Abstract
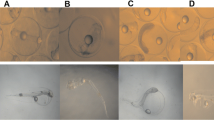
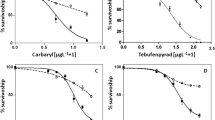
The application of many current-use pesticides has increased after the disuse of persistent, bioaccumulative or toxic ones as DDT or chlordane. Many of the used pesticides are considered less dangerous towards the environment for their physico-chemical properties. This study investigated the toxic effects of three current-use pesticides, pentachlorophenol (PCP), azinphos-methyl (AZM), and chlorpyrifos, on Mediterranean sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus early development and offspring quality. The experimental results showed that the most toxic pesticides were PCP and AZM at EC50 level. Nevertheless at low concentration PCP resulted the less toxic compound and showed EC1 value more protective than NOEC. PCP at high concentration seemed to modify cytoskeleton assembly, while at low concentrations, it could alter the deposition of the larval skeleton. OPs at low concentrations until 300 μg/l showed a similar toxicological behaviour with a trend corresponding to the pesticide concentrations. At high concentration (500 μg/l) the effect mainly observed was the embryos pre-larval arrest. This investigation highlighted the relevance to evaluate, in coastal seawaters, the levels of the used pesticides to understand the real impact on benthic populations mainly in sites characterized by intensive agriculture or floriculture activities, such as the coastal areas of the Mediterranean Sea.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aluigi MG, Falugi C (2010) Dose-dependent effects of chlorpyriphos, an organophosphate pesticide, on metamorphosis of the sea urchin, Paracentrotus lividus. Ecotoxicology 19:520–529
Aluigi MG, Angelini C, Corte G, Falugi C (2008) The sea urchin, Paracentrotus lividus, embryo as a “bioethical” model for neurodevelopmental toxicity testing. Cell Biol Toxicol 24:587–601
Arcand Y, Hawari J, Guiot SR (1995) Solubility of pentachlorophenol in aqueous solutions: the pH effect. Water Res 29:131–136
Arizzi Novelli A, Argese E, Tagliapietra D, Bettiol C, Volpi Ghirardini A (2002) Toxicity of tributyltin and triphenyltin towards early life stages of Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Environ Toxicol Chem 21:859–864
ASTM (American Society for Testing, Materials) (2004) Standard guide for conducting static acute toxicity tests with echinoid embryos. ASTM Standard Guide E 1563–98. In: Annual book of ASTM standards, Section 11: biological effects and environmental fate; biothecnology; pesticides, vol 115. ASTM, West Conshohochen
Bay S, Burgess R, Nacci D (1993) Status and applications of echinoid (Phylum: Echinodermata) toxicity test methods. In: Landis WG, Hughes JS, Lewis MA (eds) Environmental toxicology risk assessment. ASTM STP 1179. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, pp 281–302
Bellas J, Beiras R, Marino-Balsa JC, Fernandez N (2005) Toxicity of organic compounds to marine invertebrate embryos and larvae: a comparison between the sea urchin embryogenesis bioassay and alternative test species. Ecotoxicology 14:337–353
Bressan M, Marin M, Brunetti R (1995) Influence of temperature and salinity on embryonic-development of Paracentrotus lividus (lmk, 1816). Hydrobiologia 304:175–184
Burgess MR, Schweitzer KA, McKinney RA, Phelps DK (1993) Contaminated marine sediment: water column and interstitial toxic effects. Environ Toxicol Chem ETOCDK 12:127–138
Butler PA (1963) A review of fish, wildlife service investigations during 1961 and 1962. Circular 167. US Fish Wildl Serv, Washington DC
Buznikov GA, Nikitina LA, Bezuglov VV, Lauder JM, Padilla S, Slotkin TA (2001) An invertebrate model of the developmental neurotoxicity of insecticides: effects of chlorpyrifos and dieldrin in sea urchin embryos and larvae. Environ Health Perspect 109(7):651–661
Buznikov GA, Nikitina LA, Rakic LM, Milosevic I, Bezuglov VV, Lauder JM, Slotkin TA (2007) The sea urchin embryo, an invertebrate model for mammalian developmental neurotoxicity, reveals multiple neurotransmitter mechanisms for effects of CPF: therapeutic interventions and a comparison with the monoamine deplete, reserpine. Brain Res Bull 74:221–231
Cesar A, Marin A, Marin-Guirao L, Vita R (2004) Amphipod and sea urchin tests to assess the toxicity of Mediterranean sediments: the case of Portman Bay. Sci Mar 68:205–213
