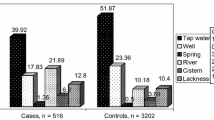
Abstract
Golestan province in north Iran is known to be a high-risk area for esophageal cancer (EC). Of a long list of multiple risk factors, this study focuses on a possible link between the epidemiologic patterns of EC and the anomalous concentration of some ions and elements in the drinking water sources. A total of 183 samples from 45 villages covering a wide range of EC mortality rates are collected and analyzed. The results demonstrate that NO3 −, SO4 2−, Sb, and Sr exceed the recommended maximum concentration level (MCL) in drinking water. This is more prominent in the villages with high esophageal cancer mortality rate, suggesting a possible link between EC incidence and water quality. Se concentration in drinking water increases from low to the high EC areas, a finding contrary to the expected trend. It is concluded that Se deficiency does not play a major role in the etiology of EC in the Golestan province. The statistical results obtained from Mann–Whitney and Kruskal–Wallis tests along with cluster analysis are consistent with the observed trend of EC mortality rate in Golestan province.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abnet, C. C., Saadatian-Elahi, M., Pourshams, A., Boffetta, P., Feizzadeh, A., Brennan, P., et al. (2004). Reliability and validity of opiate use self-report in a population at high risk for esophageal cancer in Golestan, Iran. Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Prevention, 13, 1068–1070.
Appleton, J. D., Zhang, Q., Green, K. A., Zhang, G., Ge, X., Liu, X., et al. (2006). Selenium in soil, grain, human hair and drinking water in relation to esophageal cancer in the Cixian area, Hebei province, People’s Republic of China. Applied Geochemistry, 21, 684–700.
Barrett, J. H., Parslow, R. C., McKinney, P. A., Law, G. R., & Forman, D. (1998). Nitrate in drinking water and the incidence of gastric, esophageal, and brain cancer in Yorkshire, England. Cancer Causes and Control, 9, 153–159.
Bogovski, P., & Bogovski, S. (1981). Animal species in which N-nitroso compounds induce cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 27, 471–474.
Bowman, C. A., Bobrowsky, P. T., & Selinus, O. (2003). Medical geology: New relevance in the earth sciences. Episodes, Journal of International Geosciences, 26(4), 270–277.
Brown, L. M., Hoover, R. N., Silverman, D., Baris, D., Hayes, R., Swanson, G. M., et al. (2001). Excess incidence of squamous cell esophageal cancer among U.S. Black men: Role of social class and other risk factors. American Journal of Epidemiology, 153, 114–122.
Bunnell, J. E. (2004). Medical geology: An emerging discipline on the ecosystem–human health interface. EcoHealth (Vol. 1, pp. 15–18). USA: USGS, US Department of the Interior.
Cantor, P. K. (1997). Drinking water and cancer. Cancer Causes and Control, 8, 292–308.
Centeno, J. A., Finkelman, R. B., Selinus, O. (2005). Medical geology: Impacts of the natural environment on public health. Actas da XIV Semana de Geoquimica/VIII Congresso de Geoquímica dos Países de Língua Portuguesa, Aveiro (Vol. 1, pp. 15–22).
Chen, F., Cole, P., Wen, L. F., Mi, Z. B., & Trapido, E. J. (1994). Estimates of trace-element intakes in Chinese farmers. Journal of Nutrition, 124, 196–201.
Chen, J., Geissler, C., Parpia, B., Li, J., & Campbell, T. C. (1992). Antioxidant status and cancer mortality in China. International Journal of Epidemiology, 21, 625–635.
Dissanayake, C. B., & Weerasooriya, S. V. R. (1987). Medical geochemistry of nitrates and human cancer in Sri Lanka. The International Journal of Environmental Studies, 30, 145–156.
Edige, L., & Hwang, L. (2009). Water quality and environmental health in Southern China. BSR Publication. www.bsr.org.
EPA. (2009). Drinking water contaminants. Environmental Protection Agency. 18 p. http://www.Epa.gov/safewater/contaminants/index.html.
