Abstract
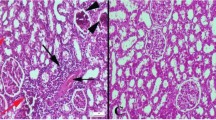
To investigate whether endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress was involved in apoptosis induced by cyanobacteria-blooming water, healthy male ICR mice were fed with water samples from cyanobacteria-blooming regions of Lake Taihu (China), including Meiliang Bay (M1 and M2), central lake region (H), macrophyte-dominated Xukou Bay (X), and tap water (control group) for three consecutive months. Hepatic and renal mRNA and protein expression of ER stress signaling molecules were measured with quantitative real-time PCR and western blotting. Compared to macrophyte-dominated and control water samples, cyanobacteria-blooming water changed hepatic ER stress signaling molecules. M1 water treatment increased the mRNA and protein levels of glucose regulation protein 78 (GRP78) and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), and decreased the mRNA levels of B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2). M2 water treatment up-regulated GRP78 mRNA and protein expression, whereas H water treatment up-regulated mRNA and protein expression of GRP78 and caspase-12. Cyanobacteria-blooming water exposure also changed mRNA and protein expression of ER stress signaling molecules in the kidneys. M1 water exposure up-regulated GRP78 mRNA and protein expression and CHOP mRNA expression, whereas M2 water treatment up-regulated caspase-12 and Bcl-2 mRNA expression. M1 and M2 cyanobacteria-blooming water exposure significantly increased relative liver weights, and induced hepatic cell apoptosis. However, cyanobacteria-blooming water treatment did not change kidney weights, and did not induce renal apoptosis compared to macrophyte-dominated and control water samples. Hence, cyanobacteria-blooming water induces hepatic apoptosis via ER stress, and ER stress may play an important role in the apparent anti-apoptotic effects on renal cells exposed to cyanobacteria-blooming water.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albina ML, Alonso V, Linares V, Belles M, Sirvent JJ, Domingo JL, Sanchez DJ (2010) Effects of exposure to BDE-99 on oxidative status of liver and kidney in adult rats. Toxicology 271(1–2):51–56
Alnemri ES, Livingston DJ, Nicholson DW, Salvesen G, Thornberry NA, Wong WW, Yuan JY (1996) Human ICE/CED-3 protease nomenclature. Cell 87(2):171
Bedard K, MacDonald N, Collins J, Cribb A (2004) Cytoprotection following endoplasmic reticulum stress protein induction in continuous cell lines. Basic Clin Pharmacol 94(3):124–131
Chen T, Zhao XY, Liu Y, Shi Q, Hua ZC, Shen PP (2004) Analysis of immunomodulating nitric oxide, iNOS and cytokines mRNA in mouse macrophages induced by microcystin-LR. Toxicology 197(1):67–77
Codd GA, Morrison LF, Metcalf JS (2005) Cyanobacterial toxins: risk management for health protection. Toxicol Appl Pharm 203(3):264–272
Cribb AE, Peyrou M, Muruganandan S, Schneider L (2005) The endoplasmic reticulum in xenobiotic toxicity. Drug Metab Rev 37(3):405–442
Ding WX, Ong CN (2003) Role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial changes in cyanobacteria-induced apoptosis and hepatotoxicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 220(1):1–7
Fawell JK, Mitchell RE, Everett DJ, Hill RE (1999) The toxicity of cyanobacterial toxins in the mouse: I Microcystin-LR. Hum Exp Toxicol 18(3):162–167
Ferri KF, Kroemer G (2001) Organelle-specific initiation of cell death pathways. Nat Cell Biol 3(11):E255–E263
Groenendyk J, Michalak M (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum quality control and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Pol 52(2):381–395
Hotamisligil GS (2010) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the inflammatory basis of metabolic disease. Cell 140(6):900–917
Huang P, Zheng Q, Xu LH (2011) The apoptotic effect of oral administration of microcystin-RR on mice liver. Environ Toxicol 26(5):443–452
Kaufman RJ (1999) Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev 13(14):1211–1233
Kohno K (2010) Stress-sensing mechanisms in the unfolded protein response: similarities and differences between yeast and mammals. J Biochem 147(1):27–33
Liu H, Miller E, van de Water B, Stevens JL (1998) Endoplasmic reticulum stress proteins block oxidant-induced Ca2+ increases and cell death. J Biol Chem 273(21):12858–12862
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T) (-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Mandl J, Meszaros T, Banhegyi G, Hunyady L, Csala M (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum: nutrient sensor in physiology and pathology. Trends Endocrin Met 20(4):194–201
Mattson MP, LaFerla FM, Chan SL, Leissring MA, Shepel PN, Geiger JD (2000) Calcium signaling in the ER: its role in neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci 23(5):222–229
McManus JFA, Mowry RW (1965) Staining methods, histological and histochemical. Hoeber Medical Division Harper and Row, New York
Mizuta T, Shimizu S, Matsuoka Y, Nakagawa T, Tsujimoto Y (2007) A Bax/Bak-independent mechanism of cytochrome c release. J Biol Chem 282(22):16623–16630
Morena I, Pichardo S, Jos A, Gomez-Amores L, Mate A, Vazquez CM, Camean AM (2005) Antioxidant enzyme activity and lipid peroxidation in liver and kidney of rats exposed to microcystin-LR administered intraperitoneally. Toxicon 45(4):395–402
Morris JA, Dorner AJ, Edwards CA, Hendershot LM, Kaufman RJ (1997) Immunoglobulin binding protein (BiP) function is required to protect cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress but is not required for the secretion of selective proteins. J Biol Chem 272(7):4327–4334
