Abstract
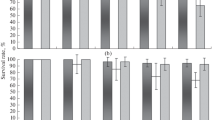
This study determined the effect of cadmium (Cd) toxicity comparatively on two copepods, Eurytemora affinis (Poppe 1880) from a temperate region (Seine Estuary, France) and Pseudodiaptomus annandalei (Sewell 1919) from a subtropical region (Danshuei Estuary, Taiwan), according to their sex and reproductive stages. In addition, the effect of Cd to their life cycle traits was quantified. In the first experiment, both copepod sexes were exposed to 40, 80, 150, 220, and 360 µg/L of Cd and a control cultured in salinity 15, except that the temperature was 18 °C for E. affinis and 26 °C for P. annandalei. This allowed calculating median lethal concentration (LC50) of Cd after 96 h. This was 120.6 µg/L Cd for P. annandalei males which were almost twice as sensitive as P. annandalei females (LC50 = 239.5 µg/L Cd). For E. affinis females, the LC50 was 90.04 µg/L Cd, reflecting a 1.4 times higher sensitivity of females than of males (LC50 = 127.75 µg/L Cd). The males of both species were similarly sensitive; however, the E. affinis females were 2.7 times more sensitive than the P. annandalei females. We also compared the sensitivity of ovigerous females (OVF) and non-ovigerous females (NOF) of both species to Cd. Mortality was higher in NOF than in OVF of both copepod species in both the control and the 40 µg/L Cd treatment. Finally, the total population, fecundity and female morphology of both copepod species were estimated after exposing one generation cycle (nauplius to adult) to 40 μg/L Cd (for E. affinis) and 160 μg/L Cd (for P. annandalei). A significant decrease in cohort production, survival and clutch size but no significant difference in the prosome length of both copepod species exposed to Cd were detected. The ratio of OVF:NOF was high in both copepod species exposed to Cd. Cd toxicity did not significantly affect the M:F sex ratio and % OVF of E. affinis. However, the effect of Cd toxicity in P. annandalei was significant in the M:F sex ratio and was in favor of females and their reproductive activities due to an increase in % OVF. Moreover, there was a significant decrease in total production of P. annandalei due to high mortality in their nauplii and copepodid developmental stages. Toxicity to Cd appears to be affected by multiple factors including sex, reproductive life stage and species. The ecological implication of Cd toxicity on E. affinis and P. annandalei copepod ecology is more related to a skewed sex ratio, low egg production, reduced hatchability and reduced survival that affects the recruitment potential of the copepod nauplii resulting in a decreasing copepod population. Mortality, reproduction and population growth of model species may provide important bio-indicators for environmental risk assessment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari TM, Marr IL, Tariq N (2004) Heavy metals in marine pollution perspective-a mini review. J Appl Sci 4:1–20
Bao VW, Koutsaftis A, Leung KM (2008) Temperature-dependent toxicities of chlorothalonil and copper pyrithione to the marine copepod ‘Tigriopus Japonicus’ and Dinoflagellate ‘Pyrocystis lunula’. Aust J Ecotoxicol 14(2/3):45
Barka S, Pavillon JF, Amiard JC (2001) Influence of different essential and non-essential metals on MTLP levels in the copepod Tigriopus brevicornis. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 128(4):479–493
Beattie JH, Pascoe D (1978) Cadmium uptake by rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri (Oncorhynchus mykiss) eggs and alevins. J Fish Biol 13(5):631–637
Benayoun G, Fowler SW, Oregioni B (1974) Flux of cadmium through euphausiids. Mar Biol 27(3):205–212
