Abstract
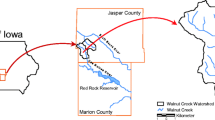
The surface waters of Rathbun Lake watershed in southern Iowa are impacted by agricultural sources of sediments and nutrients, including phosphorus (P). Because stream sediments often play an important role in regulating P concentrations in stream water, we investigated sediment–water column P relationships in four creeks within the watershed and then evaluated the relationship between sediment properties and indicators of the risk of P loss. Based on Mehlich-3-extractable P (17 to 68 mg kg−1) and degree of P saturation (2 to 12 %), stream bank and bed sediments at the four sites were unlikely to serve as major sources of P. However, equilibrium P concentrations, which ranged from 0.02 to 0.12 mg L−1, indicated that bed sediments could release P to the water column depending on dissolved P (DP) concentrations in the stream water and the time of year. The likelihood of P desorption from the sediments increased with increasing pH (r = 0.92, p < 0.01) and sand content (r = 0.78, p < 0.05), but decreased with clay content (r = −0.72, p < 0.05) and iron (Fe) (r = −0.93, p < 0.001) associated with organic matter. From these results, we speculate that changes in land use within the riparian areas may, at least initially, have little effect on P concentrations in the streams. Low concentrations of DP relative to total P (TP) in these streams, however, suggest that P loads to Rathbun Lake can be reduced if P inputs from eroded bank sediments are controlled.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, R. B., Smith, R. A., Schwarz, G. E., Boyer, E. W., Nolan, J. V., & Brakebill, J. W. (2008). Differences in phosphorus and nitrogen delivery to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River Basin. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 822–830.
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington: American Public Health Association.
Balmer, M. (2015). Rathbun Lake and watershed 2014 monitoring summary. http://rathbunlandwateralliance.blogspot.com/p/technical-reports-maps.html. Accessed 15 June 2016.
Bear, D. A., Russell, J. R., Tufekcioglu, M., Isenhart, T. M., Morrical, D. G., & Kovar, J. L. (2012). Stocking rate and riparian vegetation effects on physical characteristics of riparian zones of Midwestern pastures. Range Ecology and Management, 65, 119–128.
Becher, K. D., Kalkhoff, S. J., Schnoebelen, D. J., Barnes, K. K., & Miller, V. E. (2001). Water-quality assessment of the eastern Iowa basins—nitrogen, phosphorus, suspended sediment, and organic carbon in surface water, 1996–98 (Report 01–4175, U.S. Geological Survey). http://pubs.usgs.gov/wri/wri014175/pdf/wri01-4175.pdf. Accessed 25 June 2016.
Braster, M., Jacobson, T., & Sitzmann, V. (2001). Assessment and management strategies for the Rathbun Lake watershed. http://www.iowadnr.gov/Portals/idnr/uploads/water/watershed/files/rathbunwmp1.pdf. Accessed 15 June 2016.
Carpenter, S. R., Caraco, N. F., Correll, D. L., Howarth, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Smith, V. H. (1998). Nonpoint pollution of surface waters with phosphorus and nitrogen. Ecological Applications, 8, 559–568.
Correll, D. L. (1998). The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: a review. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27, 261–266.
Crosland, A. R., Zhao, F. J., McGrath, S. P., & Lane, P. W. (1995). Comparison of aqua regia digestion with sodium carbonate fusion for the determination of total phosphorus in soils by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy ICP. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 26, 1357–1368.
Djodjic, F., Börling, K., & Bergström, L. (2004). Phosphorus leaching in relation to soil type and soil phosphorus content. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 678–684.
Downing, J. A., & Kopaska, J. (2000). Diagnostic study of Rock Creek Lake and its watershed: recommendations for remediation. Des Moines: Iowa Department of Natural Resources.
Ekka, S. A., Haggard, B. E., Matlock, M. D., & Chaubey, I. (2006). Dissolved phosphorus concentrations and sediment interactions in effluent-dominated Ozark streams. Ecological Engineering, 26, 375–391.
Essington, M. E. (2003). Soil and water chemistry: an integrative approach. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Gee, G. W., & Bauder, J. W. (1986). Particle-size analysis. In A. Klute (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis, part 1, 2 nd edition., Agronomy Monograph 9 (pp. 383–411). Madison: ASA and SSSA.
Griffith, G. E., Omernik, J. M., Wilton, T. F., & Pierson, S. M. (1994). Ecoregions and subregions of Iowa—a framework for water quality assessment and management. Journal of the Iowa Academy of Sciences, 101, 5–13.
Haggard, B. E., & Sharpley, A. N. (2007). Phosphorus transport in stream: processes and modeling considerations. In D. Radcliffe & M. Cabrera (Eds.), Modeling phosphorus in the environment (pp. 105–130). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Haggard, B. E., Stanley, E. H., & Hyler, R. (1999). Sediment-phosphorus relationships in three north central Oklahoma streams. Transactions of American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 42, 1709–1714.