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan JY (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403(6765):98–103
Ohta T, Sueoka E, Iida N, Komori A, Suganuma M, Nishiwaki R, Tatematsu M, Kim SJ, Carmichael WW, Fujiki H (1994) Nodularin, a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1 and phosphatase-2a, is a new environmental carcinogen in male F344 rat-liver. Cancer Res 54(24):6402–6406
Oyadomari S, Araki E, Mori M (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells. Apoptosis 7(4):335–345
Paschen W (2001) Dependence of vital cell function on endoplasmic reticulum calcium levels: implications for the mechanisms underlying neuronal cell injury in different pathological states. Cell Calcium 29(1):1–11
Paschen W (2003) Endoplasmic reticulum: a primary target in various acute disorders and degenerative diseases of the brain. Cell Calcium 34(4–5):365–383
Prieto AI, Jos A, Pichardo S, Moreno I, Camean AM (2006) Differential oxidative stress responses to microcystins LR and RR in intraperitoneally exposed tilapia fish (Oreochromis sp.). Aquat Toxicol 77(3):314–321
Qin BQ, Zhu GW, Gao G, Zhang YL, Li W, Paerl HW, Carmichael WW (2010a) A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ Manage 45(1):105–112
Qin WD, Xu LZ, Zhang XX, Wang YP, Meng XY, Miao AJ, Yang LY (2010b) Endoplasmic reticulum stress in murine liver and kidney exposed to microcystin-LR. Toxicon 56(8):1334–1341
Qiu T, Xie P, Ke ZX, Li L, Guo LG (2007) In situ studies on physiological and biochemical responses of four fishes with different trophic levels to toxic cyanobacterial blooms in a large Chinese lake. Toxicon 50(3):365–376
Qiu T, Xie P, Liu Y, Li GY, Xiong Q, Hao L, Li HY (2009) The profound effects of microcystin on cardiac antioxidant enzymes, mitochondrial function and cardiac toxicity in rat. Toxicology 257(1–2):86–94
Rao RV, Hermel E, Castro-Obregon S, del Rio G, Ellerby LM, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE (2001) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program—mechanism of caspase activation. J Biol Chem 276(36):33869–33874
Rao RV, Peel A, Logvinova A, del Rio G, Hermel E, Yokota T, Goldsmith PC, Ellerby LM, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE (2002) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program: role of the ER chaperone GRP78. FEBS Lett 514(2–3):122–128
Rutkowski DT, Wu J, Back SH, Callaghan MU, Ferris SP, Iqbal J, Clark R, Miao HZ, Hassler JR, Fornek J, Katze MG, Hussain MM, Song B, Swathirajan J, Wang JY, Yau GDY, Kaufman RJ (2008) UPR Pathways combine to prevent hepatic steatosis caused by ER stress-mediated suppression of transcriptional master regulators. Dev Cell 15(6):829–840
Shen PP, Zhao SW, Zheng WJ, Hua ZC, Shi Q, Liu ZT (2003) Effects of cyanobacteria bloom extract on some parameters of immune function in mice. Toxicol Lett 143(1):27–36
Song LR, Chen W, Peng L, Wan N, Gan NQ, Zhang XM (2007) Distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in water columns: a systematic investigation into the environmental fate and the risks associated with microcystins in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. Water Res 41(13):2853–2864
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2007) Role of the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition in cell death. Apoptosis 12(5):835–840
Verkhratsky A, Toescu EC (2003) Endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ homeostasis and neuronal death. J Cell Mol Med 7(4):351–361
Wei YN, Weng D, Li F, Zou X, Young DO, Ji JG, Shen PP (2008) Involvement of JNK regulation in oxidative stress-mediated murine liver injury by microcystin-LR. Apoptosis 13(8):1031–1042
Xie P (2008) Historical development of cyanobacteria with bloom disaster in Lake Taihu. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Ye WJ, Liu XL, Tan J, Li DT, Yang H (2009) Diversity and dynamics of microcystin-Producing cyanobacteria in China’s third largest lake, Lake Taihu. Harmful Algae 8(5):637–644
Yu SZ (1995) Primary prevention of hepatocellular-carcinoma. J Gastroen Hepatol 10(6):674–682
Zhang D, Xie P, Liu YQ, Qiu T (2009a) Transfer, distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in the aquatic food web in Lake Taihu, China, with potential risks to human health. Sci Total Environ 407(7):2191–2199
Zhang H, Zhang J, Zhu Y (2009b) Identification of microcystins in waters used for daily life by people who live on Tai Lake during a serious cyanobacteria dominated bloom with risk analysis to human health. Environ Toxicol 24(1):82–86
Zhang ZY, Qin WD, Cheng SP, Xu LZ, Wang T, Zhang XX, Wu B, Yang LY (2011) Assessing the toxicity of ingested Taihu Lake water on mice via hepatic histopathology and matrix metalloproteinase expression. Ecotoxicology 20(5):1047–1056
Zong WX, Li C, Hatzivassiliou G, Lindsten T, Yu QC, Yuan J, Thompson CB (2003) Bax and Bak can localize to the endoplasmic reticulum to initiate apoptosis. J Cell Biol 162(1):59–69
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2008CB418102). The authors sincerely thank Professor Long Yi, from Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, Medical School of Nanjing University, for the histopathological evaluations of liver and kidney tissues of mice.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare having no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, W., Yang, L., Zhang, X. et al. Cyanobacteria-blooming water samples from Lake Taihu induce endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver and kidney of mice. Ecotoxicology 21, 1495–1503 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0903-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-012-0903-6