Beyrend-Dur D, Kumar R, Rao TR, Souissi S, Cheng SH, Hwang JS (2011) Demographic parameters of adults of Pseudodiaptomus annandalei (Copepoda Calanoida): temperature, salinity and generation effects. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 404:1–14
Beyrend-Dur D, Souissi S, Hwang JS (2013) Population dynamics of calanoid copepods in the subtropical mesohaline Danshuei Estuary (Taiwan) and typhoon effects. Ecol Res 28(5):771–780
Boeckman CJ, Bidwell JR (2006) The effects of temperature, suspended solids, and organic carbon on copper toxicity to two aquatic invertebrates. Water Air Soil Pollut 171(1-4):185–202
Boulangé-Lecomte C, Forget-Leray J, Xuereb B (2014) Sexual dimorphism in Grp78 and Hsp90A heat-shock protein expression in the estuarine copepod Eurytemora affinis. Cell Stress Chaperones 19(4):591–597
Bustamante P, Teyssié JL, Fowler S, Cotret O, Danis B, Warnau M (2002) Biokinetics of cadmium and zinc accumulation and depuration at different stages in the life cycle of the cuttlefish Sepia officinalis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 231:167–177
Chandler GT, Green AS (1996) A 14-day harpacticoid copepod reproduction bioassay for laboratory and field contaminated muddy sediments. Tech Aquat Toxicol 1:23–39
Chen Q, Sheng J, Lin Q, Gao Y, Lv J (2006) Effect of salinity on reproduction and survival of the copepod Pseudodiaptomus annandalei Sewell, 1919. Aquaculture 258:575–582
Chen SHI (2011) The acute toxicity of heavy metals to Pseudodiaptomus Annandalei and the effect on ingestion. J Anhui Agric Sci 12:129
Cole S, Codling ID, Parr W, Zabel T, Nature E, Heritage SN (1999) Guidelines for managing water quality impacts within UK European marine sites. Swindon: Water Research Centre. www.ukmarinesac.org.uk/pdfs/water_quality.pdf
Cripe GM, Cripe CR (1990) Comparative acute sensitivity of selected estuarine and marine crustaceans toxic substances, EPA 600/X-90/358. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Gulf Breeze, FL
Daniels RE, Allan JD (1981) Life table evaluation of chronic exposure to a pesticide. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 38(5):485–494
Dauvin JC (2008) Effects of heavy metal contamination on the macrobenthic fauna in estuaries: the case of the Seine estuary. Mar Pollut Bull 57(1):160–169
David V, Sautour B, Chardy P, Leconte M (2005) Long-term changes of the zooplankton variability in a turbid environment: The Gironde estuary (France). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64(2):171–184
De Loof A (2015) The essence of female–male physiological dimorphism: differential Ca2+-homeostasis enabled by the interplay between farnesol-like endogenous sesquiterpenoids and sex-steroids? The Calcigender paradigm. Gen Comp Endocrinol 211:131–146
Devreker D, Souissi S, Forget-Leray J, Leboulenger F (2007) Effects of salinity and temperature on the post-embryonic development of Eurytemora affinis (Copepoda; Calanoida) from the Seine estuary: a laboratory study. J Plankton Res 29(suppl_1):i117–i133
Devreker D, Souissi S, Winkler G, Forget-Leray J, Leboulenger F (2009) Effects of salinity, temperature and individual variability on the reproduction of Eurytemora affinis (Copepoda; Calanoida) from the Seine estuary: a laboratory study. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 368(2):113–123
Devreker D, Souissi S, Molinero JC, Beyrend-Dur D, Gomez F, Forget-Leray J (2010) Tidal and annual variability of the population structure of Eurytemora affinis in the middle part of the Seine Estuary during 2005. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 89(4):245–255
Dipinto LM, Coull BC, Chandler GT (1993) Lethal and sublethal effects of the sediment-associated PCB aroclor 1254 on a meiobenthic copepod. Environ Toxicol Chem 12(10):1909–1918
Dittman EK, Buchwalter DB (2010) Manganese bioconcentration in aquatic insects: Mn oxide coatings, molting loss, and Mn (II) thiol scavenging. Environ Sci Technol 44(23):9182–9188