Haggard, B. E., Ekka, S. A., Matlock, M. D., & Chaubey, I. (2004). Phosphate equilibrium between stream sediments and water: potential effect of chemical amendments. Transactions of American Society of Agricultural Engineers, 47, 1113–1118.
Haggard, B. E., Smith, D. R., & Brye, K. R. (2007). Variations in stream water and sediment phosphorus among select Ozark catchments. Journal of Environmental Quality, 36, 1725–1734.
Hatfield, J. L., McMullen, L. D., & Jones, C. S. (2009). Nitrate-nitrogen patterns in the Raccoon River Basin related to agricultural practices. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 64, 190–199.
Hongthanat, N., Kovar, J. L., & Thompson, M. L. (2011). Sorption indices to estimate risk of soil phosphorus loss in the Rathbun Lake watershed, Iowa. Soil Science, 176, 237–244.
House, W. A., & Denison, F. H. (2000). Factors influencing the measurement of equilibrium phosphorus concentrations in river sediments. Water Research, 34, 1187–1200.
Ige, D. V., Akinremi, O. O., & Flaten, D. N. (2005). Environmental index for estimating the risk of phosphorus loss in calcareous soils of Manitoba. Journal of Environmental Quality, 34, 1944–1951.
Iowa Department of Natural Resources (IDNR). (2015a). Iowa’s Section 303(d) impaired waters listings. http://www.iowadnr.gov/Environment/WaterQuality/WaterMonitoring/ImpairedWaters.aspx. Accessed 15 June 2016.
Iowa Department of Natural Resources (IDNR). (2015b). Iowa’s STORET/WQX database. https://programs.iowadnr.gov/iastoret/Default.aspx. Accessed 15 June 2016.
Iowa Department of Natural Resources (IDNR). (2015c). Stream nutrient criteria to protect aquatic life. http://www.iowadnr.gov/Environmental-Protection/Water-Quality/Water-Quality-Standards Accessed 15 June 2016.
Jacobson, L. M., David, M. B., & Drinkwater, L. E. (2011). A spatial analysis of phosphorus in the Mississippi River basin. Journal of Environmental Quality, 40, 931–941.
Jarvie, H. P., Jürgens, M. D., Williams, R. J., Neal, C., Davies, J. J. L., Barrett, C., & White, J. (2005). Role of river bed sediments as sources and sinks of phosphorus across two major eutrophic UK river basins: the Hampshire Avon and Herefordshire Wye. Journal of Hydrology, 304, 51–74.
Jarvie, H. P., Sharpley, A. N., Withers, P. J. A., Scott, J. T., Haggard, B. E., & Neal, C. (2013). Phosphorus mitigation to control river eutrophication: murky waters, inconvenient truths and ‘post-normal’ science. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42, 295–304.
Jaynes, D. B., Hatfield, J. L., & Meek, D. W. (1999). Water quality in Walnut Creek watershed: herbicides and nitrate in surface waters. Journal of Environmental Quality, 28, 45–59.
Kleinman, P. J. A., & Sharpley, A. N. (2002). Estimating phosphorus sorption saturation from Mehlich-3 data. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 33, 1825–1839.
Koski-Vähälä, J., & Hartikainen, H. (2001). Assessment of the risk of phosphorus loading due to resuspended sediment. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 960–966.
Laubel, A., Kronvang, B., Hald, A. B., & Jensen, C. (2003). Hydro-morphological and biological factors influencing sediment and phosphorus loss via bank erosion in small lowland rural streams in Denmark. Hydrologic Processes, 17, 3443–3463.
Loeppert, R. L., & Inskeep, W. P. (1996). Iron. In D. L. Sparks (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis, part 3, SSSA book series 5 (pp. 639–664). Madison: ASA and SSSA.
McDaniel, M. D., David, M. B., & Royer, T. V. (2009). Relationships between benthic sediments and water column phosphorus in Illinois streams. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38, 607–617.
McDowell, R. W., & Sharpley, A. N. (2001). A comparison of fluvial sediment phosphorus (P) chemistry in relation to location and potential to influence stream P concentrations. Aquatic Geochemistry, 7, 255–265.
McDowell, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., & Folmar, G. (2003). Modification of phosphorus export from an eastern USA catchment by fluvial sediment and phosphorus inputs. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 99, 187–199.
Mehlich, A. (1984). Mehlich 3 soil extractant: a modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 15, 1409–1416.
Murphy, J., & Riley, J. R. (1962). A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27, 31–36.
Nair, V. D., Portier, K. M., Graetz, D. A., & Walker, M. L. (2004). An environmental threshold for degree of phosphorus saturation in sandy soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 107–113.
Nellesen, S. L., Kovar, J. L., Haan, M. M., & Russell, J. R. (2011). Grazing management effects on stream bank erosion and phosphorus delivery to a pasture stream. Canadian Journal of Soil Science, 91, 385–395.
Nelson, D. W., & Sommers, L. E. (1982). Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. In A. L. Page (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis, part 2, 2 nd edition, agronomy monograph 9 (pp. 539–580). Madison: ASA and SSSA.
