Abstract
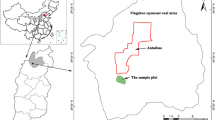
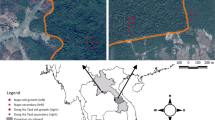
Afforestation of native tree species is often recommended for ecological restoration in mining areas, but the understanding of the ecological processes of restored vegetation is quite limited. In order to provide insight of the ecological processes of restored vegetation, in this study, we investigate the development of the population structure and spatial distribution patterns of restored Robinia pseudoacacia (ROPS) and Pinus tabuliformis (PITA) mixed forests during the 17 years of the mine spoil period of the Pingshuo opencast mine, Shanxi Province, China. After a 17-year succession, apart from the two planted species, Ulmus pumila (ULPU), as an invasive species, settled in the plot along with a large number of small diameter at breast height (DBH) size. In total, there are 10,062 living individual plants, much more than that at the plantation (5105), and ROPS had become the dominant species with a section area with a breast height of 9.40 m2 hm−2 and a mean DBH of 6.72 cm, much higher than both PITA and ULPU. The DBH size classes of all the total species showed inverted J-shaped distributions, which may have been a result of the large number of small regenerated ULPU trees. The DBH size classes of both ROPS and PITA showed peak-type structures with individuals mainly gathering in the moderate DBH size class, indicating a relatively healthy DBH size class structure. Meanwhile, invasive ULPU were distributed in a clear L shape, concentrating on the small DBH size class, indicating a relatively low survival rate for adult trees. Both ROPS and PITA species survival in the plantation showed uniform and aggregated distribution at small scales and random with scales increasing. ULPU showed a strong aggregation at small scales as well as random with scales increasing. Both the population structure and spatial distribution indicated that ROPS dominates and will continue to dominate the community in the future succession, which should be continuously monitored.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, Z. K. (2001). Land reclamation and ecological restoration in industrial and mining area. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press.
Bai, Z. K., Zhao, J. K., Li, J. C., Wang, W. Y., Lu, C. E., Ding, X. Q., Chai, S. J., & Chen, J. J. (1999). Ecosystem damage in a large opencast coal mine—a case study on Pingshuo surface coal mine, China (in Chinese). Acta Ecologica Sinica, 19, 870–875.
Bai, Z. K., Zhao, J. K., Wang, Z. G., Li, J. C., Lu, C. E., Wang, W. Y., & Zhang, L. C. (2003). Abandoned land reclamation and ecological reconstruction on strip mining area on Loess Plateau (1986∼2001) (in Chinese). Energy of Environmental Protection, 17(1), 13–16.
Benayas, J. M. R., Newton, A. C., Diaz, A., & Bullock, J. M. (2009). Enhancement of biodiversity and ecosystem services by ecological restoration: a meta-analysis. Science, 325, 1121–1124.
Cao, Q. G., Zhang, G. P., Niu, L. L., & Yang, W. W. (2007). The analysis and research of artificial ROPS’s physiological and ecological characteristics in Loess Plateau in the west of Shanxi (in Chinese). Research of Soil Water Conservation, 14(3), 330–335.
Condit, R. (1995). Research in large, long-term tropical forest plots. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 10, 18–22.
Condit, R., Ashton, P. S., Baker, P., Bunyavejchewin, S., Gunatilleke, S., Gunatilleke, N., Hubbell, S. P., Foster, R. B., Itoh, A., LaFrankie, J. V., Lee, H. S., Losos, E., Manokaran, N., Sukumar, R., & Yamakura, T. (2000). Spatial patterns in the distribution of tropical tree species. Science, 288, 1414–1418.
Courtney, R., Mullen, G., & Harrington, T. (2009). An evaluation of revegetation success on bauxite residue. Restoration Ecology, 17(3), 350–358.
Druckenbrod, D. L., Shugart, H. H., & Davies, I. (2005). Spatial pattern and process in forest stands within the Virginia piedmont. Journal of Vegetation Science, 16, 37–48.
Dutta, R. K., & Agrawal, M. (2003). Restoration of opencast coal mine spoil by planting exotic tree species: a case study in dry tropical region. Ecological Engineering, 21, 143–151.
