Abstract
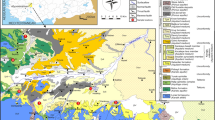
The paper deals with the hydrochemical characterization and water quality assessment of springs emerging from the Archaean crystalline basements at the foothills of Western Ghat mountains in the highlands and Neogene sedimentary formations in the coastal lowlands of Kerala in south west India. A total of 19 springs from two important river basins of southern Kerala such as Ithikkara and Kallada river basins were studied for 18 physico-chemical (temperature, pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), dissolved oxygen (DO), total hardness (TH), Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, CO3 2−, HCO3 −, Cl−, SO4 2− , NO3 −, SiO2, Fe2+, and F− ) as well as bacteriological parameters. The discharge computations show that free-falling type of springs in the area discharge about 256.23 million liters of water a year. A comparative study between the spring water samples of highland and lowland regions reveal that the quality of spring water, except pH and bacteriological contents, satisfies the standards set by the Bureau of Indian Standards and World Health Organization for drinking water. Spring water samples collected from the lowlands register high value of Na+ and Cl− compared with the highlands. Bicarbonate, Ca2+, Mg2+, and K+ values are high in highland than lowland springs. The present study reveals that the spring water sources in the region can be developed as an alternate source for drinking water, provided pH correction and proper disinfection are done prior to its end use.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA. (2005). Standard methods for examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association.
Appelo, C. A. J., & Postma, D. (2005). Geochemistry, ground water and pollution. Leiden: A. A Balkema Publishers. 542.
Babu, K. N., Jalaja, S., Ajithkumar, A., & Sunilkumar, S. (2003). Hydrochemistry of the spring water sources at Varkala. Proc. 15th Kerala Science Congress, 41–44.
Bajpai, R. K., & Narayan, P. K. (2005). Natural analogue study of Resubelpara group of thermal springs at Garo Hills, Meghalaya for demonstration of safe geological disposal of nuclear waste. Current Science, 88, 986–989.
Berner, E. K., & Berner, R. A. (1995). Global environment: water. New Jersey: Air and Geochemical Cycle. Prentice-Hall. 360.
BIS (2003). Indian standard drinking water specifications, IS 10500:1991, edition 2.2.
CESS. (1984). Resources atlas of Kerala. Trivandrum: Central for Earth Science Studies.
CGWB. (2009). Ground water information booklet of Kollam district. Central Ground Water Board, Thiruvananthapuram: Kerala state.
Chandra, K. C. S., & Ramaiah, N. R. P. (2007). Springs in the limestone environment of Karnataka. Journal of Geological Society of India, 69, 1111–1117.
Chow, V. T. (1964). Hand book of applied hydrology: a compendium of water resources technology. New York: Mc Graw- Hill Company.
CPCB. (2008). Guidelines for water quality management. New Delhi: Central Pollution Control Board.
CWRDM (1988). Impact of deforestation on hydrological parameters in the Western Ghats region of Kerala. Report submitted to the Department of Environment, Forest & Wild life, Ministry of Environment and Forests, Govt. of India, Centre for Water Resource Development and Management, 169.
Darling, W. G., & Gooddy, D. C. (2006). The hydrogeochemistry of methane: evidence from English groundwaters. Chemical Geology, 229, 293–312.
Dash, A., Palita, K. S., & Ptra, K. (2013). Physico-chemical analysis of thermal spring of Atri in the district of Khudra, Odisha, India. International Journal of Chemical Sciences and Applications, 4(2), 97–104.
Dudeja, D., & Biyani, A. K. (2009). Hydrogeochemical analysis of groundwater in shallow aquifers of Doon Valley, Uttarakhand. Quarterly Journal of Geological association and Research Centre, Balaghat, 17, 7–21.
Eaton, F. M. (1950). Significance of carbonate in irrigation waters. Soil Science, 69, 123–133.
Ghanem, M., & Ghannam, S. (2010). Spring water hydrochemistry along the north–south profile in the Jordan Valley. Asian Journal of Earth Sciences, 3(3), 122–129.