Doi M, Toledo JD, Golez MSN, De los Santos M (1997) Preliminary investigation of feeding performance of larvae of early red-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides, reared with mixed zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 358:259–263
Dur G, Souissi S, Schmitt FG, Beyrend-Dur D, Hwang JS (2011) Mating and mate choice in Pseudodiaptomus annandalei (Copepoda: Calanoida). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 402(1):1–11
Escher BI, Hermens JL (2002) Modes of action in ecotoxicology: their role in body burdens, species sensitivity, QSARs, and mixture effects. Environ Sci Technol 36(20):4201–4217
Fang TH, Hsiao SH, Nan FH (2014) Nineteen trace elements in marine copepods collected from the coastal waters off northeastern Taiwan. Cont Shelf Res 91:70–81
Fang TH, Hwang JS, Hsiao SH, Chen HY (2006) Trace metals in seawater and copepods in the ocean outfall area off the northern Taiwan coast. Mar Environ Res 61:224–243
Fang TH, Lin CL (2002) Dissolved and particulate trace metals and their partitioning in a hypoxic estuary: the Danshuei estuary in northern Taiwan. Estuaries 25(4):598–607
FAO/BOBP (1999) Fishery Harbor Manual on the prevention of Pollution-Bay of Bengal Program Ja Sciortino, R Ravikumar. www.fao.org/docrep/x5624e/x5624e05.htm#topofpage
Fisher NS, Stupakoff I, Sañudo-Wilhelmy S, WenXiong W, Teyssié JL, Fowler SW, Crusius J (2000) Trace metals in marine copepods: a field test of a bioaccumulation model coupled to laboratory uptake kinetics data. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 194:211–218
Forget J, Pavillon JF, Menasria MR, Bocquene G (1998) Mortality and LC 50 values for several stages of the marine copepod Tigriopus brevicornis (Müller) exposed to the metals arsenic and cadmium and the pesticides atrazine, carbofuran, dichlorvos, and malathion. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 40(3):239–244
Gismondi E, Cossu-Leguille C, Beisel JN (2013) Do male and female gammarids defend themselves differently during chemical stress? Aquat Toxicol 140:432–438
Gnanamoorthy P, Manimaran K, Ashok Prabu V, Selvam T (2012) Cadmium toxicity study of copepod (Oithona similis). Int J Curr Trends Res 1(1):8–12
Golez MN, Takahashi T, Ishimarul T, Ohno A (2004) Post-embryonic development and reproduction of Pseudodiaptomus annandalei (Copepoda: Calanoida). Plankton Biol Ecol 51(1):15–25
Hagopian-Schlekat T, Chandler GT, Shaw TJ (2001) Acute toxicity of five sediment-associated metals, individually and in a mixture, to the estuarine meiobenthic harpacticoid copepod Amphiascus tenuiremis. Mar Environ Res 51(3):247–264
Hall LW, Ziegenfuss MC, Anderson RD, Lewis BL (1995) The effect of salinity on the acute toxicity of total and free cadmium to a Chesapeake Bay copepod and fish. Mar Pollut Bull 30(6):376–384
Hinck JE, Schmitt CJ, Ellersieck MR, Tillitt DE (2008) Relations between and among contaminant concentrations and biomarkers in black bass (Micropterus spp.) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio) from large US rivers, 1995–2004. J Environ Monit 10(12):1499–1518
Hsiao SH, Fang TH (2013) Trace metal contents in male, non-ovigerous and ovigerous females, and the egg sacs of the marine copepod, Euchaeta concinna Dana, 1849 (Copepoda, Euchaetidae), collected from the southern East China Sea. Crustacean 86(11):1410–1424
Hsiao SH, Hwang JS, Fang TH (2010) The heterogeneity of the contents of trace metals in the dominant copepod species in the seawater around northern Taiwan. Crustacean 83:179–194
Hutchinson TH, Williams TD, Eales GJ (1994) Toxicity of cadmium, hexavalent chromium and copper to marine fish larvae (Cyprinodon variegatus) and copepods (Tisbe battagliai). Mar Environ Res 38(4):275–290
