Abstract
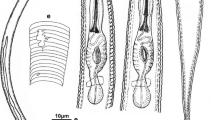
A new root-lesion nematode was isolated from sugarcane (Saccharum sinensis Roxb.) in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China. Morphology and molecular analyses of rRNA small subunit (SSU), D2D3 expansion domains of large subunit (LSU D2D3) and internal transcribed spacer (ITS) confirmed that this nematode is different from other previously described root-lesion nematodes. Herein it is described, illustrated and named as Pratylenchus parazeae n. sp. This new species is characterised by plain and smooth En face, three lip annuli, stylet with anteriorly rounded to indented knobs, 17.0–19.0 μm long, lateral field composed of four lines with areolated outer bands at vulval region, vulva position 68.9–74.9 %, small, oval and empty spermatheca, and a subhemispherical tail usually with smooth terminus and sometimes with a more or less pronounced dorsally indented terminus. Phylogenetic trees inferred from BI analysis based on SSU, LSU D2D3 and ITS revealed that P. parazeae n. sp. can be distinguished from all described root-lesion nematodes, especially from the most closely related species P. zeae. A species-specific duplex PCR was also developed to separate the new species from other nematode species.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Banna, L., Williamson, V., & Gardner, S. L. (1997). Phylogenetic analysis of nematodes of the genus Pratylenchus using nuclear 26S rDNA. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 7(1), 94–102.
Al-Banna, L., Ploeg, A. T., Williamson, V. M., & Kaloshian, I. (2004). Discrimination of six Pratylenchus species using PCR and species-specific primers. Journal of Nematology, 36(2), 142–146.
Bachand, G. D., & Castello, J. D. (2001). Immunolocalization of tomato mosaic tobamovirus in roots of red spruce seedlings. Journal of Phytopathology, 149, 415–419.
Bajaj, H. K., & Bhatti, D. S. (1984). New and known species of Pratylenchus Filipjev, 1936 (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) from Haryana, India, with remarks on intraspecific variations. Journal of Nematology, 16(4), 360–367.
Bickford, D., Lohman, D. J., Sodhi, N. S., Ng, P. K., Meier, R., Winker, K., Ingram K. K., & Das, I. (2007). Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22(3), 148–155.
Blok, V. C., Malloch, G., Harrower, B., Phillips, M. S., & Vrain, T. C. (1998). Intraspecific variation in ribosomal DNA in populations of the potato cyst nematode Globodera pallida. Journal of Nematology, 30(2), 262.
Brown, J. K., Frohlich, D. R., & Rosell, R. C. (1995). The sweetpotato or silverleaf whiteflies: biotypes of Bemisia tabaci or a species complex? Annual Review of Entomology, 40(1), 511–534.
Cadet, P., & Spaull, V. W. (2005). Nematode parasites of sugarcane. In M. Luc, R. A. Sikora, & J. Bridge (Eds.), Plant-parasitic nematodes in subtropical and tropical agriculture (2nd ed., pp. 645–674). Wallingford: CAB International.
Castillo, P., & Vovlas, N. (2007). Pratylenchus (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae): Diagnosis, Biology, Pathogenicity and Management. In D. J. Hunt & R. N. Perry (Eds.), Nematology monographs and perspectives 6 (p. 529). Leiden: Brill.
Castillo, P., Trapero-Casas, J. L., & Jiménez-Díaz, R. M. (1995). Effect of time, temperature, and inoculum density on reproduction of Pratylenchus thornei in carrot disk cultures. Journal of Nematology, 27(1), 120–124.
Castillo, P., Vovlas, N., & Jiménez-Díaz, R. M. (1998). Pathogenicity and histopathology of Pratylenchus thornei populations on selected chickpea genotypes. Plant Pathology, 47(3), 370–376.
Chen, D. Y., Ni, H. F., Yen, J. H., & Tsay, T. T. (2009). Identification of a new recorded root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus zeae (Nematoda: Tylenchoidea, Pratylenchidae) from corn plantations in Taiwan. Plant Pathology Bulletin, 18(2), 111–118.
Cherry, T., Szalanski, A. L., Todd, T. C., & Powers, T. O. (1997). The internal transcribed spacer region of Belonolaimus (Nemata: Belonolaimidae). Journal of Nematology, 29(1), 23.
Chizhov, V. N., Chumakova, O. A., Subbotin, S. A., & Baldwin, J. G. (2006). Morphological and molecular characterization of foliar nematodes of the genus Aphelencholdes: A. fragariae and A. ritzemabosi (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from the Main Botanical Garden of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Russian Journal of Nematology, 14(2), 179–184.
