Abstract
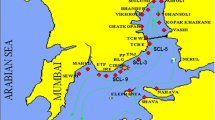
Bottom sediments reflect in general the relative contamination of a sea area. Therefore, a great deal of monitoring work has been dedicated to the analysis of bottom sediments. Izmir Bay is a very important pollution centre in Turkish Aegean coast region due to a densely populated community, industrial complex and maritime transportation, and there are many streams flowing into the bay that pass through a number of industrial and agricultural areas. It had received the majority of domestic and industrial wastewaters until the wastewater treatment plant was constructed. It is well known that sediments play an important role as reservoirs of a fraction of the pollution in aquatic systems. Therefore, sediment samples were collected monthly from three stations which are located in the inner part of the bay during the period January to December 2003. Temporal variations and seasonal changes on their 210Po and 210Pb contents were examined, and the activity concentrations of 210Po and 210Pb were found to vary from 43±6 to 132±12 and 27±5 to 91±9 Bq kg − 1 dry wt, respectively. The highest values of those natural radionuclides were measured at Karşıyaka Station because of the current systems of the bay. Seasonally, the 210Pb levels were found to increase during the winter time for all the stations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Masri, M. S., Mamish, S. & Budeir, Y. (2002). The impact of phosphate loading activities on near marine environment: the Syrian coast, Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 58(1), 35–44.
Atgin, R. S., El-Agha, O., Zararsız, A., Kocataş, A., Parlak, H., & Tuncel, G. (2000). Investigation of the sediment pollution in Izmir Bay: Trace elements. Spectrochimica Acta. Part B, Atomic Spectroscopy, 55(7), 1151–1164. doi:10.1016/S0584-8547(00)00231-7.
Balkas, T., & Tuncer, S. (1989). Natural characteristics of the Izmir Bay and the impact of the wastewater. Split, PAP/RAC.
Bergin, F., Kucuksezgin, F., Uluturhan, E., Barut, I. F., Meric, E., Avsar, N., et al. (2006). The response of benthic foraminifera and ostracoda to heavy metal pollution in Gulf of Izmir (Eastern Aegean Sea). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 66(3–4), 368–386. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2005.09.013.
Boisson, F., Miquel, J.-C., Cotret, O., & Fowler, S. W. (2001). 210Po and 210Pb cycling in a hydrothermal vent zone in the coastal Aegean Sea. The Science of The Total Environment, 281(1–3), 111–119.
Demirkurt, E., Uysal, H., & Parlak, H. (1990). The levels of heavy metals accumulation in some benthic organisms living in Izmir Bay. Rapport de la Comission Internationale pour l’Exploration Scientifique de la Mer Méditerranée, 32(1), 127.
Filibeli, A., Yılmaz, R., & Alyanak, I. (1995). Dredged material of Izmir harbor: Its behavior and pollution potential. Water Science and Technology, 32(2), 105–113. doi:10.1016/0273-1223(95)00575-8.
Flynn, W. W. (1968). The determination of low levels of polonium-210 in environmental materials. Analytica Chimica Acta, 43, 221–227.
Gasco, C., Anton, M. P., Pozuelo, M., Meral, J., Gonzalez, A. M., Papucci, C., et al. (2002). Distributions of Pu, Am and Cs in margin sediments from the western Mediterranean (Spanish coast). Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 59, 75–89. doi:10.1016/S0265-931X(01)00037-6.
Kontas, A., Kucuksezgin, F., Altay, O., & Uluturhan, E. (2004). Monitoring of eutrophication and nutrient limitation in the Izmir Bay (Turkey) before and after wastewater treatment plant. Environment International, 29(8), 1057–1062. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00098-9.
Küçüksezgin, F., & Balcı, A. (1994). Heavy metal concentrations in selected organisms from Izmir Bay. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 28(5), 333–335. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(94)90161-9.
Küçüksezgin, F., Uluturhan, E., Kontas, A., & Altay, O. (2002). Trace metal concentrations in edible fishes from Izmir Bay, Eastern Aegean. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 44(8), 827–832. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00110-8.
Kucuksezgin, F., Kontas, A., Altay, O., Uluturhan, E., & Darılmaz, E. (2006). Assessment of marine pollution in Izmir Bay: Nutrient, heavy metal and total hydrocarbon concentrations. Environment International, 32(1), 41–51. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.04.007.
Malins, D. C. (1981). Marine organic chemistry; evolution, composition, interactions and chemistry of organic matter in seawater. In E. K. Duursma & R. Dawson (Eds.), Elsevier oceanography series (xiv + 521 pp., Vol. 31, pp. 288–289). Amsterdam and New York: Elsevier Science Publishers
Malins, D. C. (1989). Contaminated marine sediments: Assessment and remediation (508 pp.). Washington, DC: The National Academy Press.