Cripe GM, Goodman LR, Hansen DJ (1984) Effect of chronic exposure to EPN and to guthion on the critical swimming speed and brain acetylcholinesterase activity of Cyprinodon variegatus. Aquatic Toxicol. 5:255–266
Davis HC, Hidu H (1969) Effects of pesticides on embryonic development of clams and oysters and on survival and growth of the larvae. Fish Bull 67(2):393–404
Dunnett CW (1964) New tables for multiple comparisons with a control. Biometrics 20:482–491
ERMA (2009) Environmental Risk Management Authority Decision ERMA New Zealand Decision: Application HRC07002. http://www.ermanz.govt.nz/news-events/archives/media-releases/2009/mr-20091106.html
Falugi C, Prestipino G (1987) Effects of some inhibitors on the cholinergic system active during the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus development. In: Boudouresque CF (ed) Colloque International sur Paracentrotus lividus. Gis Posidonie publ, Marseilles, pp 147–155
Falugi C, Pieroni M, Drews U, Stengel P, Lammerding-Koppel M (1992) Possible functions of the “embryonic” cholinergic system present in gametes at fertilization. In: Scalera Liaci L, Canicattì C (eds) Echinoderm research. Balkema press, Rotterdam, pp 161–164
Foster S, Thomas M, Korth W (1998) Laboratory derived acute toxicity of selected pesticides to Ceriodaphnia dubia Aust. J Ecotoxicol 4:53–59
Harrison PK, Falugi C, Angelini C, Whitaker MJ (2002) Muscarinic signalling affects intracellular calcium concentration during the first cell cycle of sea urchin embryos. Cell Calcium 31(6):289–297
Hartgers EM, Heugens EHW, Deneer JW (1999) Effect of lindane on the clearance rate of Daphnia magna. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 36:399–404
His E, Seaman MNL (1993) Effects of twelve pesticides on larvae of oysters (Crassosstrea gigas) and on two species of unicellular marine algae (Isochrysis galbana and Chaetoceros calcitrans). Comm Meet Int Counc Explor Sea CM-ICES/E 22:1–8
His E, Heyvang I, Geffard O, De Mountadouin X (1999) A comparison between oyster (Crassostrea gigas) and sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) larval bioassay for toxicological studies. Wat Res 7:1706–1718
Hutchinson TT, Scholz N, Guhl W (1998) Analysis of the ECETOC aquatic toxicity (EAT) database IV–Comparative toxicity of chemical substances to freshwater versus saltwater organisms. Chemosphere 36(1):143–153
Johnson WW, Finley MT (1980) Handbook of acute toxicity of chemicals to fish and aquatic invertebrates. Resource publication 137. US Department of Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service, Washington DC, p 65
Kaiser KLE, Valdmanis I (1981) Apparent octanol/water partition coefficients of pentachlorophenol as a function of pH. Can J Chem 60:2104–2106
Key PB, Fulton MH (1993) Lethal and sublethal effects of chlorpyrifos exposure on adult and larval stages of the grass shrimp Palaemonetes pugio. J Environ Sci Health B 28(5):621–640
Kobayashi N (1991) Marine pollution bioassay by using sea urchin eggs in the Tanabe Bay, Wakayama Prefecture, Japan, 1970–1987. Marine Pollut Bull 23:709–713
Kobayashi N (1995) Bioassay data for marine pollution using echinoderms. In: Cheremisinoff PN (ed) Encyclopedia of environmental control technology. Gulf Publ Co, Houston, pp 539–609
Kobayashi N, Okamura H (2002) Effects of new antifouling compounds on the development of sea urchin. Mar Pollut Bull 44:748–751
LeBlanc GA, Bain LJ (1997) Chronic toxicity of environmental contaminants: sentinels and biomarkers. Environ Health Perspect 105:65–80
Leung KMY, Morritt D, Wheeler JR, Whitehouse P, Sorokin N, Toy R, Holt M, Crane M (2001) Can saltwater toxicity be predicted from freshwater data? Mar Pollut Bull 42(11):1007–1013
Mansueto C, Gianguzza M, Dolcemascolo G, Pellerito L (1993) Effects of tributyltin (IV) chloride exposure on early embryonic stages of Ciona intestinalis in vivo and ultrastructural investigations. Appl Organomet Chem 7:391–399
Manzo S (2004) Sea urchin embryotoxicity test: proposal for a simplified bioassay. Ecotox Environ Safety 57(2):123–128
Manzo S, Torricelli L (2000) Preliminary findings about Regione Campania (South Italy) coastal water ecotoxicological data. Abstract book of II, National Conference of Sea Science, Geneva, 21/25 November, 223
Manzo S, Buono S, Cremisini C (2006) Toxic effects of Irgarol and Diuron on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus early development, fertilization, and offspring quality. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 51:61–68
