Abstract
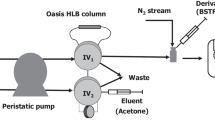
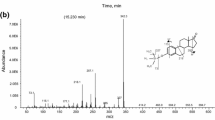
A procedure using pre-column trimethylsilyl derivatization and gas chromatography/ mass spectrometry (GC/MS) was developed and applied in determining trace estrogens in complex matrix. Main conditions were optimized, including pH value, salinity of water sample, elution reagents, clean procedure, derivative solvent and temperature. The optimized method was used to determine steroid estrogens in surface water and effluents of wastewater treatment plant (WWTP). Low detection limits of 0.01, 0.03, 0.03, 0.07, 0.09 and 0.13 ng/l for DES, E1, E2, EE2, E3 and EV, respectively were obtained under optimism condition. No apparent interferences appeared in chromatography in comparison with ultrapure water blank. Mean recovery ranged from 72.6% to 111.0% with relative standard deviation of 1.1–4.6% for spiked surface water, and from 66.6% to 121.1% with relative standard deviation of 1.5–4.7% for spiked effluent of WWTP. The results suggested that the optimized method provides a robust solution for the determination of trace steroid estrogens in complex matrix.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alda, M. J. L., & Barceló, D. (2001). Review of analytical methods for the determination of estrogens and progestogens in waste waters. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 371(4), 437–447.
Baronti, C., Curini, R., D’Ascenzo, G., Di, C. A., Gentili, A., & Samperi, R. (2000). Monitoring natural and synthetic estrogens at activated sludge sewage treatment plants and in a receiving river water. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(24), 5059–5066.
Beck, I. C., Bruhn, R., Gandrass, J., & Ruck, W. (2005). Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of estrogenic compounds in coastal surface water of the Baltic Sea. Journal of Chromatography A, 1090(1–2), 98–106.
Benijts, T., Lambert, W., & DeLeenheer, A. (2004). Analysis of multiple endocrine disruptors in environmental waters via wide-spectrum solid-phase extraction and dual-polarity ionization LC-ion trap-MS/MS. Analytical Chemistry, 76(3), 704–711.
Bila, D., Montalvao, A. F., Azevedo, D., & Dezotti, M. (2007). Estrogenic activity removal of 17[beta]-estradiol by ozonation and identification of by-products. Chemosphere, 69(5), 736–746.
Chen, C. Y., Wen, T. Y., Wang, G. S., Cheng, H. W., Lin, Y. H., & Lien, G. W. (2007). Determining estrogenic steroids in Taipei waters and removal in drinking water treatment using high-flow solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Science of the Total Environment, 378(3), 352–365.
Cui, C. W., Ji, S. L., & Ren, H. Y. (2006). Determination of steroid estrogens in wastewater treatment plant of a contraceptives producing factory. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 121(1–3), 409–419.
Desbrow, C., Routledge, E. J., Brighty, G. C., Sumpter, J. P., & Waldock, M. (1998). Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environmental Science & Technology, 32(11), 1549–1558.
Fawell, J. K., Sheahan, D., James, H. A., Hurst, M., & Scott, S. (2001). Oestrogens and oestrogenic activity in raw and treated water in Seven Trent Water. Water Research, 35(5), 1240–1244.
Feigelson, H. S., & Henderson, E. B. (1996). Estrogens and breast cancer. Carcinogenesis, 17(11), 2279–2284.
Ferguson, P. L., Iden, C. R., McElroy, A. E., & Brownawell, B. J. (2001). Determination of steroid estrogens in wastewater by immunoaffinity extraction coupled with HPLC-electrospray-MS. Analytical Chemistry, 73(16), 3890–3895.
Graham, J. D., Bain, L. D., Richer, K. J., Jackson, A. T., Tung, L., & Horwitz, K. B. (2000). Thoughts on tamoxifen resistant breast cancer. Are coregulators the answer or just a red herring? Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 74(5), 255–259.