Goldich, S. S. (1938). A study in rock weathering. Journal of Geology, 46, 23–27.
GSI. (2005). Geology and mineral resources of the states of India, part IX—Kerala. Geological Survey of India, Miscellaneous Publication No., 30, 21–22.
Ibeneme, S. I., Ukive, L. N., Essien, A. G., Nwagbara, J. O., Nweze, C. A., Chinemelu, E. S., & Ivonye, C. A. (2013). Assessment of the chemical characteristics of a spring water source at Ife-Owutu, Ezinihite-Mbaise, South Eastern Nigeria. American Journal of Engineering Research, 2(10), 282–290.
Jang, C. S., Chen, J. S., Lin, B. U., & Liu, W. C. (2012). Characterizing hydrochemical properties of springs in Taiwan based on their geological origins. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 184, 63–75.
Jeelani, G. H. (2005). Chemical quality of spring waters of Anantanag. Kashmir, Journal of Geological Society of India, 66, 453–462.
Jeelani, G. H., Bhat, A. N., Shivanna, K., & Bhat, M. Y. (2011). Geochemical characterisation of surface water and spring water in SE Kashmir Valley, Western Himalaya: implication to water-rock interaction. Journal of Earth System Science, 120(5), 921–932.
Kelepertsis, A., Tziritis, E., Kelepertsis, E., Leontakianakos, G., & Pallas, K. (2009). Hydrogeochemical characterisitics and genetic implications of Edipsos thermal springs, North Euboea, Greece. Central European Journal of Geosciences, 1(3), 241–250.
Migaszewski, Z.M., & Galuszkaa, A. (2003). Assessment of environmental pollution in selected national parks of Poland based on geochemical and biogeochemical studies. Pol. Geol. Inst. Central Archive, Kiellce
Ogundana, A.K., & Aladejana, J.A. (2014). Geophysical and hydrochemical valuation of springwater potential and quality within the basement complex of Southwestern Nigeria. The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES), 3(5), 45–55.
Padmalal, D., Maya, K., Babu, K. N., Baiju, R. S., & Baburaj, B. (2012). Hydrochemical characterisation and water quality assessment of the coastal springs of southern Kerala, India. Journal of Applied Geochemistry, 14, 466–481.
Pichamuthu, C. S. (1967). Physical geography of India. Delhi: National Book Trust (India). 244.
Piper, A.M. (1953). A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Washington D.C.
Rajesh, H. M., & Santosh, M. (1996). Fluorapatite from alkaline pegmaltites of Kerala Khondalite Belt: a petrologic and fluid inclusion study. Journal of Geological Society of India, 48, 637–646.
Ramanathan, A., & Chandrasekharam, D. (1997a). Geochemistry of Rajpur and Puttur thermal springs of the west coast India. Journal of Geological Society of India, 49, 559–565.
Ramanathan, A., & Chandrasekharam, D. (1997b). Geochemistry of Rajpur and Puttur thermal springs of the west coast. India, Journal of Geological Society of India, 49, 559–565.
Rao, S. (2008). Factors controlling the salinity in ground water in parts of Guntur district, Andra Pradesh, India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 138, 327–341.
Reddy, D. V., Nagabhushanam, P., & Perters, E. (2011). Village environs as source of nitrate contamination in groundwater: a case study in basaltic geo-environment in central India. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 174, 481–492.
Richards, L. A. (1954). Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali solid. US Department of Agriculture Agriculture Handbook, 60, 160.
Saidet Saldutti (2009). The assessment of fecal coliform bacteria in Cumberland Valley Springs. Graduate Project. Shippenburg University
Sarin, M. M., Krishnaswamy, S., Dilli, K., Somayajulu, B. L. K., & Moore, W. S. (1989). Major ion chemistry of the Ganga-Brahmaputra riversystem: weathering processes and fluxes to the Bay of Bengal. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53, 997–100.
Schoeller, H., (1965). Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development. Water Resources, Series No. 33, UNESCO, 44–52.
