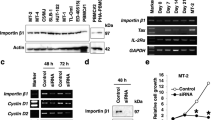
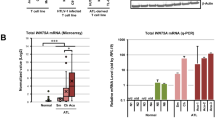
Abstract
Since treatment options for adult T cell leukemia (ATL) associated with human T cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) fail to obtain long-term response, novel therapies targeting ATL-dysregulated pathways are necessary. Dysregulated nuclear import and export machinery is common in malignancies. This study aimed to investigate the potential of exportin-1 (XPO1), which mediates nuclear export of cargos, as a target in ATL. RT-PCR and western blotting were performed to determine XPO1 expression. We evaluated XPO1’s effects on cell proliferation and viability through WST-8 assays, cell cycle and apoptosis via Hoechst 33342 staining and flow cytometry, and intracellular signaling cascades using western blotting. XPO1 expression was upregulated in HTLV-1-infected T cells. XPO1 knockdown reduced cell proliferation. XPO1 inhibitor KPT-330 also reduced proliferation, increased DNA damage, and induced G1 cell cycle arrest and caspase-dependent apoptosis. KPT-330 downregulated cell cycle regulators (CDK2/4/6, cyclin D2, c-Myc and phosphorylated pRb) and anti-apoptotic proteins (XIAP, c-IAP1/2, survivin and Mcl-1), and upregulated p53, p21 and Bak. KPT-330 suppressed XPO1 and increased the nuclear localization of cargos (NF-κB RelA and its negative regulator IκBα, protein phosphatase 2A and its inhibitor SET, p53 and its negative regulator MDM2, p21, p27, FOXO1 and pRb). KPT-330 treatment resulted in the abrogation of aberrant pathways (NF-κB, Akt and STAT3/5) simultaneously through the activation of tumor suppressor proteins and inhibition of oncogenes and proliferative/survival factors. These findings encourage investigating the use of KPT-330 in clinical trials targeting ATL.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials used in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Iwanaga M, Watanabe T, Yamaguchi K (2012) Adult T-cell leukemia: a review of epidemiological evidence. Front Microbiol 3:322
Mohanty S, Harhaj EW (2020) Mechanisms of oncogenesis by HTLV-1 Tax. Pathogens 9:543
Ishida T, Jo T, Takemoto S, Suzushima H, Uozumi K, Yamamoto K, Uike N, Saburi Y, Nosaka K, Utsunomiya A, Tobinai K, Fujiwara H, Ishitsuka K, Yoshida S, Taira N, Moriuchi Y, Imada K, Miyamoto T, Akinaga S, Tomonaga M, Ueda R (2015) Dose-intensified chemotherapy alone or in combination with mogamulizumab in newly diagnosed aggressive adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma: a randomized phase II study. Br J Haematol 169:672–682
Ogura M, Imaizumi Y, Uike N, Asou N, Utsunomiya A, Uchida T, Aoki T, Tsukasaki K, Taguchi J, Choi I, Maruyama D, Nosaka K, Chen N, Midorikawa S, Ohtsu T, Tobinai K (2016) Lenalidomide in relapsed adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma or peripheral T-cell lymphoma (ATLL-001): a phase 1, multicentre, dose-escalation study. Lancet Haematol 3:e107–e118
Tsukasaki K, Marçais A, Nasr R, Kato K, Fukuda T, Hermine O, Bazarbachi A (2020) Diagnostic approaches and established treatments for adult T cell leukemia lymphoma. Front Microbiol 11:1207
Cook LB, Phillips AA (2021) How I treat adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 137:459–470
Nachmias B, Schimmer AD (2020) Targeting nuclear import and export in hematological malignancies. Leukemia 34:2875–2886
Ishikawa C, Senba M, Mori N (2021) Importin β1 regulates cell growth and survival during adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma therapy. Invest New Drugs 39:317–329
Liu S, Qiao W, Sun Q, Luo Y (2021) Chromosome region maintenance 1 (XPO1/CRM1) as an anticancer target and discovery of its inhibitor. J Med Chem 64:15534–15548
Miyoshi I, Kubonishi I, Yoshimoto S, Akagi T, Ohtsuki Y, Shiraishi Y, Nagata K, Hinuma Y (1981) Type C virus particles in a cord T-cell line derived by co-cultivating normal human cord leukocytes and human leukaemic T cells. Nature 294:770–771