Hernando, M. D., Mezcua, M., Gomez, M. J., Malato, O., Aguera, A., & Fernandez, A. A. R. (2004). Comparative study of analytical methods involving gas chromatography-mass spectrometry after derivatization and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of selected endocrine disrupting compounds in wastewaters. Journal of Chromatography A, 1047(1), 129–135.
Hu, J., Zhang, H., & Chang, H. (2005). Improved method for analyzing estrogens in water by liquid chromatography-electrospray mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1070(1–2), 221–224.
Isobe, T., Shiraishi, H., Yasuda, M., Shinoda, A., Suzuki, H., & Morita, M. (2003). Determination of estrogens and their conjugates in water using solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 984(2), 195–202.
Jeannot, R., Sabik, H., Sauvard, E., Dagnac, T., & Dohrendorf, K. (2002). Determination of endocrine-disrupting compounds in environmental samples using gas and liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 974(1–2), 143–159.
Johnson, A. C., Belfroid, A., & Di, C. A. (2000). Estimating steroid oestrogen inputs into activated sludge treatment works and observations on their removal from the effluent. The Science of The Total Environment, 256(2–3), 163–173.
Johnson, A. C., & Sumpter, J. P. (2001). Removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals in activated sludge treatment works. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(24), 4697–4703.
Kuster, M., Alda, M. J. L., & Barceló, D. (2005). Estrogens and progestogens in wastewater, sludge, sediments, and soil (pp. 1–24). Berlin: Springer.
Kuster, M., Maria, J. L. A., & Barcelo, D. (2004). Analysis and distribution of estrogens and progestogens in sewage sludge, soils and sediments. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 23(10–11), 790–798.
Lai, K. M., Johnson, K. L., Scrimshaw, M. D., & Lester, J. N. (2000). Binding of waterborne steroid estrogens to solid phases in river and estuarine systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(18), 3890–3894.
Larsson, D. G. J., Adolfsson, E. M., Parkkonen, J., Pettersson, M., Berg, A. H., Olsson, P. E., et al. (1999). Ethinyloestradiol an undesired fish contraceptive? Aquatic Toxicology, 45(2–3), 91–97.
López, A. M. J., & Barceló, D. (2001). Use of solid-phase extraction in various of its modalities for sample preparation in the determination of estrogens and progestogens in sediment and water. Journal of Chromatography A, 938(1–2), 145–153.
Matejicek, D., Houserova, P., & Kuban, V. (2007). Combined isolation and purification procedures prior to the high-performance liquid chromatographic-ion-trap tandem mass spectrometric determination of estrogens and their conjugates in river sediments. Journal of Chromatography A, 1171(1–2), 80–89.
Maurício, R., Diniz, M., Petrovic, M., Amaral, L., Peres, I., Barceló, D., et al. (2006). A characterization of selected endocrine disrupter compounds in a Portuguese wastewater treatment plant. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118(1–3), 75–87.
Nakada, N., Shinohara, H., Murata, A., Kiri, K., Managaki, S., Sato, N., et al. (2007). Removal of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) during sand filtration and ozonation at a municipal sewage treatment plant. Water Research, 41(19), 4373.
Peck, M. R., Labadie, P., Minier, C., & Hill, E. M. (2007). Profiles of environmental and endogenous estrogens in the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha. Chemosphere, 69(1), 1–8.
Quintana, J. B., Carpinteiro, J., Rodriguez, I., Lorenzo, R. A., Carro, A. M., & Cela, R. (2004). Determination of natural and synthetic estrogens in water by gas chromatography with mass spectrometric detection. Journal of Chromatography A, 1024(1–2), 177–185.
Rodgers, G. T. P., Jobling, S., Morris, S., Kelly, C., Kirby, S., Janbakhsh, A., et al. (2000). Long-term temporal changes in the estrogenic composition of treated sewage effluent and its biological effects on fish. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(8), 1521–1528.