Hwang JS, Kumar R, Hsieh CW, Kuo AY, Souissi S, Hsu MH, Chen QC (2010) Patterns of zooplankton distribution along the marine, estuarine and riverine portions of the Danshuei ecosystem in northern Taiwan. Zool Stud. 49(3):335–352
Jeng WL, Han BC (1994) Sedimentary coprostanol in Kaohsiung harbor and the Danshuei estuary, Taiwan. Mar Pollut Bull 28(8):494–499
Jiang JL, Gui-zhong W, Li-sheng W, Shao-jing L (2012) Construction of suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) library of copepod Pseudodiaptomous annandalei and its ferritin cDNA cloning and differential expression under nickel stress. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 23(7):1973–1978
Jiang XD, Wang GZ, li SJ, He JF (2007) Heavy metal exposure reduces hatching success of Acartia pacifica resting eggs in the sediment. J Environ Sci 19(6):733–737
Jiang JL, Wang GZ, Mao MG, Wang KJ, Li SJ, Zeng CS (2013) Differential gene expression profile of the calanoid copepod, Pseudodiaptomus annandalei, in response to nickel exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 157(2):203–211
Katona SK (1975) Copulation in the copepod Eurytemora affinis (Poppe, 1880). Crustaceana 28(1):89–95
Khan MAQ, Ahmed SA, Catalin B, Khodadoust A, Ajayi O, Vaughn M (2006) Effect of temperature on heavy metal toxicity to juvenile crayfish, Orconectes immunis (Hagen). Environ Toxicol 21(5):513–520
Khan MAQ, Ahmed SA, Salazar A, Gurumendi J, Khan A, Vargas M, Von Catalin B (2007) Effect of temperature on heavy metal toxicity to earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (Annelida: Oligochaeta). Environ Toxicol 22(5):487–494
Ko FC, We NY, Chou LS (2014) Bioaccumulation of persistent organic pollutants in stranded cetaceans from Taiwan coastal waters. J Hazard Mater 277:127–133
Korsman JC, Schipper AM, De Hoop L, Mialet B, Maris T, Tackx ML, Hendriks AJ (2014) Modeling the impacts of multiple environmental stress factors on estuarine copepod populations. Environ Sci Technol 48(10):5709–5717
Krupa EG (2005) Population densities, sex ratios of adults, and occurrence of malformations in three species of cyclopoid copepods in waterbodies with different degrees of eutrophy and toxic pollution. J Mar Sci Technol 13(3):226–237
Kwok KW, Souissi S, Dur G, Won EJ, Lee JS (2015) Copepods as references species in estuarine and marine waters. In: Amiard-Triquet C, Amiard JC, Mouneyrac C (eds) Aquatic ecotoxicology: advancing tools for dealing with emerging risks. London: Academic Press, p 281–308
Liao IC, Su HM, Chang EY (2001) Techniques in Finfish larviculture in Taiwan. Aquaculture 200:1–31
Lira VF, Santos GAP, Derycke S, Larrazabal MEL, Fonsêca-Genevois VG, Moens T (2011) Effects of barium and cadmium on the population development of the marine nematode Rhabditis (Pellioditis) marina. Mar Environ Res 72(4):151–159
Le Dean L, Devineau J (1985) In search of standardization: a comparison of toxicity bioassays on two marine crustaceans (Palaemon serratus and Tigriopus brevicornis). Revue des Travaux de l’Institut des Pêches Maritimes 49(3-4):187–198
Lee KW, Raisuddin S, Hwang DS, Park HG, Lee JS (2007) Acute toxicities of trace metals and common xenobiotics to the marine copepod Tigriopus japonicus: evaluation of its use as a benchmark species for routine ecotoxicity tests in Western Pacific coastal regions. Environ Toxicol 22(5):532–538
Lotufo GR, Fleeger JW (1997) Effects of sediment-associated phenanthrene on survival, development and reproduction of two species of meiobenthic copepods. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 151(1):91–102
Luoma SN, Rainbow PS (2005) Why is metal bioaccumulation so variable? Biodynamics as a unifying concept. Environ Sci Technol 39:1921–1931
Marcus N (2004) An overview of the impacts of eutrophication and chemical pollutants on copepods of the coastal zone. Zool Stud 43(2):211–217