Cobb, N. A. (1917). A new parasitic nema found infesting cotton and potatoes. Journal of Agricultural Research, 11, 27–33.
Corbett, D. C. M., & Clark, S. A. (1983). Surface features in the taxonomy of Pratylenchus species. Revue de Nématologie, 6(1), 85–98.
De Luca, F., Troccoli, A., Duncan, L. W., Subbotin, S. A., Waeyenberge, L., Moens, M., & Inserra, R. N. (2010). Characterisation of a population of Pratylenchus hippeastri from bromeliads and description of two related new species, P. floridensis n. sp. and P. parafloridensis n. sp. from grasses in Florida. Nematology, 12(6), 847–868.
De Luca, F., Reyes, A., Troccoli, A., & Castillo, P. (2011). Molecular variability and phylogenetic relationships among different species and populations of Pratylenchus (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) as inferred from the analysis of the ITS rDNA. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 130(3), 415–426.
De Luca, F., Troccoli, A., Duncan, L. W., Subbotin, S. A., Waeyenberge, L., Coyne, D. L., Brentu, F. C., & Inserra, R. N. (2012). Pratylenchus speijeri n. sp. (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae), a new root-lesion nematode pest of plantain in West Africa. Nematology, 14(8), 987–1004.
FAO (1997). Fiji/FAO Asia Pacific Sugar Conference. http://www.fao.org/docrep/005/x0513e/x0513e18.htm. Accessed 1 June 2014.
Feng, Z. X. (2001). Plant nematology (p. 208). Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Publishing.
Filipjev, I. N. (1936). On the classification of the Tylenchinae. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 3(2), 80–82.
Filipjev, I. N., & Schuurmans Stekhoven, J. H. (1941). A Manual of agricultural helminthology (p. 878). Leiden: Brill.
FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS statistical database (FAOSTAT) (2010). FAOSTAT production statistics of Sugarcane. Online database. http://faostat.fao.org/site/567/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=567. Accessed 1 June 2014.
Godfrey, G. H. (1929). A destructive root disease of pineapples and other plants due to Tylenchus brachyurus n. sp. Phytopathology, 19, 611–629.
Graham, T. W. (1951). Nematode root rot of tobacco and other plants. In South Carolina Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin, 390 (p. 25). South Carolina Agricultural Experiment Station, Clemson Agricultural College.
Handoo, Z. A., Carta, L. K., & Skantar, A. M. (2001). Morphological and molecular characterisation of Pratylenchus arlingtoni n. sp., P. convallariae and P. fallax (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae). Nematology, 3(6), 607–618.
Hernández, M., Jordana, R., Goldaracena, A., & Pinochet, J. (2000). SEM observations of nine species of the genus Pratylenchus Filipjev, 1936 (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae). Journal of Nematode Morphology and Systematics, 3(2), 165–174.
Huelsenbeck, J. P., & Ronquist, F. (2001). MR BAYES: bayesian inference of phylogenetic tress. Bioinformatics, 17(8), 1754–1755.
Hugall, A., Stanton, J., & Moritz, C. (1999). Reticulate evolution and the origins of ribosomal internal transcribed spacer diversity in apomictic Meloidogyne. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16(2), 157–164.
Kühn, J. (1857). Über das Vorkommen von Anguillulen in erkrankten Blüthenköpfen von Dipsacus fullonum L. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 9, 129–137.
Lal, A., & Khan, E. (1990). Species of Pratylenchus Filipjev, 1936 and Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945 (Nematoda:Tylenchida) found associated with forest trees in northern India. Indian Journal of Nematology, 19(1), 44–50.
Larget, B., & Simon, D. L. (1999). Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithms for the Bayesian analysis of phylogenetic trees. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 16, 750–759.
Li, Q. W. (2000). Improved technology of modern sugarcane (p. 340). Guangzhou: South China University of Technology Press.
Loof, P. A. A. (1960). Taxonomic studies on the genus Pratylenchus (Nematoda). Tijdschrift over Plantenziekten, 66(2), 29–90.
Luc, M. (1958). Les nématodes et le flétrissement des cotonniers dans le Sud-Ouest de Madagascar. Coton et Fibres Tropicales, 13(2), 1–18.
Mizukubo, T., Toida, Y., Keereewan, S., & Yoshida, M. (1990). Pratylenchus subranjani n. sp. (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) from maize in Thailand. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 25(2), 311–318.