Filcheva, E., Noustorova, M., Gentcheva-Kostadinova, S. V., & Haigh, M. J. (2000). Organic accumulation and microbial action in surface coal-mine spoils, Pernik, Bulgaria. Ecology and Engineering, 15, 1–15.
Gao, F. L., Qin, X. L., & Yang, Z. (2008). The exploration of Pinus tabuliformis’ biological characteristics and its growth rhythm (in Chinese). Modern Agriculture in Science and Technology, 21, 19.
Guo, X. Y., Zhang, J. T., & Gong, H. L. (2004). The studies of niche gradient changes of the main species in the process of vegetation restoration in Antaibao coal mine (in Chinese). Journal of Plant Physiology, 24(12), 2329–2334.
Guo, X. Y., Zhang, J. T., & Gong, H. L. (2005). The change of species diversity in the process of vegetation restoration in the reclamation area of Antaibao coal mine (in Chinese). Journal of Ecology, 25(4), 763–770.
Haigh, M. J., & Gentcheva-Kostadinova, S. (2002). Ecological erosion control on coal-spoil banks: an evaluation. Ecological Engineering, 18, 371–377.
Hao, Z. Q., Zhang, J., Song, B., Ye, J., & Li, B. H. (2007). Vertical structure and spatial associations of dominant tree species in an old-growth temperate forest. Forest Ecological Management, 252, 1–11.
Harms, K. E., Wright, S. J., Calderon, O., Hernandez, A., & Herre, E. A. (2000). Pervasive density-dependent recruitment enhances seedling diversity in a tropical forest. Nature, 404, 493–495.
He, F. L., Legendre, P., & LaFrankie, J. V. (1997). Distribution patterns of tree species in a Malaysian tropical rain forest. Journal of Vegetation Science, 8, 105–114.
Jefferson, L. V. (2004). Implications of plant density on the resulting community structure of mine site land. Restoration Ecology, 12, 429–438.
Jha, A. K., & Singh, J. S. (1992). Influence of microsites on redevelopment of vegetation on coal mine spoils in a dry tropical environment. Journal of Environmental Management, 36, 95–116.
Keskin, K., & Makineci, E. (2009). Some soil properties on coal mine spoils reclaimed with black locust (Robinia pceudoacacia L.) and umbrella pine (Pinus pinea L.) in Agacli-Istanbul. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 159, 407–414.
Kuznetsova, T., Rosenvald, K., Ostonen, I., Helmisaari, H. S., Mandre, M., & Lõhmus, K. (2010). Survival of black alder (Alnus glutinosa L.), silver birch (Betula pendula Rothm) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) seedlings in a reclaimed oil shale mining area. Ecological Engineering, 36, 495–502.
Li, M. S. (2006). Ecological restoration of mineland with particular reference to the metalliferous mine wasteland in China: a review of research and practice. Science of the Total Environment, 357, 38–53.
Li, J. C., & Bai, Z. K. (2000). Land reclamation and ecological reconstruction of opencast coal mine: the research and practice of Pingshuo opencast coal mine. Beijing: Science Press.
Li, K. R., & Wang, Y. M. (1990). Study on the water condition and productivity of Robinia pseudoacacia forest in Loess tableland (in Chinese). Benton Soil Water Conservation, 6, 58–65.
Lõhmus, P., Rosenvald, R., Lõhmus, A. (2006). Effectiveness of solitary retention tress for conserving epiphytes: differential short-term response of bryophytes and lichens. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 36, 1319–1330.
Mendes, F. P. F., Vasconcellos, L. F., de Paula, A. M., & Cardoso, E. J. B. N. (2010). Evaluating the potential of forest species under “microbial management” for the restoration of degraded mining areas. Water Air Soil Pollution, 208, 79–89.
Moora, M., & Jõgar, U. (2006). Competitive responses of the rare Viola elatior and the common Viola mirabilis. Plant Ecology, 184, 105–110.
Moreno-de las Heras, M., Nicolau, J. M., & Espigares, T. (2008). Vegetation succession in reclaimed coal-mining slopes in a Mediterranean-dry environment. Ecological Engineering, 34, 168–178.