Schoeller, H. (1977). Geochemistry of groundwater. In: Groundwater studies—an international guide for research and practice. UNESCO, 15, 1–18.
Scott, T. M., Means, G. H., Meegan, R. P., Means, R. C., Upchurch, S. B., Copeland, R. E., Jones, J., Roberts, T., & Willet, A. (2004). Bulletin 66: Springs of Florida. Florida Geological Survey, Tallahassee. FL; ISSN 0271–7832.
Sherpa, M. T., Das, S., & Thakur, N. (2013). Physicochemical analysis of hot water springs of Sikkim–Polok Tatopani, Borong Tatopani and Reshi Tatopani. Recent Research in Science and Technology, 5(1), 63–67.
Singh, R., Kanwar, S. S., Jaggi, G. S., & Kartha, K. N. R. (2004). Geochemistry of thermal springs from Bhutan. Himalaya. Journal of Geological Society of India, 64, 191–198.
Singh, A. K., Mondal, G. C., Kumar, S., Singh, T. B., Tewary, B. K., & Sinha, A. (2007). Major ion chemistry, weathering processes and water quality assessment in upper catchment of Damodar River basin, India. Environmental Geology, 54, 745–758.
Singh, A. K., Tewary, B. K., & Sinha, A. (2011). Hydrochemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in part of Noida metropolitan city, Uttar Pradesh. Journal of Geological Society of India, 78, 523–554.
Singh, A. K., Raj, B., Tiwari, A. K., & Mahato, M. K. (2013). Evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality in the Jhansi district of Bundelkhand region, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 70, 1125–1247.
Song, S. R., Chen, Y. L., Liu, C. M., Ku, W. Y., Chen, H. F., Liu, Y. J., Kuo, L. W., Yang, T. F., Chen, C. H., Liu, T. K., & Lee, M. (2005). Hydrochemical changes in spring waters in Taiwan: implications for evaluating sites for earthquake precursory monitoring. TAO, 16(4), 745–762.
Sooryanarayana, K. R., & Kezo, V. (2008). Spring water management in Meghalaya. Journal of Geological Society of India, 69, 194–213.
Talabi, A. O., Afolagboye, O. L., Tijani, M. N., Aladejana, J. A., & Ogundana, A. K. (2014). Hydrogeochemistry of some selected springs waters in Ekiti Basement Complex Area, South Western Nigeria. The International Journal of Engineering and Science; 3(2), 19–30.
Todd, D. K. (1980). Ground water hydrology (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley. 552.
Vaz, G. G., Subha Rao, V., & Ravikumar, V. (2006). Thermal springs in Indian coastal areas of the Palk Bay: their implication in relation to lineaments, coastal morphology and seismicity. Journal of Geological Society of India, 68, 596–569.
Walling, D. E. (1980). Water in the catchment ecosystem. In A. M. Gower (Ed.), Water quality in catchment ecosystems (pp. 1–47). New York: John Wiley and Sons.
WHO. (2006). Guidelines for drinking-water quality, recommendations (3rd ed.). Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wilcox, L.V. (1955). Classification and use of irrigation waters. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Circ. 969, Washington, D.C., 19.
Zhao, J., Wang, C., Jin, Z., Sun, G., & Xiao, J. (2009). Seasonal variation in nature and chemical compositions of spring water in Cuihua Mountain, Shaanxi Province, Central China. Environmental Geology, 57, 1753–1760.
Acknowledgments
The authors (HCN and DP) thank the Director, National Centre for Earth Science Studies, for encouragement and support. Thanks are also due to Department of School of Environment Studies, Cochin University of Science and Technology (CUSAT), and Sophisticated Test and Instrumentation Centre (STIC), CUSAT, for facilities. The authors thank Mr. Vinod P.G., GeoVin Solutions, Kerala, for preparation of thematic maps. The critical comments, encouraging advices and suggestions of the anonymous referees helped immensely in improving the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, H.C., Padmalal, D. & Joseph, A. Hydrochemical assessment of tropical springs—a case study from SW India. Environ Monit Assess 187, 48 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4164-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4164-0