Pant, H. K., & Reddy, K. R. (2001). Phosphorus sorption characteristics of estuarine sediments under different redox conditions. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 1474–1480.
Patrick, W. H., & Khalid, R. A. (1974). Phosphate release and sorption by soils and sediments: effect of aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Science, 186, 53–55.
Pierzynski, G. M., Sims, J. T., & Vance, G. F. (2005). Soils and environmental quality (3rd ed.). Boca Raton: Taylor and Francis.
Pote, D. H., & Daniel, T. C. (2009). Total phosphorus and total dissolved phosphorus in water samples. In J. L. Kovar & G. M. Pierzynski (Eds.), Methods of phosphorus analysis for soils, sediments, residuals, and waters, 2 nd edition (Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin 408, pp. 112–116). Blacksburg: Virginia Polytechnic University.
Reddy, K. R., & DeLaune, R. D. (2008). Biogeochemistry of wetlands: science and applications. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Reddy, K. R., O’Connor, G. A., & Gale, P. M. (1998). Phosphorus sorption capacities of wetland soils and stream sediments impacted by dairy effluent. Journal of Environmental Quality, 27, 438–447.
SAS Institute. (2003). SAS 9.1 for Windows, Version 9.1.. Cary: SAS Institute, Inc.
Schilling, K. E., Isenhart, T. M., Palmer, J. A., Wolter, C. F., & Spooner, J. (2011). Impacts of land-cover change on suspended sediment transport in two agricultural watersheds. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 47, 672–686.
Schoumans, O. F. (2009). Determination of the degree of phosphate saturation in noncalcareous soils. In J. L. Kovar & G. M. Pierzynski (Eds.), Methods of phosphorus analysis for soils, sediments, residuals, and waters, 2 nd edition (Southern Cooperative Series Bulletin 408, pp. 29–32). Blacksburg: Virginia Polytechnic University.
Sharpley, A. N., Daniel, T., Sims, T., Lemunyon, J., Stevens, R., & Parry, R. (2003). USDA-ARS Report 149. Washington: U.S. Government Printing Office. Agricultural phosphorus and eutrophication, 2nd edition.
Sharpley, A., Jarvie, H. P., Buda, A., May, L., Spears, B., & Kleinman, P. (2013). Phosphorus legacy: Overcoming the effects of past management practices to mitigate future water quality impairment. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42, 1308–1326.
Sims, J. T., Maguire, R. O., Leytem, A. B., Gartley, K. L., & Pautler, M. C. (2002). Evaluation of Mehlich 3 as an agri-environmental soil phosphorus test for the Mid-Atlantic United States of America. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 66, 2016–2032.
Taylor, A. W., & Kunishi, H. M. (1971). Phosphate equilibria on stream sediment and soil in a watershed draining an agricultural region. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 19, 827–831.
Tomer, M. D., Moorman, T. B., & Rossi, C. G. (2008). Assessment of the Iowa River’s South Fork watershed: part 1. Water quality. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 63(6), 360–370.
Tomer, M. D., Wilson, C. G., Moorman, T. B., Cole, K. J., Heer, D., & Isenhart, T. M. (2010). Source-pathway separation of multiple contaminants during a rainfall-runoff event in an artificially drained agricultural watershed. Journal of Environmental Quality, 39, 882–895.
Tufekcioglu, M., Schultz, R. C., Isenhart, T. M., Russell, J. R., Kovar, J. L., & Bear, D. A. (2012). Stream bank erosion as a source of sediment and phosphorus in grazed pastures of the Rathbun Lake Watershed in southern Iowa, USA. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 67, 545–555.
U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE). (2007). 2006 annual water quality program report—Kansas city district. Kansas City: USACE.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). (2003). Strategy for water quality standards and criteria: Setting priorities to strengthen the foundation for protecting and restoring the nation’s waters, EPA-823-R-03-010. Washington: USEPA.
Zaimes, G. N., Schultz, R. C., & Isenhart, T. M. (2004). Stream bank erosion adjacent to riparian forest buffers, row-crop fields, and continuously-grazed pastures along Bear Creek in central Iowa. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 59, 19–27.
Zaimes, G. N., Schultz, R. C., & Isenhart, T. M. (2008). Streambank soil and phosphorus losses under different riparian land-uses in Iowa. Journal of American Water Resources Association, 44, 935–947.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Douglas Bear, Mustafa Tufekcioglu, Jay Berkey, and Teresita Chua for technical support. We also thank the USDA Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service 406 Program and the Leopold Center for Sustainable Agriculture at Iowa State University for providing financial support. Mention of trade names does not imply recommendation or endorsement by Iowa State University or the USDA Agricultural Research Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hongthanat, N., Kovar, J.L., Thompson, M.L. et al. Phosphorus source—sink relationships of stream sediments in the Rathbun Lake watershed in southern Iowa, USA. Environ Monit Assess 188, 453 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5437-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5437-6