Fan, C., Cole, P., Mi, Z. B., & Xing, L. Y. (1992). Dietary trace elements and esophageal cancer mortality in Shanxi, China. Epidemiology, 3, 402–406.
Ferlay, J., Bray, F., Pisani, P., & Parkin, D. M. (2004). GLOBOCAN 2002: Cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide. IARC CancerBase No 5 (2nd ed.). Lyon: IARC Press.
Finkelman, R. B., Skinner, H. C. W., Plumlee, G. S., & Bunnell, J. E. (2001, November 20–23). Medical geology. Geotimes.
Frechen, M., Kehl, M., Rolf, C., Sarvati, R., & Skowronek, A. (2009). Loess chronology of the Caspian Low land in Northern Iran. Quaternary International, 198, 220–233.
Gammon, M. D., Schoenberg, J. B., Ahsan, H., Risch, H. A., Vaughan, T. L., Chow, W. H., et al. (1997). Tobacco, alcohol, and socioeconomic status and adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastric cardia. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 89, 1277–1284.
Gray, E. M., & Morgan-Jones, M. (1980). A comparative study of nitrate levels at three adjacent ground-water sources in a chalk catchment area west of London. Groundwater, 18(2), 159–167.
Golestan Cancer Registry Office. (2006). Annual report.
Hill, M. J. (1997). Nutrition and human cancer. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 833, 68–78.
Iriondo, M. H., & Kröhling, D. M. (2007). Non-classical types of loess. Sedimentary Geology, 202, 352–368.
Islami, F., Kamangar, F., Nasrollahzadeh, D., Moller, H., Boffetta, P., & Malekzadeh, R. (2009a). Oesophageal cancer in Golestan province, a high-incidence area in northern Iran—a review. European Journal of Cancer, 45, 3156–3165.
Islami, F., Pourshams, A., Nasrollahzadeh, D., Kamangar, F., Fahimi, S., Shakeri, R., et al. (2009b). Tea drinking habits and oesophageal cancer in a high risk area in northern Iran: Population based case–control study. British Medical Journal, 338, b929.
Jabbari, A., Besharat, S., & Semnani, Sh. (2008). Role of silica in esophageal cancer. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 14, 3106–3107.
Jaskiewicz, K., Marasas, W. F., Rossouw, J. E., Van Niekerk, F. E., & Heine Tech, E. W. (1988). Selenium and other mineral elements in populations at risk for esophageal cancer. Cancer, 62, 2635–2639.
Kamangar, F., Malekzadeh, R., Dawsey, S. M., & Saidi, F. (2007). Esophageal cancer in northeastern Iran: A review. Archives of Iranian Medicine, 10, 70–82.
Kehl, M., Frechen, M., & Skowronek, A. (2005). Paleosols derived from loess and loess-like sediments in the basin of Perspolis, Southern Iran. Quaternary International, 140(141), 135–149.
Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Esmaeili, A., & Rastmanesh, F. (2010). The source of fluoride toxicity in Muteh area, Isfahan, Iran. Environmental Earth Science, 61, 777–786.
Kmet, J., & Mahboubi, E. (1972). Esophageal cancer in the Caspian littoral of Iran: Initial studies. Science, 175, 846–853.
Mark, S. D., Qiao, Y. L., Dawsey, S. M., Wu, Y. P., Katki, H., Gunter, E. W., et al. (2000). Prospective study of serum selenium levels and incident esophageal and gastric cancers. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 92, 1753–1763.
Munoz, N., & Day, N. E. (1996). Esophageal cancer. In D. Schottenfeld & J. F. Fraumeni Jr. (Eds.), Cancer epidemiology and prevention (2nd ed., pp. 681–706). New York: Oxford University Press.
National Research Council of America. (1978). Nitrates: An environmental assessment. Washington, DC: National Academic Press.
Nouarie, M., Pourshams, A., Kamangar, F., Sotoudeh, M., Derakhshan, M. H., Akbari, M. R., et al. (2004). Ecologic study of serum selenium and upper gastrointestinal cancers in Iran. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 10, 2544–2546.