Yamamoto N, Okada M, Koyanagi Y, Kannagi M, Hinuma Y (1982) Transformation of human leukocytes by cocultivation with an adult T cell leukemia virus producer cell line. Science 217:737–739
Koeffler HP, Chen IS, Golde DW (1984) Characterization of a novel HTLV-infected cell line. Blood 64:482–490
Poiesz BJ, Ruscetti FW, Gazdar AF, Bunn PA, Minna JD, Gallo RC (1980) Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7415–7419
Miyoshi I, Kubonishi I, Sumida M, Hiraki S, Tsubota T, Kimura I, Miyamoto K, Sato J (1980) A novel T-cell line derived from adult T-cell leukemia. Gan 71:155–156
Sugamura K, Fujii M, Kannagi M, Sakitani M, Takeuchi M, Hinuma Y (1984) Cell surface phenotypes and expression of viral antigens of various human cell lines carrying human T-cell leukemia virus. Int J Cancer 34:221–228
Tanaka Y, Yoshida A, Takayama Y, Tsujimoto H, Tsujimoto A, Hayami M, Tozawa H (1990) Heterogeneity of antigen molecules recognized by anti-tax1 monoclonal antibody Lt-4 in cell lines bearing human T cell leukemia virus type I and related retroviruses. Jpn J Cancer Res 81:225–231
Bretones G, Delgado MD, León J (2015) Myc and cell cycle control. Biochim Biophys Acta 1849:506–516
Sahu RP, Batra S, Srivastava SK (2009) Activation of ATM/Chk1 by curcumin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Br J Cancer 100:1425–1433
Fofaria NM, Kim SH, Srivastava SK (2014) Piperine causes G1 phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in melanoma cells through checkpoint kinase-1 activation. PLoS ONE 9:e94298
Williams AB, Schumacher B (2016) p53 in the DNA-damage-repair process. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6:a026070
Tai YT, Landesman Y, Acharya C, Calle Y, Zhong MY, Cea M, Tannenbaum D, Cagnetta A, Reagan M, Munshi AA, Senapedis W, Saint-Martin JR, Kashyap T, Shacham S, Kauffman M, Gu Y, Wu L, Ghobrial I, Zhan F, Kung AL, Schey SA, Richardson P, Munshi NC, Anderson KC (2014) CRM1 inhibition induces tumor cell cytotoxicity and impairs osteoclastogenesis in multiple myeloma: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Leukemia 28:155–165
Mendonca J, Sharma A, Kim HS, Hammers H, Meeker A, De Marzo A, Carducci M, Kauffman M, Shacham S, Kachhap S (2014) Selective inhibitors of nuclear export (SINE) as novel therapeutics for prostate cancer. Oncotarget 5:6102–6112
Aubrey BJ, Kelly GL, Janic A, Herold MJ, Strasser A (2018) How does p53 induce apoptosis and how does this relate to p53-mediated tumour suppression? Cell Death Differ 25:104–113
Taylor JM, Nicot C (2008) HTLV-1 and apoptosis: role in cellular transformation and recent advances in therapeutic approaches. Apoptosis 13:733–747
Grassmann R, Aboud M, Jeang KT (2005) Molecular mechanisms of cellular transformation by HTLV-1 Tax. Oncogene 24:5976–5985
Viatour P, Merville M-P, Bours V, Chariot A (2005) Phosphorylation of NF-κB and IκB proteins: implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci 30:43–52
Azmi AS, Uddin MH, Mohammad RM (2021) The nuclear export protein XPO1 – from biology to targeted therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 18:152–169
Roth J, Dobbelstein M, Freedman DA, Shenk T, Levine AJ (1998) Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of the hdm2 oncoprotein regulates the levels of the p53 protein via a pathway used by the human immunodeficiency virus rev protein. EMBO J 17:554–564
Freedman DA, Levine AJ (1998) Nuclear export is required for degradation of endogenous p53 by MDM2 and human papillomavirus E6. Mol Cell Biol 18:7288–7293
Walker CJ, Oaks JJ, Santhanam R, Neviani P, Harb JG, Ferenchak G, Ellis JJ, Landesman Y, Eisfeld AK, Gabrail NY, Smith CL, Caligiuri MA, Hokland P, Roy DC, Reid A, Milojkovic D, Goldman JM, Apperley J, Garzon R, Marcucci G, Shacham S, Kauffman MG, Perrotti D (2013) Preclinical and clinical efficacy of XPO1/CRM1 inhibition by the karyopherin inhibitor KPT-330 in Ph+ leukemias. Blood 122:3034–3044
Millward TA, Zolnierowicz S, Hemmings BA (1999) Regulation of protein kinase cascades by protein phosphatase 2A. Trends Biochem Sci 24:186–191