McCahon CP, Pascoe D (1988) Increased sensitivity to cadmium of the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex (L.) during the reproductive period. Aquat Toxicol 13(3):183–193
Medina M, Barata C, Telfer T, Baird DJ (2002) Age-and sex-related variation in sensitivity to the pyrethroid cypermethrin in the marine copepod Acartia tonsa Dana. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42(1):17–22
Michalec FG, Holzner M, Menu D, Hwang JS, Souissi S (2013) Behavioral responses of the estuarine calanoid copepod Eurytemora affinis to sub-lethal concentrations of waterborne pollutants. Aquat Toxicol 138:129–138
Michibata H (1981) Uptake and distribution of cadmium in the egg of the teleost. Oryzias Latipes 19(6):691–696
Mirenda RJ (1986) Toxicity and accumulation of cadmium in the crayfish, Orconectes virilis (Hagen). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 15(4):401–407
Mohammed EH, Wang G, Xu Z, Liu Z, Wu L (2011) Physiological response of the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus experimentally exposed to cadmium. Aquac Aquar Conserv Legis Int J Bioflux Soc 4(1):99–107
Moraitou-Apostolopoulou M, Verriopoulos G (1982) Individual and combined toxicity of three heavy metals, Cu, Cd and Cr for the marine copepod Tisbe holothuriae. Hydrobiologia 87(1):83–87
Oberdörster E, Brouwer M, Hoexum-Brouwer T, Manning S, McLachlan JA (2000) Long-term pyrene exposure of grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio, affects molting and reproduction of exposed males and offspring of exposed females. Environ Health Perspect 108:641–646
Pane L, Mariottini GL, Lodi A, Giacco E (2008) Effects of heavy metals on laboratory reared Tigriopus fulvus Fischer (Copepoda: Harpacticoida). Heavy metal pollution. Nova Science Publishers, Hauppauge, NY, p 157–165
Quintin JY (2014) Surveillance écologique site du Blayais rapport scientifique. Ifremer 30–129
Ritterhoff J, Zauke GP (1997) Influence of body length, life-history status and sex on trace metal concentrations in selected zooplankton collectives from the Greenland Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 34(8):614–621
Roberts MH, Leggett AT (1980) Egg extrusion as a Kepone-clearance route in the blue crab, Callinectes sapidus. Estuaries 3(3):192–199
Roberts Jr MH, Warinner JE, Tsai CF, Wright D, Cronin LE (1982) Comparison of estuarine species sensitivities to three toxicants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 11(6):681–692
Sarkar SK, Singh BN, Choudhury A (1985) Copepod components of inshore zooplankton of the Bay of Bengal off Sagar island, west Bengal, India. Curr Sci 54:1217–1220
Sadovskaya I, Souissi A, Souissi S, Grard T, Lencel P, Greene CM, Usov AI (2014) Chemical structure and biological activity of a highly branched (1 → 3, 1 → 6)-β-d-glucan from Isochrysis galbana. Carbohydr Polym. 111:139–148
Sornom P, Felten V, Médoc V, Sroda S, Rousselle P, Beisel JN (2010) Effect of gender on physiological and behavioural responses of Gammarus roeseli (Crustacea Amphipoda) to salinity and temperature. Environ Pollut. 158(5):1288–1295
Souissi A, Souissi S, Devreker D, Hwang JS (2010) Occurrence of intersexuality in a laboratory culture of the copepod Eurytemora affinis from the Seine estuary (France). Mar Biol 157(4):851–861
Souissi A, Souissi S, Hwang JS (2016) Evaluation of the copepod Eurytemora affinis life history response to temperature and salinity increases. Zool Stud 55:4, http://zoolstud.sinica.edu.tw/55.htm
Sroda S, Cossu-Leguille C (2011) Effects of sub-lethal copper exposure on two gammarid species: which is the best competitor? Ecotoxicology 20(1):264–273
Stringer TJ, Glover CN, Keesing V, Northcott GL, Tremblay LA (2012) Development of a harpacticoid copepod bioassay: selection of species and relative sensitivity to zinc, atrazine and phenanthrene. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 80:363–371