Pedrol, N., Puig, C. G., Souza, P., Forján, R., Vega, F. A., Asensio, V., González, L., Cerqueira, B., Covelo, E. F., & Andrade, L. (2010). Soil fertility and spontaneous revegetation in lignite spoil banks under different amendments. Soil Tillage Research, 110, 134–142.
Ruiz-Jaen, M. C., & Aide, T. M. (2005). Restoration success: how is it being measured? Restoration Ecology, 13, 569–577.
Shibata, M., Kikuchi, S., Tanaka, H., Sueyoshi, M., Yoshimaru, H., & Niiyama, K. (2009). Effects of population density, sex morph, and tree size on reproduction in a heterodichogamous maple Acer mono, in a temperate forest of Japan. Ecological Research, 24, 1–9.
Shrestha, R. K., & Lal, R. (2006). Ecosystem carbon budgeting and soil carbon sequestration in reclaimed mine soil. Environment International, 32, 781–796.
Šourková, M., Frouz, J., & Šantrůčková, H. (2005). Accumulation of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus during soil formation on alder spoil heaps after brown-coal mining, near Sokolov (Czech Republic). Geoderma, 124, 203–214.
van der Vyver, M. L., Cowling, R. M., Campbell, E. E., & Difford, M. (2012). Active restoration of woody canopy dominants in degraded South African semi-arid thicket is neither ecologically nor economically feasible. Applied Vegetation Science, 15, 26–34.
Wang, X. G., Hao, Z. Q., Ye, J., Zhang, J., Li, B. H., & Yao, X. L. (2008). Spatial pattern of diversity in an old-growth temperate forest in Northeastern China. Acta Oecologica, 33, 345–354.
Wang, X. G., Wiegand, T., Hao, Z. Q., Li, B. H., Ye, J., & Lin, F. (2010). Species associations in an old-growth temperate forest in north-eastern China. Journal of Ecology, 98(3), 674–685.
Wiegand, T., & Moloney, K. A. (2004). Rings, circles and null-models for point pattern analysis in ecology. Oikos, 104, 209–229.
Wong, M. H. (2003). Ecological restoration of mine degraded soils, with emphasis on metal contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 50, 775–780.
Xia, H. P., & Cai, X. A. (2002). Ecological restoration technologies for mined lands: a review. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 13(11), 1471–1477.
Zhang, J. T. (2005). Succession analysis of plant communities in abandoned croplands in the Eastern Loess Plateau of China. Journal of Arid Environments, 63(2), 458–474.
Zhang, J., Hao, Z. Q., Song, B., Li, B. H., Wang, X. G., & Ye, J. (2009). Fine-scale species co-occurrence patterns in an old-growth temperate forest. Forest Ecological Management, 257(10), 2115–2120.
Zhang, C., Jiang, W. B., & Han, J. (2010a). The discussion of Ulmus pumila and its application in landscaping (in Chinese). China Agricultural Science B, 26(10), 202–206.
Zhang, J., Song, B., Li, B. H., Ye, J., Wang, X. G., & Hao, Z. Q. (2010b). Spatial patterns and associations of six congeneric species in an old-growth temperate forest. Acta Oecologica, 36, 29–38.
Zhao, Z. Q., Bai, Z. K., Zhang, Z., Guo, D. G., Li, J. C., Xu, Z. G., & Pan, Z. G. (2012). Population structure and spatial distributions patterns of 17-year old plantation in a reclaimed spoil of Pingshuo opencast mine. China Ecological Engineering, 44, 147–151.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Foundation for Public Welfare of the Ministry of Land and Resources of China (no. 201411017). We are grateful to Prof. Hao Zhanqing for the guidance during the plot establishment and vegetation survey, and Pingshuo Opencast Coal Mining Company for providing the study site. We are also grateful for the help provided by Dr. Guo Donggang and Prof. Li Jinchuan for the vegetation survey and basic data processing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Wang, L., Bai, Z. et al. Development of population structure and spatial distribution patterns of a restored forest during 17-year succession (1993–2010) in Pingshuo opencast mine spoil, China. Environ Monit Assess 187, 431 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4391-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4391-z