Malins, D. C., McChain, B. B., Myers, M. S., Brown, D. W., Sparks, A. K., Marato, J. F., et al. (1984). Toxic chemicals and abnormalities in fish and shellfish from urban bays of puget sound. Marine Environment Research, 14(1–4), 527–528
Misitano, D. A., Casillas, E., & Haley, C. R. (1994). Effects of contaminated sediments on viability, length, DNA and protein content of larval surf smelt, Hypomesus pretiosus. Marine Environmental Research, 37(1), 1–21. doi:10.1016/0141-1136(94)90060-4.
National Research Council. Committee on Evaluation of EPA Guidelines for Exposure to Naturally Occuring Radioactive Materials (1999). Evaluation of guidelines for exposures to technologically enhanced naturally occuring radioactive materials (294 pp.).
Parfenov, Yu D. (1974). Polonium-210 in the environment and in the human organism. Atomic Energy Review, 12, 75.
Radokovitch, O., Sanchez-Cabeza, J. A., Abassi, A., Masqué, P. & Heussner, S. (2003). Meso and small-scale variations of 210Pb fluxes on the Northwestern Mediterranean continental margins, Continental Shelf Research, 23(7), 693–715.
Robbins, J. A. & Edgington, D. N. (1975). Determination of recent sedimentation rates in Lake Michigan using Pb-210 and Cs-137, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 39(3), 285–304.
Saueia, C. H. R., & Mazzilli, B. P. (2006). Distribution of natural radionuclides in the production and use of phosphate fertilizers in Brazil. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 89, 229–239. doi:10.1016/j.jenvrad.2006.05.009.
Stewart, G., Cochran, J. K., Xue, J., Lee, C., Wakeham, S. G., Armstrong, R. A., et al. (2007). Exploring the connection between 210Po and organic matter in the Northwestern Mediterranean, Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 54(3), 415–427.
Sunlu, U. (2004). The state of the marine pollution in The Bay of Izmir. Workshop on artificial reef applications in fisheries and water quality enhancement. 24/09/2004.E.Ü. Su Ürünleri Fakültesi. Urla-İskele.
Sunlu, F. S., & Sunlu, U. (2001). Temporal variations of nutrients and chlorophyll a in Urla Coast (Izmir Bay-Aegean Sea-Turkey). In The 36th CIESM congress proceedings (Vol. 36, p. 420). Monte-Carlo, Monaco, 24–28 September.
Sunlu, U., Egemen, Ö., & Kaymakçı, A. (1998). Trace metals in mediterranean mussel mytilus galloprovincialis (L. 1758) and in surficial sediments from Urla-İskele, Izmir-Turkey. In International semposium on marine pollution extended synopsis (pp. 645–646). Monte-Carlo, Monaco.
Sunlu, U., Büyükışık, B., Koray, T., von Bröckel, K., Sunlu, F. S., Sever, T. M., et al. (2007). The effects of “Izmir big channel” waste-water treatment project to the lower throphic level of Izmir Bay (Aegean Sea Turkey). TÜBİTAK-CAYDAG Project No. 102Y116, Scientific Project Final Report (266p.). (In Turkish).
Tateda, Y., Carvalho, F. P., Fowler, S. W., & Miquel, J.-C. (2003). Fractionation of 210Po and 210Pb in coastal waters of the NW Mediterranean continental margin. Continental Shelf Research, 23(3–4), 295–316. doi:10.1016/S0278-4343(02)00167-X.
Uğur, A., Yener, G., Topçuoğlu, S., Sunlu, U., Aközcan, S., & Özden, B. (2006a). 210Po in Mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) and sediments along the Turkish coast of the Aegean Sea. Radioactivity in the Environment, 8, 272–280.
Uğur, A., Yener, G., Topçuoğlu, S., Sunlu, U., & Karalı, T. (2006b). 210Po and 210Pb in marine ecosystem of Aegean Sea Turkish Coast. International Atomic Energy Agency, IAEA Research Contract Project No, TUR 12641.
Uysal, H., & Tuncer, S. (1982). Levels of heavy metals on some commercial food species in the Bay of Izmir (Turkey).VIes Journées Etud. Poll.Cannes, CIESM (pp. 323–327).
Yılmas, Z. (1995). Investigation of lead pollution originated from terrestrial area at Izmir Bay, Ph.D. Thesis, Dokuz Eylül University, The Institute of Marine Sciences and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saçan, S., Uğur, A., Sunlu, U. et al. The 210Po and 210Pb levels in surface sediment samples in the Izmir Bay (Aegean Sea-Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 161, 575–582 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0769-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0769-0