Su HM, Cheng SH, Chen TI, Su MS (2005) Culture of copepods and applications to marine finfish larval rearing in Taiwan. In: Copepods in Aquaculture. Marcus NH, O'Bryen PJ, Lee C-S (eds) Blackwell, Oxford. p 183–194
Sullivan BK, Buskey E, Miller DC, Ritacco PJ (1983) Effects of copper and cadmium on growth, swimming and predator avoidance in Eurytemora affinis (Copepoda). Mar Biol 77(3):299–306
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology. Springer, Basel, p 133–164
Tlili S, Ovaert J, Souissi A, Ouddane B, Souissi S (2016) Acute toxicity, uptake and accumulation kinetics of nickel in an invasive copepod species: Pseudodiaptomus marinus. Chemosphere 144:1729–1737
Toudal K, RiisgArd HU (1987) Acute and sublethal effects of cadmium on ingestion, egg production and life-cycle development in the copepod Acartia tonsa. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 37:141–146
Volz DC, Chandler GT (2004) An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for lipovitellin quantification in copepods: a screening tool for endocrine toxicity. Environ Toxicol Chem 23(2):298–305
Wang WX, Fisher NS (1998) Accumulation of trace elements in a marine copepod. Limnol Oceanogr 43(2):273–283
Wang X, Zauke GP (2004) Size-dependent bioaccumulation of metals in the amphipod Gammarus zaddachi (Sexton 1912) from the River Hunte (Germany) and its relationship to the permeable body surface area. Hydrobiologia 515(1-3):11–28
Watras CJ, Back RC, Halvorsen S, Hudson RJM, Morrison KA, Wente SP (1998) Bioaccumulation of mercury in pelagic freshwater food webs. Sci Total Environ 219(2):183–208
Winkler G, Souissi S, Poux C, Castric V (2011) Genetic heterogeneity among Eurytemora affinis populations in Western Europe. Mar Biol 158:1841–1856
Yu WK, Shi YF, Fong CC, Chen Y, Van De Merwe JP, Chan AK, Wu RS (2013) Gender-specific transcriptional profiling of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) liver upon BDE-47 exposure. Comp Biochem Physiol Part D 8(3):255–262
Zamora LM, King CK, Payne SJ, Virtue P (2015) Sensitivity and response time of three common Antarctic marine copepods to metal exposure. Chemosphere 120:267–272
Acknowledgements
This study is part of a collaboration between Professor Sami Souissi of the Univ. Lille, CNRS, Univ. Littoral Côte d’Opale, UMR 8187, LOG, Laboratoire d’Océanologie et de Géosciences, 62930 Wimereux, France, and Professor Jiang-Shiou Hwang of the Institute of Marine Biology, National Taiwan Ocean University, 20224 Keelung, Taiwan. We appreciate the short-term financial sponsorship from the President of National Taiwan Ocean University to conduct a part of this research in France. This study was also funded the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST). This study is a contribution to the Associated International Laboratory (LIA-Taiwan) granted by the University of Lille since 2017 and to the project CPER 2014-2020 MARCO funded by the French government and the region Hauts-de-France as well as to the project ECOTONES of the GIP Seine-Aval. We are grateful to Edouard Husson and Dr. Yen-Ju Pan for their great assistance and support and also Dr. Sofiène Tlili for his constructive comments on the experimental protocol. We thank Prof. Hans-Uwe Dahms for his comments on the revised version of the MS. This manuscript was edited by Wallace Academic Editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadiene, E.U., Bialais, C., Ouddane, B. et al. Differences in lethal response between male and female calanoid copepods and life cycle traits to cadmium toxicity. Ecotoxicology 26, 1227–1239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1848-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1848-6