Abstract
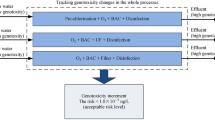
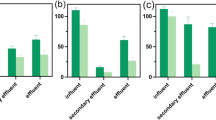
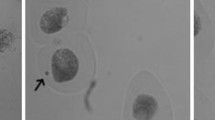
Water from the Liuxihe Reservoir (a source of drinking water for Guangzhou City, P. R. China) was analyzed for semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) and the results were used for a potential health impact assessment and genotoxicity test with the microalgae Euglena gracilis. The SVOCs were tested using USEPA Method 525.2, and the health risk assessment was conducted at a screening level using the hazard quotient (HQ) approach. Alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis (comet assay) was used to evaluate DNA damage and determine the genotoxicity of the source water. The concentrations of the SVOCs in Liuxihe Reservoir were very low and phthalic acid esters were the main SVOCs present. The mean HQ values of pollutants were all less than one, indicating no risk. However, the lifetime carcinogenic risks (LCRs) were found to be close to the threshold of 1.00E−5. The results show that the water in the Liuxihe Reservoir might pose a potential carcinogenic risk to local residents. The highly concentrated extracts of the water samples could induce DNA damage in the microalgal cells and a dose–effect relationship was identified. These results showed that Liuxihe Reservoir water, as a source of drinking water, could pose a potential LCR to local consumers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcha F, Arzul G, Rousseau S, Bardouil M (2008) Comet assay in phytoplankton as biomarker of genotoxic effects of environmental pollution. Mar Environ Res 66:59–61
Aoyama K, Iwahori K, Miyata N (2003) Application of Euglena gracilis cells to comet assay: evaluation of DNA damage and repair. Mutat Res 538:155–162
Azizullah A, Richter P, Ullah W, Ali I, Häder D-P (2013) Ecotoxicity evaluation of a liquid detergent using the automatic biotest ECOTOX. Ecotoxicology 22(6):1043–1052
Burkhardt MR, Zaugg SD, Burbank TL, Olson MC, Iverson JL (2005) Pressurized liquid extraction using water/isopropanol coupled with solid-phase extraction cleanup for semivolatile organic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH), and alkylated PAH homolog groups in sediment. Anal Chim Acta 549:104–116
Checcucci A, Colombetti G, Ferrara R, Lenci F (1976) Action spectra for photoaccumulation of green and colorless Euglena: evidence for identification of receptor pigments. Photochem Photobiol 23:51–54
Collins AR (2004) The Comet assay for DNA damage and repair principles, applications, and limitations. Mol Biotechnol 26:249–261
DeMiguel E, Iribarren I, Chacon E, Ordonez A, Charlesworth S (2007) Risk-based evaluation of the exposure of children to trace elements in playgrounds in Madrid (Spain). Chemosphere 66:505–513
Faßbender C, Braunbeck T (2013) Reproductive and genotoxic effects in zebrafish after chronic exposure to methyl methanesulfonate in a multigeneration study. Ecotoxicology 22(5):825–837
Greenberg AE, Clesceri LS, Eaton AD (1992) Standard method for examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Han BP (2010) Reservoir ecology and limnology in China: a retrospective comment. J Lake Sci 22(2):151–160
Han BP, Li T, Lin XD (2003) Eutrophication situation and control strategies of large and medium-sized service reservoirs in Guangdong Province. Science, Beijing
Hartley WR, Englande AJ, Harrington DJ (1999) Health risk assessment of groundwater contaminated with methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE). Water Sci Technol 39:305–310
Katsoyiannis A, Samara C (2005) Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the conventional activated sludge treatment process: fate and mass balance. Environ Res 97:245–257
Kavcar P, Sofuoglu A, Sofuoglu SC (2009) A health risk assessment for exposure to trace metals via drinking water ingestion pathway. Int J Hyg Environ Health 212:216–227