Mundo-Ocampo, M., Troccoli, A., Subbotin, S. A., Cid, J., Baldwin, J. G., & Inserra, R. N. (2008). Synonymy of Afenestrata with Heterodera supported by phylogenetics with molecular and morphological characterisation of H. koreana comb. n. and H. orientalis comb. n. (Tylenchida: Heteroderidae). Nematology, 10(5), 611–632.
Nandakumar, C., & Khera, S. (1970). A new nematode species, Pratylenchus mulchandi from millets of Rajasthan. Indian Phytopathology, 22(3), 359–363.
Onapitan, J. A., & Amosu, J. O. (1982). Pathogenicity and histopathology of Pratylenchus brachyurus and Helicotylenchus pseudorobustus on sugarcane. Nematropica, 12(1), 51–60.
Palomares-Rius, J. E., Castillo, P., Liebanas, G., Vovlas, N., Landa, B. B., Navas-Cortes, J. A., & Subbotin, S. A. (2010). Description of Pratylenchus hispaniensis n. sp. from Spain and considerations on the phylogenetic relationship among selected genera in the family Pratylenchidae. Nematology, 12(3), 429–451.
Palomares-Rius, J. E., Guesmi, I., Horrigue-Raouani, N., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Liébanas, G., & Castillo, P. (2014). Morphological and molecular characterisation of Pratylenchus oleae n. sp. (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) parasitizing wild and cultivated olives in Spain and Tunisia. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 140(1), 53–67.
Posada, D., & Crandall, K. A. (1998). Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14(9), 817–818.
Powers, T. O., Todd, T. C., Burnell, A. M., Murray, P. C. B., Fleming, C. C., Szalanski, A. L., Adams, B. A., & Harris, T. S. (1997). The rDNA internal transcribed spacer region as a taxonomic marker for nematodes. Journal of Nematology, 29(4), 441.
Reid, A., Manzanilla-López, R. H., & Hunt, D. J. (2003). Nacobbus aberrans (Thorne, 1935) Thorne & Allen, 1944 (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae); a nascent species complex revealed by RFLP analysis and sequencing of the ITS-rDNA region. Nematology, 5(3), 441–451.
Ryss, A. Y. (1988). Root parasitic nematodes of the family Pratylenchidae (Tylenchida) of the World Fauna (p. 367). Leningrad: USSR.
Ryss, A. Y. (2002). Phylogeny and evolution of the genus Pratylenchus according to morphological data (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Zoosystematica Rossica, 10(2), 257–273.
Setterquist, R. A., Smith, G. K., Jones, R., & Fox, G. E. (1996). Diagnostic probes targeting the major sperm protein gene that may be useful in the molecular identification of nematodes. Journal of Nematology, 28(4), 414–421.
Sher, S. A., & Allen, M. W. (1953). Revision of the genus Pratylenchus (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). University of California Publications in Zoology, 57(6), 441–470.
Siddiqi, M. R. (2000). Tylenchida parasites of plants and insects (2nd ed., p. 864). Wallingford: CABI Publishing.
Siddiqi, M. R., Dabur, K. R., & Bajaj, H. K. (1991). Descriptions of three new species of Pratylenchus Filipjev, 1936 (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae). Nematologia Mediterranea, 19(1), 1–7.
Subbotin, S. A., Vierstraete, A., De Ley, P., Rowe, J., Waeyenberge, L., Moens, M., & Vanfleteren, J. R. (2001). Phylogenetic relationships within the cyst-forming nematodes (Nematoda, Heteroderidae) based on analysis of sequences from the ITS regions of ribosomal DNA. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 21(1), 1–16.
Subbotin, S. A., Sturhan, D., Chizhov, V. N., Vovlas, N., & Baldwin, J. G. (2006). Phylogenetic analysis of Tylenchida Thorne, 1949 as inferred from D2 and D3 expansion fragments of the 28S rRNA gene sequences. Nematology, 8(3), 455–474.
Subbotin, S. A., Ragsdale, E. J., Mullens, T., Roberts, P. A., Mundo-Ocampo, M., & Baldwin, J. G. (2008). A phylogenetic framework for root-lesion nematodes of the genus Pratylenchus (Nematoda): evidence from 18S and D2-D3 expansion segments of 28S ribosomal RNA genes and morphological characters. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 48(2), 491–505.
