Abstract
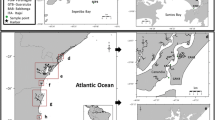
Surface sediment samples were analyzed for organotins namely tributyltin (TBT), dibutyltin and monobutyltin from six areas located in the Gulf of Cádiz (14 stations), Spain. The total butyltin ranged between undetected and 1,580 ng Sn g−1. TBT generally prevailed in most of the samples, suggesting fresh inputs of butyltin compounds and/or less degradation of TBT. The observed levels of butyltins at several sites are much higher than that required to induce toxic effect on marine organisms, suggesting that these sediments are polluted with butyltin compounds. The clam Ruditapes philippinarum was used for studying bioaccumulation of butyltins by exposing them to contaminated sediments from the Gulf of Cádiz over a period of 28 days under laboratory conditions. Biota-sediment accumulation factor (BSAF) ranged from 0.44 to 3.99.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Allah AMA (1995) Occurrence of organotin compounds in water and biota from Alexandria harbour. Chemosphere 30:707–715
Alzieu C, Michel P, Tolosa I, Bacci E, Mee LD, Readman JW (1991) Organotin compounds in Mediterranean: a continuing cause for concern. Mar Environ Res 32:261–270
ANZECC/ARMCANZ (2000) Australian and New Zealand guidelines for fresh and marine water quality. Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council/Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand, Canberra
Beaumont AR, Newman PB (1986) Low levels of tributyltin reduce growth of marine micro-algae. Mar Pollut Bull 17:457–461
Bhosle NB, Garg A, Jadhav S, Harji R, Sawant SS, Venkat K, Anil AC (2004) Butyltins in water, biofilm, animals and sediments of the west coast of India. Chemosphere 57:897–907
Blanca AL (2008) Environmental levels, toxicity and human exposure to tributyltin (TBT)-contaminated marine environment. A review. Environ Int 34:292–308
Bortoli A, Troncon A, Dariol S, Pellizzato F, Pavoni B (2003) Butyltins and phenyltins in biota and sediments from the Lagoon of Venice. Oceanologia 45:7–23
Chiavarini S, Massanisso P, Nicolai P, Nobili C, Morabito R (2003) Butyltins concentration levels and imposex occurrence in snails from the Sicilian coasts (Italy). Chemosphere 50:311–319
Coelho MR, Bebianno MJ, Langston WJ (2002) Routes of TBT uptake in the clam Ruditapes decussatus. I. Water and sediments as vectors of TBT uptake. Mar Environ Res 54:179–192
Delado CL, Wada N, Mark W, Rosegrant Meijer S, Mahfuzuddin A (2003) Fish to 2020. Supply and demand in changing global markets. Jointly published by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), Washington DC and World Fish Center, Penang, Malaysia
Díez S, Abalos M, Bayona JM (2002) Organotin contamination in sediments from the Western Mediterranean enclosures following 10 years of TBT regulation. Wat Res 36:905–918
El Rayis OA (1985) Re-assesment of the titration method for determination of organic carbon in recent sediment. Rapp Comm Int Mediterr Contam Toxicol 35:348–353
EPA (1999) Topics related to the superfund TBT study at the harbour island site, waterway sediment operable unit. Technical memorandum. US Army. Corps of Engineers and US Environmental Protection Agency, Region 10, Seattle, WA
ESI (1999) Tributyltin in marine sediments and the bioaccumulation of tributyltin: combined data report. Prepared for the Port of Seattle, Lockheed Martin, Shipyards, and Todd Shipyards, for submittal to US Environmental Protection Agency, Region 10, Seattle, WA. EVS Solutions, Inc., Seattle, WA
Evans SM, Birchenough AC, Brancato MS (2000) The TBT ban: out of the frying pan into the fire? Mar Pollut Bull 40:204–211
Gabrielides GP, Alzieu C, Readman JK, Bacci E, Aboul Dahab O, Salihoglu I (1990) MED POL survey of organotins in the Mediterranean. Mar Poll Bull 21:233–237