Kelly MG, Cazaubon A, Coring E, Dell’Uomo A, Ector L, Goldsmith B, Guasch H, Hurlimann J, Jarlman A, Kawecka B, Kwandrans J, Laugaste R, Lindstrom EA, Leitao M, Marvan P, Padisak J, Pipp E, Prygiel J, Rott E, Sabater S, Van Dam H, Vizinet J (1998) Recommendations for the routine sampling of diatoms for water quality assessments in Europe. J Appl Phycol 10:215–224
Kleinsasser NH, Wallner BC, Harreus UA, Kleinjung T, Folwacny M, Hickel R, Kehe K, Reichl FX (2004) Genotoxicity and cytotoxicity of dental materials in human lymphocytes as assessed by the single cell microgel electrophresis (comet assay). J Dent 32:229–234
Konca K, Lankoff A, Banasik A, Lisowska H, Kuszewski T, Gozdz S, Kozaz A, Wojcik A (2003) A cross-platform public domain PC image-analysis program for the comet assay. Mutat Res 534:15–20
Li GC, Xia XH, Yang ZF, Wang R, Voulvoulis N (2006) Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the middle and lower reaches of the yellow river, China. Environ Pollut 144:985–993
Li M, Hu CW, Gao XY, Xu Y, Qian X, Brown MT, Cui YB (2009) Genotoxicity of organic pollutants in source of drinking water on microalgae Euglena gracilis. Ecotoxicology 18(6):669–676
Lin QQ, Hu R, Han BP (2003) Effect of hydrodynamics on nutrient and phytoplankton distribution in Liuxihe Reservoir. Acta Ecologica Sinica 23:2278–2284 (in Chinese)
Liu M, Lin YJ, Zeng F, Cui KY, Luo X, Zeng ZX (2007) The distribution and composition of phthalate esters in the sediment of urban lakes in Guangzhou. Acta Sci Circumst 27:1377–1383 (in Chinese)
Liu H, Liang HC, Liang Y, Zhang D, Wang C, Cai HS, Shvartsev SL (2010) Distribution of phthalate esters in alluvial sediment: a case study at JiangHan Plain, Central China. Chemosphere 78:382–388
Lopes PA, Pinheiro T, Santos MC, Mathias ML, Collares-Pereira MJ, Viegas-Crespo AM (2001) Response of antioxidant enzymes in freshwater fish populations (Leuciscus alburnoides complex) to inorganic pollutants exposure. Sci Total Environ 280:153–163
Marcelo EL, Gustavo AM, Thiago BF, Fabio LSS, Flávio G, Kildare M, Marcia A, Mecia MO (2012) Euglena gracilis as a model for the study of Cu2+ and Zn2+ toxicity and accumulation in eukaryotic cells. Environ Pollut 120(3):779–786
Matsumoto M, Hirata-Koizumi M, Ema M (2008) Potential adverse effects of phthalic acid esters on human health: a review of recent studies on reproduction. Regul Toxicol Pharm 50:37–49
MHPRC (2007) Annual report of China health statistics. Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. http://www.moh.gov.cn/publicfiles/business/htmlfiles/zwgkzt/ptjnj/200807/37168.htm
Minier C, Abarnou A, Jaouen-Madoulet A, Le Guellec AM, Tutundiian R, Bocquene G, Leboulenger F (2006) A pollution-monitoring pilot study involving contaminant and biomarker measurements in the Seine Estuary, France, using zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha). Environ Toxicol Chem 25:112–119
Ministry of Water Resources Water Resources Division (2006) The notice On strengthening the management of reservoir safety. http://www.mwr.gov.cn/zwzc/zcfg/bmfggfxwj/200604/t20060410_156086.html
MWRPRC (2007) Determination of semivolatile organic compounds in water by solid phase extraction-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (gc/ms) of China
Niu JP, Liu YP, Ruan Y, Ding GW (2006) Investigation of environmental hormone level in Lanzhou Reach of Yellow River. J Environ Health 23:527–529 (in Chinese)
Papis E, Davies SJ, Jha AH (2011) Relative sensitivity of fish and mammalian cells to the antibiotic, trimethoprim: cytotoxic and genotoxic responses as determined by neutral red retention, Comet and micronucleus assays. Ecotoxicology 20(1):208–217
Sha YJ, Xia XH, Xiao XQ (2006) Distribution characters of phthalic acid ester in the waters middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. China Environ Sci 26:120–124 (in Chinese)
Shao B, Hu JY, Yang M, An W, Tao S (2005) Nonylphenol and nonylphenol ethoxylates in river water, drinking water, and fish tissues in the area of Chongqing, China. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:467–473