Swofford, D. L. (1998). PAUP*-Phylogenetic Analyses Using Parsimony (* and other Methods). Version 4 b10 (p. 128). Sunderland: Sinauer Associates.
Taheri, Z. M., Maafi, Z. T., Subbotin, S. A., Pourjam, E., & Eskandari, A. (2013). Molecular and phylogenetic studies on Pratylenchidae from Iran with additional data on Pratylenchus delattrei, Pratylenchoides alkani and two unknown species of Hirschmanniella and Pratylenchus. Nematology, 15(6), 633–651.
Tamura, K., Dudley, J., Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2003). MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 24(8), 1596–1599.
Tanha Maafi, Z., Subbotin, S. A., & Moens, M. (2003). Molecular identification of cyst-forming nematodes (Heteroderidae) from Iran and a phylogeny based on the ITS sequences of rDNA. Nematology, 5(1), 99–111.
Tepper, H. B. (1992). Benzyladenine promotes shoot initiation in empty leaf axils of Stellaria media L. Journal of Plant Physiology, 140(2), 241–243.
Tepper, H. B. (1993). Developmental features accompanying the imposition and release of apical dominance in pea. Journal of Plant Physiology, 142(6), 722–729.
Thorne, G., & Malek, R. B. (1968). Nematodes of the northern Great Plains. Part I. Tylenchida (Nemata: Secernentea) South Dakota: South Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station, Technical Bulletin, 31 p. 111.
Uehara, T., Mizukubo, T., Kushida, A., & Momota, Y. (1998a). Identification of Pratylenchus penetrans (Cobb) by PCR using ITS-based species-specific primers. Japanese Journal of Nematology, 28(1), 1–7.
Uehara, T., Mizukubo, T., Kushida, A., & Momota, Y. (1998b). Identification of Pratylenchus coffeae and P. loosi using specific primers for PCR amplification of ribosomal DNA. Nematologica, 44(4), 357–368.
Villard, P., & Malausa, T. (2013). SP-Designer: a user-friendly program for designing species-specific primer pairs from DNA sequence alignments. Molecular Ecology Resources, 13(4), 755–758.
Vovlas, N., Troccoli, A., Palomares-Rius, J. E., De Luca, F., Liébanas, G., Landa, B. B., Subbotin, S. A., & Castillo, P. (2011). Ditylenchus gigas n. sp. parasitizing broad bean: a new stem nematode singled out from the Ditylenchus dipsaci species complex using a polyphasic approach with molecular phylogeny. Plant Pathology, 60(4), 762–775.
Vrain, T. C., Wakarchuk, D. A., Levesque, A. C., & Hamilton, R. I. (1992). Intraspecific rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism in the Xiphinema americanum group. Fundamental and Applied Nematology, 15(6), 563–573.
Waeyenberge, L., Ryss, A., Moens, M., Pinochet, J., & Vrain, T. C. (2000). Molecular characterisation of 18 Pratylenchus species using rDNA restriction fragment length polymorphism. Nematology, 2(2), 135–142.
Waeyenberge, L., Viaene, N., & Moens, M. (2009). Species-specific duplex PCR for the detection of Pratylenchus penetrans. Nematology, 11(6), 847–857.
Wei, J. L., Huang, C. H., Shang, X. K., Pan, X. H., Huang, D. F., & Wang, B. H. (2012). Nematode species and their distribution in sugarcane fields in Guangxi. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 43(2), 184–186.
Zeidan, A. B., & Geraert, E. (1991). Pratylenchus from Sudan, with the description of two new species (Nemata: Tylenchida). Revue de Nematologie, 14, 221–229.
Zhuo, K., Cui, R. Q., Ye, W. M., Luo, M., Wang, H. H., Hu, X. N., & Liao, J. L. (2010). Morphological and molecular characterization of Aphelenchoides fujianensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Aphelenchoididae) from Pinus massoniana in China. Zootaxa, 2509, 39–52.
Zimmermann, A. (1898). De Nematoden der koffiewortels. Deel I. Mededeelingen uit's Lands Plantentuin, 27, 1–64.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by National Key Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, grant number 2013CB127501), the Planning Project for Science and Technology in Guangzhou City (grant number 11A62100574) and the special fund for agro-scientific research in the public interest of China (grant numbers 201103018 and 200903040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhuo, K., Ye, W. et al. Morphological and molecular charaterisation of Pratylenchus parazeae n. sp. (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae) parasitizing sugarcane in China. Eur J Plant Pathol 143, 173–191 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0674-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-015-0674-z