Shareef, A., Parnis, C. J., Angove, M. J., Wells, J. D., & Johnson, B. B. (2004). Suitability of N,O-bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide and N-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-N-methyltrifluoroacetamide as derivatization reagents for the determination of the estrogens estrone and 17[alpha]-ethinylestradiol by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1026(1–2), 295–300.
Solé, M., Porte, C., & Barceló, D. (2001). Analysis of the estrogenic activity of sewage treatment works and receiving waters using vitellogenin induction in fish as a biomarker. TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 20(9), 518–525.
Sun, Q., Deng, S., Huang, J., Shen, G., & Yu, G. (2008). Contributors to estrogenic activity in wastewater from a large wastewater treatment plant in Beijing, China. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 25(1), 20–26.
Ternes, T. A., Stumpf, M., Mueller, J., Haberer, K., Wilken, R. D., & Servos, M. (1999). Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants—I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. The Science of The Total Environment, 225(1–2), 81–90.
Vethaak, A. D., Lahr, J., Schrap, S. M., Belfroid, A. C., Rijs, G. B. J., Gerritsen, A., et al. (2005). An integrated assessment of estrogenic contamination and biological effects in the aquatic environment of The Netherlands. Chemosphere, 59(4), 511–524.
Wang, Y., Hu, W., Cao, Z., Fu, X., & Zhu, T. (2005). Occurrence of endocrine-disrupting compounds in reclaimed water from Tianjin, China. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 383(5), 857–863.
Xiao, X., McCalley, D. V., & McEvoy, J. (2001). Analysis of estrogens in river water and effluents using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-negative chemical ionisation mass spectrometry of the pentafluorobenzoyl derivatives. Journal of Chromatography A, 923(1–2), 195–204.
Xu, X., Keefer, L. K., Waterhouse, D. J., Saavedra, J. E., Veenstra, T. D., & Ziegler, R. G. (2004). Measuring seven endogenous ketolic estrogens simultaneously in human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 76(19), 5829–5836.
Xu, X., Roman, J. M., Veenstra, T. D., VanAnda, J., Ziegler, R. G., & Issaq, H. J. (2006). Analysis of fifteen estrogen metabolites using packed column supercritical fluid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 78(5), 1553–1558.
Xu, X., Veenstra, T. D., Fox, S. D., Roman, J. M., Issaq, H. J., Falk, R., et al. (2005). Measuring fifteen endogenous estrogens simultaneously in human urine by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 77(20), 6646–6654.
Yu, Z., Xiao, B., Huang, W., & Peng, P. (2004). Sorption of steroid estrogens to soils and sediments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23(3), 531–539.
Zha, J., Sun, L., Zhou, Y., Spear, P., Ma, M., & Wang, Z. (2008). Assessment of 17-ethinylestradiol effects and underlying mechanisms in a continuous, multi-generation exposure of the Chinese rare minnow (Gobiocypris rarus). Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 226(3), 298–308.
Zhang, H., & Henion, J. (1999). Quantitative and qualitative determination of estrogen sulfates in human urine by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry using 96-well technology. Analytical Chemistry, 71(18), 3955–3964.
Zhou, Y., Wang, Z., & Jia, N. (2007). Formation of multiple trimethylsilyl derivatives in the derivatization of 17[alpha]-ethinylestradiol with BSTFA or MSTFA followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry determination. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19(7), 879–884.
Zuo, Y., & Zhang, K. (2005). Suitability of N,O-bis (trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide as derivatization reagent for the determination of the estrogens estrone and 17 [alpha]-ethinylestradiol by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1095(1–2), 201–202.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Zhou, J., Xu, Y. et al. An alternative method for the determination of estrogens in surface water and wastewater treatment plant effluent using pre-column trimethylsilyl derivatization and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Environ Monit Assess 158, 35–49 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0563-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0563-4