Manzo S, Buono S, Cremisini C (2008) Predictability of copper, irgarol, and diuron combined effects on sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54:57–68
Marin MG, Moschino V, Cima F, Celli C (2000) Embryotoxicity of butyltin compounds to the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Mar Environ Res 50:231–235
Martello LB, Tjeerdema RS, Smith WS, Kauten RJ, Crosby DG (1998) Influence of salinity on the actions of pentachlorophenol in Haliotis as measured by in vivo 31P-NMR spectroscopy. Aquat Toxicol 41:229–250
Mayer FL Jr (1987) Acute toxicity handbook of chemicals to estuarine organisms. EPA/600/8–87/017. Environmental Research Laboratory, Gulf Breeze, p 274
Mitchell P (1961) Coupling of phosphorylation to electron and hydrogen transfer by a chemiosmotic type of mechanism. Nature 191:144–148
Mitchell P, Moyte J (1967) Acid-base titration across the membrane system of rat liver mitochondria. Catalysis by uncouplers. Biochem J 104:588–600
Moore DRJ, Caux PY (1997) Estimating low toxic effects. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:794–801
Morale A, Coniglio L, Angelini C, Cimoli G, Bolla A, Alleteo D, Russo P, Falugi C (1998) Biological effects of a neurotoxic pesticide at low concentrations on sea urchin early development. A teratogenic assay. Chemosphere 37(14–15):3001–3010
Morton MG, Mayer FL Jr, Dickson KL, Waller WT, Moore JC (1997) Acute and chronic toxicity of azinphos-methyl to two estuarine species, Mysidopsis bahia and Cyprinodon variegatus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 32:436–441
Muir J, Eduljee G (1999) PCP in the freshwater and marine environment of the European Union. Sci Total Environ 236:41–56
Muir DC, Teixeira C, Wania F (2004) Empirical and modeling evidence of regional atmospheric transport of current-use pesticides. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:2421–2432
Muller F (2000) Agrochemicals: composition, production, toxicology, applications. Wiley, Toronto, p 541
Nimmo DR, McEwen LC (1994) Pesticides. In: Calow P (ed) Handbook of Ecotoxicology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 155–203
Ozretic B, Krajnovic-Ozretic (1985) Morphological and biochemical evidence of the toxic effect of pentachlorophenol on the developing embryos of the sea urchin. Aquat Toxicol 7:255–263
Pagano G, Cipollaro M, Corsale G, Esposito A, Ragucci E, Giordano GG, Trieff NM (1986) The sea urchin: bioassay for the assessment of damage from environmental contaminants. In: Cairns J (ed) Community toxicity testing. ASTM STP920. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, pp 66–92
Pagano G, Corsale G, Esposito A, Dinnel PA, Romana LA (1989) Use of sea urchin sperm and embryo bioassay in testing the sublethal toxicity of realistic pollutant level. Adv Appl Biotech Ser 5:153–163
Pagano G, Iaccarino M, Guida M, Manzo S, Oral R, Romanelli R, Rossi M (1996a) Cadmium toxicity in spiked sediment to sea urchin embryos and sperm. Mar Environ Res 42:54–55
Pagano G, His E, Beiras R, De Biase A, Korkina LG, Iaccarino M, Oral R, Qiuniou Warnau M, Trieff NM (1996b) Cytogenetic, developmental, and biochemical effects of aluminium, iron, and their mixture in sea urchins and mussels. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 31:466–474
Pagano G, Korkina LG, Iaccarino M, De Biase A, Deva IB, Doroniu YK, Guida M, Melluso G, Oral R, Trieff NM, Warnau M (2001) Developmental, cytogenetic and biochemical effects in sea-urchinbioassays. In: Garrignos P, Walker CH, Barth H, Narbonne JF (eds) Biomarkers in marine ecosystems: a pratical approach. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 85–129
Pesando D, Huitorelb P, Dolcinia V, Angelinic C, Guidettid P, Falugic C (2003) Biological targets of neurotoxic pesticides analysed by alteration of developmental events in the Mediterranean sea urchin, Paracentrotus lividus. Mar Environ Res 55:39–57
Portmann JE, Wilson KW (1971) The toxicity of 140 substances to the brown shrimp and other marine animals. MAFF Shellfish information leaflet No 22. Essex, England, p 12
Repetto G, Jos A, Hazen MJ, Molero ML, del Peso A, Salguero M, Castillo PD, Rodriguez-Vicente MC, Repetto M (2001) A test battery for the ecotoxicological evaluation of pentachlorophenol. Toxicol In Vitro 15(4–5):503–509
Ringwood Huffman A (1992) Comparative sensitivity of gametes and early developmental stages of a sea urchin species (Echinometra mathei) and a bivalve species (Isognomon californicum) during metal exposures. Arch Environ Contain Toxicol 22:265–288