Shen L, Lin GF, Tan JW, Shen JH (2000) Genotoxicity of surface water samples from Meiliang bay, Taihu Lake, Eastern China. Chemosphere 41:129–132
Shen X, Liu Y, Xian QM, Zou HX, Sun C, Gao SX (2006) Monitoring of semi-volatile organic compounds in source water of Taihu Lake. Environ Pollut Control 28:396–398 (in Chinese)
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR (1988) A simple technique for quantity of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Sun F, Chen J, Tong Q, Zeng S (2007) Integrated risk assessment and screening analysis of drinking water safety of a conventional water supply system. Water Sci Technol 56:47–56
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221
Trenfield MA, Ng JC, Noller B, Markich SJ, van Dam RA (2012) Dissolved organic carbon reduces uranium toxicity to the unicellular eukaryote Euglena gracilis. Ecotoxicology 21(4):1013–1023
USEPA (1985) Development of statistical distributions or ranges of standard factors used in exposure assessments. http://www.epa.gov/ncea/pdfs/efh/references/AL.PDF
USEPA (1989) Risk assessment guidance for superfund volume i : Human health evaluation manual (part a). http://www.epa.gov/oswer/riskassessment/ragsa/pdf/rags-vol1-pta_complete.pdf
USEPA (1995) Determination of organic compounds in drinking water by liquid-solid extraction and capillary column gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. vol Method 525.2
USEPA (1997) Exposure factors handbook. http://www.epa.gov/ncea/pdfs/efh/efh-complete.pdf
USEPA (2004) Risk assessment guidance for superfund volume i: Human health evaluation manual (part e, supplemental guidance for dermal risk assessment)
USEPA (2008) Ecological risk assessment step 2 screening-level exposure estimate and risk calculation. http://www.epa.gov/R5Super/ecology/html/erasteps/erastep2.html
USERDC (2005) Data gap analysis and database expansion of parameters for munitions constituents. http://www.dtic.mil/cgibin/GetTRDoc?Location=U2&doc=GetTRDoc.pdf&AD=ADA443236
Wang CY, Li BF, Hao JS, Li GK (2006) Determination of phthalate esters in Hongfeng Lake and its pollution source. J Guizhou Edu Institu (Nat Sci) 17:42–44 (in Chinese)
Wang S, Qian X, Han BP (2010) Modeling the Effects of Inflow and Outflow Volume on Turbidity Variation in Liuxihe Reservoir. Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering (iCBBE), 2010 4th International Conference: 1–4
Wu B, Zhang Y, Zhang XX, Cheng SP (2010) Health risk from exposure of organic pollutants through drinking water consumption in Nanjing, China. B Environ Contam Tox 84:46–50
Xie ZY, Ebinghaus R, Temme C, Lohmann R, Caba A, Ruck W (2007) Occurrence and air-sea exchange of phthalates in the Arctic. Environ Sci Technol 41:4555–4560
Xu C, Shu WQ, Luo CH, Cao J (2007) Water environmental health risk assessment of PAHs and PAEs in the three Gorges Reservoir. Res Environ Sci 20:57–60 (in Chinese)
TOXNET. http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Zeng F, Cui KY, Xie ZY, Wu L, Luo DL, Chen LX, Lin YJ, Liu M, Sun JX (2009) Distribution of phthalate esters in urban soils of subtropical city, Guangzhou, China. J Hazard Mater 164:1171–1178
Zhao RS, Wang XT, Wei AX, Xu XB (2004) Determination of trihalomethanes in drinking water from Beijing, People’s Republic of China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 73:111–116
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Key Project of Unite Program of NSFC (National Natural Science Foundation of China) and Guangdong Province (No. U0733007).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Li, M., Cui, Y. et al. Potential health impact and genotoxicity analysis of drinking source water from Liuxihe Reservoir (P.R. China). Ecotoxicology 23, 647–656 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1181-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-014-1181-2