Garg A, Bhosle NB (2005) Butyltin compounds in the Oyster Saccostrea cucculata, from the west coast of India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 75:982–988
Gómez-Ariza JL, Morales E, Giraldez I (1998) Spatial distribution of butyltin and phenyltin compounds on the Huelva Coast (southwest Spain). Chemosphere 37:937–950
Hoch M (2001) Organotin compounds in the environment—an overview. Appl Geochem 16:719–743
IMO (2003) Antifouling systems. International convention on the control of harmful antifouling systems on ships, 2001. International Maritime Organization, London
Jacobsen JA (2000) Organotin compounds in the Danish marine environment: analysis and fate studies. PhD, Roskilde University and the National Environmental Research Institute, Roskilde, Denmark
Kannan K, Tanabe S, Iwata H, Tatsukawa R (1995) Butyltins in muscle and liver of fish collected from certain Asian and Oceanian countries. Environ Pollut 90:279–290
Langston WJ, Burt GR (1991) Bioavailability and effects of sediment-bound TBT in deposit-feeding clams, Scrobicularia plana. Mar Environ Res 32:61–77
Lee CC, Hsieh CY, Tien CJ (2006) Factors influencing organotin distribution in different marine environmental compartments, and their potential health risk. Chemosphere 65:547–559
Morabito R, Chiavarini S, Cremisi C (1995) Speciation of organotin compounds in environmental samples by GC–MS. In: Quevauviller P, Maier E, Griepink B (eds) Quality assurance for environmental analysis. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 435–463
Quevauviller P, Lavigne R, Pinel R, Astruc M (1989) Organotin in sediments and mussels from Sado Estuarine systems (Portugal). Environ Poll 57:149–166
Rajendran RB, Tao H, Miyazaki A, Ramesh R, Ramachandran S (2001) Determination of butyl-, octyl- and tributylmonomethyltin compounds in a marine environment (Bay of Bengal, India) using gas chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Environ Monitor 3:627–634
Riba I, DelValls TA, Forja JM, Gómez-Parra A (2003) Comparative toxicity of contaminated sediment from a mining spill using two amphipods species: Corophium volutator and Ampelisca brevicornmis. Bull Environ Toxicol Chem 71:1061–1068
Salazar MH, Salazar SM (1991) Assessing site-specific effects of TBT contamination with mussel growth rates. Mar Environ Res 32:131–150
Scrimshaw MD, Wahlen R, Catterick T, Lester JN (2005) Butyltin compounds in a sediment core from the old Tilbury basin, London, UK. Mar Pollut Bull 50:1500–1507
Stephenson M (1991) A field bioassay approach to determining tributyltin toxicity to oyster in California, US. Mar Environ Res 32:51–60
Tolosa I, Merlini L, de Bertrand N, Bayona JM, Albaiges J (1992) Occurrence and fate of tributyl and triphenyltin compounds in western Mediterranean coastal enclosures. J Environ Toxicol Chem 11:145–155
Wade TL, Garcia-Romero B, Brooks JM (1990) Butyltins in sediments and bivalves from U.S. coastal areas. Chemosphere 20:647–662
Acknowledgments
The work was partially funded by the Ministry for Science and Education through grants CTM2005-07282-C03-01/02/TECNO, PET2006-0685-00, PET2006-0685-01 and the ‘Junta de Andalucia’ through Excellence projects RNM-3924. D. Dra. I. Riba thanks the Spanish program ‘Ramón y Cajal’ for supporting her research. Rocio Anton thanks the Ministry of Education for funding her contract to the University of Cádiz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garg, A., Antón-Martín, R., García-Luque, E. et al. Distribution of butyltins (TBT, DBT, MBT) in sediments of Gulf of Cádiz (Spain) and its bioaccumulation in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum . Ecotoxicology 18, 1029–1035 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-009-0380-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-009-0380-8