Santiago EC, Kwan CS (2007) Endocrine-disrupting phenols in selected rivers and bays in the Philippines. Mar Pollut Bull 54:1036–1046
Scholze M, Boedeker W, Faust M, Backhaus T, Altenburger R, Grimme H (2001) A general best-fit method for concentration response curves and the estimation of low effect concentrations. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:448–457
Sciarrino S, Matranga V (1995) Effects of retinoic acid and dimethylsulfoxide on the morphogenesis of the sea urchin embryo. Cell Biol Int 19(8):675–680
Scott A (2008) “Europe Rejects Appeal for Use of Azinphos-methyl Pesticide”. Chemical Week. http://www.chemweek.com/envirotech/regulatory/13435.html. Accessed Aug 11 2008
Scow K, Goyer M, Payne E, Perwak J, Thomas R, Wallace D, Walker P, Wood M, Delpire L (1980) An exposure and risk assessment for pehtachlorophenol. Final report. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA-440/4–81/021, Washington DC
Shelley LK, Balfry KS, Ross PS, Kennedy CJ (2009) Immunotoxicological effects of a sub-chronic exposure to selected current-use pesticides in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquatic Toxicol 92:95–103
Shief JN, Choa ML, Chen CY (2001) Statistical comparisons of the no-observed-effect concentration and the effective concentration at 10% inhibition (EC10) in algal toxicity test. Water Sci Technol 43:141–146
Skalski JR (1981) Statistical inconsistencies in the use of no-observed-effect levels in toxicity testing. In: Branson DR, Dickson KL (eds) Aquatic Toxicology and Hazard Assessment: Fourth Conference. ASTM STP 737. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, pp 377–387
Spromberg JA, Meador JP (2006) Relating chronic toxicity responses to population level effects: a comparison of population-level parameters for three salmon species as a function of low-level toxicity. Ecol Model 199:240–252
Timchalk C (2001) Organophosphate pharmacokinetics. In: Krieger R (ed) Handbook of pesticide toxicology, vol 2. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 929–951
Tomlin C (ed) (1994) The pesticide manual. Tenth edition. British Crop Protection Council, p 1341
Tomlin C (ed) (2006) The pesticide manual. 14th edition British Crop Protection Council (BCPC), p 1350
US EPA (2002) Interim Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Chlorpyrifos. http://www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/REDs/chlorpyrifos_ired.pdf
US EPA (2009) Reregistration Eligibility Decision for Azinphos-Methyl. www.epa.gov/oppsrrd1/reregistration/azm/phaseout_fs.htm
US EPA (1993) A linear interpolation method for sublethal toxicity: the inhibition concentration (ICp) approach. National Effluent Toxicity Assessment Center Technical Report 03–93. Environmental Research Laboratory, Duluth
Van Der Hoeven N, Noppert F, Annegaaike L (1997) How to measure no effect. Part I: towards a new measure of chronic toxicity in ecotoxicology. Introduction and workshop results. Environmetrics 8:241–248
Van Wijngaarden RPA, Brock TCM, Douglas MT (2005) Effects of chlorpyrifos in freshwater model ecosystems: do experimental conditions change ecotoxicological threshold levels? Pest Manag Sci 61:923–935
Volpi Ghirardini A, Arizzi Novelli A (2001) A sperm cell toxicity test procedure for the Mediterranean species Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Environ Technol 22:439–445
Whiting VK, Gripe GM, Lepo JE (1996) Effects of the anionic surfactant, sodium dodecyl sulfate, on newly-hatched Blue crabs, Callinectes sapidus, and other routinely tested estuarine crustaceans Arch. Environ Contam Toxicol 31:293–295
Worthing CR (ed) (1991) The pesticide manual: a world compendium. Ninth Edition. The British Crop Protection Council
Zha J, Wang Z, Schlenk D (2006) Effects of pentachlorophenol on the reproduction of Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Chemico-Biological Interactions 161:26–36
Zuñiga M, Roa R, Larrain A (1995) Sperm cell bioassay with the sea urchin Arbacia spatuligera on samples from two polluted chilean coastal sites. Mar Pollut Bull 30:313–319
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buono, S., Manzo, S., Maria, G. et al. Toxic effects of pentachlorophenol, azinphos-methyl and chlorpyrifos on the development of Paracentrotus lividus embryos. Ecotoxicology 21, 688–697 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0827-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-011-0827-6