Jardin F, Pujals A, Pelletier L, Bohers E, Camus V, Mareschal S, Dubois S, Sola B, Ochmann M, Lemonnier F, Viailly PJ, Bertrand P, Maingonnat C, Traverse-Glehen A, Gaulard P, Damotte D, Delarue R, Haioun C, Argueta C, Landesman Y, Salles G, Jais JP, Figeac M, Copie-Bergman C, Molina TJ, Picquenot JM, Cornic M, Fest T, Milpied N, Lemasle E, Stamatoullas A, Moeller P, Dyer MJ, Sundstrom C, Bastard C, Tilly H, Leroy K (2016) Recurrent mutations of the exportin 1 gene (XPO1) and their impact on selective inhibitor of nuclear export compounds sensitivity in primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma. Am J Hematol 91:923–930
Kataoka K, Nagata Y, Kitanaka A, Shiraishi Y, Shimamura T, Yasunaga J, Totoki Y, Chiba K, Sato-Otsubo A, Nagae G, Ishii R, Muto S, Kotani S, Watatani Y, Takeda J, Sanada M, Tanaka H, Suzuki H, Sato Y, Shiozawa Y, Yoshizato T, Yoshida K, Makishima H, Iwanaga M, Ma G, Nosaka K, Hishizawa M, Itonaga H, Imaizumi Y, Munakata W, Ogasawara H, Sato T, Sasai K, Muramoto K, Penova M, Kawaguchi T, Nakamura H, Hama N, Shide K, Kubuki Y, Hidaka T, Kameda T, Nakamaki T, Ishiyama K, Miyawaki S, Yoon SS, Tobinai K, Miyazaki Y, Takaori-Kondo A, Matsuda F, Takeuchi K, Nureki O, Aburatani H, Watanabe T, Shibata T, Matsuoka M, Miyano S, Shimoda K, Ogawa S (2015) Integrated molecular analysis of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Nat Genet 47:1304–1315
Chen C, Siegel D, Gutierrez M, Jacoby M, Hofmeister CC, Gabrail N, Baz R, Mau-Sorensen M, Berdeja JG, Savona M, Savoie L, Trudel S, Areethamsirikul N, Unger TJ, Rashal T, Hanke T, Kauffman M, Shacham S, Reece D (2018) Safety and efficacy of selinexor in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Blood 131:855–863
Tabe Y, Kojima K, Yamamoto S, Sekihara K, Matsushita H, Davis RE, Wang Z, Ma W, Ishizawa J, Kazuno S, Kauffman M, Shacham S, Fujimura T, Ueno T, Miida T, Andreeff M (2015) Ribosomal biogenesis and translational flux inhibition by the selective inhibitor of nuclear export (SINE) XPO1 antagonist KPT-185. PLoS ONE 10:e0137210
Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (2008) Apoptotic signaling by c-MYC. Oncogene 27:6462–6472
Ichikawa T, Nakahata S, Fujii M, Iha H, Morishita K (2015) Loss of NDRG2 enhanced activation of the NF-κB pathway by PTEN and NIK phosphorylation for ATL and other cancer development. Sci Rep 5:12841
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Fujisaki Cell Center, Hayashibara Biochemical Laboratories, Inc. for providing HUT-102 and MT-1 cells, Dr. Naoki Yamamoto (Tokyo Medical and Dental University) for providing MT-2 and MT-4 cells, Dr. Diane Prager (UCLA School of Medicine) for providing SLB-1 cells, Dr. Masahiro Fujii (Niigata University) for providing TL-OmI cells, and Dr. Yuetsu Tanaka (University of the Ryukyus) for providing Lt-4 antibody. Recombinant human IL-2 was provided by Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. The measurement of protein concentrations and flow cytometric analyses were performed at the University of the Ryukyus Center for Research Advancement and Collaboration. We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for their assistance with English language editing.
Funding
This study was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI (17K07175).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: N.M.; methodology: C.I. and N.M.; formal analysis and investigation: C.I. and N.M.; writing-original draft preparation: C.I.; writing-reviewing and editing: N.M.; funding acquisition: C.I.; resources: N.M.; supervision: N.M.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of this study.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable.
Conflict of interests
No competing interests or conflict of interest is reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, C., Mori, N. Exportin-1 is critical for cell proliferation and survival in adult T cell leukemia. Invest New Drugs 40, 718–727 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-022-01250-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-022-01250-6