationship with extractable soil cadmium. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 74, 267–280.
He, Q. P., & Singh, B. R. (1994b). Crop uptake of cadmium from phosphorus fertilizers: I. Yield and cadmium content. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 74, 251–265.
Hernandez, L., Probst, A., Probst, J. L., & Ulrich, E. (2003). Heavy metal distribution in some French forest soils: evidence for atmosphere contamination. Science of the Total Environment, 312, 195–210.
Hu, Y., Liu, X., Bai, J., Shih, K., Zeng, E. Y., & Cheng, H. (2013). Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 6150–6159.
Ju, X. T., Kou, C. L., Christie, P., Dou, Z. X., & Zhang, F. S. (2007). Changes in the soil environment from excessive application of fertilizers and manures to two contrasting intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environmental Pollution, 145, 497–506.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants (Fourth ed.). London: Taylor &Francis.
Kelepertzis, E. (2014). Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Mediterranean: insights from Argolida basin, Peloponnese, Greece. Geoderma, 221-222, 82–90.
Khan, K., Lu, Y., Khan, H., Ishtiaq, M., Khan, S., Waqas, M., Wei, L., & Wang, T. (2013). Heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops and their health risks in Swat District, northern Pakistan. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 58, 449–458.
Lindsay, W. L. (1979). Chemical equilibrium in soils. NewYork: Wiley Interscience.
Lu, Q., Bai, J., Gao, Z., Zhao, Q., & Wang, J. (2016). Spatial and seasonal distribution and risk assessments for metals in a Tamarix chinensis wetland, China. Wetlands, 36, S125–S136.
Mapanda, F., Mangwayana, E. N., Nyamangara, J., & Giller, K. E. (2005). The effect of long-term irrigation using wastewater on heavy metal contents of soils under vegetables in Harare, Zimbabwe. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 107, 151–165.
Mar, S. S., Okazaki, M., & Motobayashi, T. (2012). The influence of phosphate fertilizer application levels and cultivars on cadmium uptake by Komatsuna (Brassica rapa L. var. perviridis). Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 58, 492–502.
Mico, C., Peris, M., Sanchez, J., & Recatala, L. (2006a). Heavy metal content of agricultural soils in a Mediterranean semiarid area: the Segura River Valley (Alicante, Spain). Spanish Journal of Agricultural Research, 4, 363–372.
Mico, C., Recatala, L., Peris, M., & Sanchez, J. (2006b). Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere, 65, 863–872.
Muller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins-Veran-derungen seitt. Umschan, 79, 778–783.
Naveedullah., Hashmi, M. Z., Yu, C., Shen, H., Duan, D., Shen, C., Lou, L., & Chen, Y. (2013). Risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in agricultural soils of Siling Reservoir Watershed in Zhejiang Province, China. BioMed Research International, 2013, Article ID 290306, 10 pages.
Nazzal, Y., Howari, F. M., Jafri, M. K., Naeem, M., & Ghrefat, H. (2015). Risk ssessment through evaluation of potentially toxic metals in the surface soils of the Qassim area, Central Saudi Arabia. Italian Journal of Geosciences, 135, 210–216.
Nelson D. W., & Sommers L. E. (1996). Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In Methods of soil analysis, part 3. Chemical methods (pp. 961–1009). Madison: SSSA. Book ser. N°5.
Oyedele, D. J., Asonugho, C., & Awotoye, O. O. (2006). Heavy metals in soil and accumulation by edible vegetables after phosphate fertilizer application. Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 5, 1446–1453.
Reeve, J. R., Endelman, J. B., Miller, B. E., & Hole, D. J. (2012). Residual effects of compost on soil quality and dryland wheat yield sixteen years after compost application. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 76, 278–285.
Roberts, T. L. (2014). Cadmium and phosphorous fertilizers: the issues and the science. Procedia Engineering, 83, 52–59.
Sparks, D. L. (1996). Methods of soil analysis part 3—chemical methods. Madison: SSSA, American Society of Agronomy.
StatSoft Inc. (1992). Statistica for Windows (computer program manual). Tulsa: StatSoft, Inc.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–627.
Tabatabai, M. A. (1996). Sulfur. In D. L. Sparks, A. L. Page, P. A. Helmke, & R. H. Loeppert (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis part 3—chemical methods. Madison: SSSA, American Society of Agronomy.
Toth, G., Hermann, T., Da Silva, M. R., & Montanarella, L. (2016). Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environment International, 88, 299–309.
Turekian, K. K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Geological Society of America Bulletin Journal, 72, 175–192.
USEPA (1994). Method 3051, microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils and oils. In Test methods for evaluating solid waste, physical/chemical methods, 3rd ed. U.S.
VROM. (2001). The new Dutch list. Soil quality standards, Netherlands Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and Environment. Department of Soil Protection, The Hague.
Wentz, D. (2001). Salt tolerance of plants. Agri-facts—practical information for Alberta’s agriculture industry. Agdex 518–17.
Wu, J., Song, J., Li, W., & Zheng, M. (2016). The accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural land and the associated potential ecological risks in Shenzhen, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 1428–1440.
Xiao, R., Bai, J., Lu, Q., Zhao, Q., Gao, Z., Wen, X., & Liu, X. (2015). Fractionation, transfer, and ecological risks of heavy metals in riparian and ditch wetlands across a 100-year chronosequence of reclamation in an estuary of China. Science of the Total Environment, 517, 66–75.
Xu, Y. G., Yu, W. T., Ma, Q., & Zhou, H. (2015). Potential risk of cadmium in a soil-plant system as a result of long-term (10 years) pig manure application. Plant, Soil and Environment, 61, 352–357.
Ye, C., Li, S., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, Q. (2011). Assessing soil heavy metal pollution in the water-level-fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Journal of Hazard Materials, 191, 366–372.
Zoffoli, H. J. O., Amaral-Sobrinho, N. M., Zonta, E., Luisi, M. V., Marcon, G., & Tolon-Becerra, A. (2013). Inputs of heavy metals due to agrochemical use in tobacco fields in Brazil’s Southern Region. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185, 2423–2437.
Acknowledgements
The investigators of research project no. ALC012 thank the Promising Research Center in Biological Control and Agricultural Information, Al-Qassim University, Buraydah, KSA, for providing funding and unlimited support and help. The authors are also grateful to the Department of Soil Science, College of Food, and Agricultural Sciences, King Saud University, for providing research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Wabel, M.I., Sallam, A.EA.S., Usman, A. et al. Trace metal levels, sources, and ecological risk assessment in a densely agricultural area from Saudi Arabia. Environ Monit Assess 189, 252 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5919-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-5919-1