Okhravi, R., & Amini, A. (2001). Characteristics and provenance of the loess deposits of the Gharatikan watershed in Northeast Iran. Global and Planetary Change, 28, 11–22.
Parkin, D. M., Bray, F., Ferlay, J., & Pisani, P. (2005). Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 55(2), 74–108.
Pearce, F. M. (1991). The use of ICP-MS for the analysis of natural waters and an evaluation of sampling techniques. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 13(2), 50–55.
Pourshams, A., et al. (2010). The Golestan cohort study—a prospective study of esophageal cancer in northern Iran. International Journal of Epidemiology, 39, 52–59.
Rozycki, S. Z. (1991). Loess and loess-like deposits (pp. 76–107). Wroclaw: The Publishing House of the Polish Academy of sciences.
Selinus, O. (2002). Medical geology. Method, theory and practice. In P. T. Bobrowsky (Ed.), Geoenvironmental mapping. Rotterdam: Balkema Press.
Selinus, O. (2004). Medical geology: An emerging speciality. Terrae, 1(1), A1–A8.
Selinus, O., Centeno, J., Finkelman, R., Fuge, R., Lindh, U., & Smedley, P. (Eds.). (2005). Essentials of medical geology: impacts of the natural environment on public health. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press.
Semnani, S., Roshandel, G., Zendehbad, A., Keshtkar, A., Rahimzadeh, H., Abdolahi, N., et al. (2010). Soil selenium level and esophageal cancer: An ecological study in a high risk area for esophageal cancer. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 24, 174–177.
Semnani, S., Sadjadi, A., Fahimi, S., Nouraie, M., Naeimi, M., Kabir, J., et al. (2006). Declining incidence of esophageal cancer in the Turkmen Plain, eastern part of the Caspian Littoral of Iran: A retrospective cancer surveillance. Cancer Detection and Prevention, 30, 14–19.
Stout, W. L., Fales, S. A., Muller, L. D., Schnabel, R. R., Priddy, W. E., & Elwinger, G. F. (1997). Nitrate leaching from cattle urine and faeces in Northwest USA. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61, 1787–1794.
Tuyns, A. J. (1983). Oesophageal cancer in nonsmoking drinkers and in nondrinking smokers. International Journal of Cancer, 32, 443–444.
Tzonou, A., Lipworth, L., Garidou, A., Signorello, L. B., Lagiou, P., et al. (1996). Diet and risk of esophageal cancer by histologic type in a low-risk population. International Journal of Cancer, 68, 300–304.
Wei, W. Q., Abnet, C. C., Qiao, Y. L., Dawsey, S. M., Dong, Z. W., Sun, X. D., et al. (2004). Prospective study of serum selenium concentrations and esophageal and gastric cardia cancer, heart disease, stroke, and total death. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 79, 80–85.
WHO. (2004). Guidelines for drinking water quality (p. 515). Geneva: World Health Organization.
World Bank and SEPA. (2007). Cost of pollution in China: Economic estimates of physical damages. The World Bank Group.
Wu, K., & Li, K. (2007). Association between esophageal cancer and drought in China by using Geographic Information System. Environmental International, 33, 603–608.
Yang, C. Y., Chiu, H. F., Cheng, M. F., Tsai, S. S., Hung, C. F., & Lin, M. C. (1999). Esophageal cancer mortality and total hardness levels in Taiwan’s drinking water. Environmental Research Section A, 81, 301–308.
Yang, C. X., Wang, H. Y., Wang, Z. M., Du, H. Z., Tao, D. M., Mu, X. Y., et al. (2005). Risk factors for esophageal cancer: a case control study in southwestern China. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 6, 48–53.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to M. Korei of Geological survey of Iran for financially supporting this research. We would also like to extend our thanks to the research committee of Shiraz University for logistic helps.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F., Najmeddin, A. et al. Quality of drinking water and high incidence rate of esophageal cancer in Golestan province of Iran: a probable link. Environ Geochem Health 34, 15–26 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-011-9377-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-011-9377-3