Summary
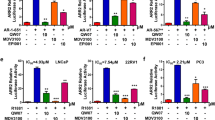
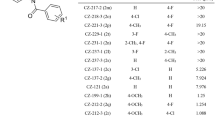
Current therapeutic strategy for advanced prostate cancer is to suppress the androgen receptor (AR) signaling. However, lethal castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) arises due to AR reactivation via multiple mechanisms, including mutations in the AR and cross-talk with other pathways such as NF-κB. We have previously identified two ionone-based antiandrogens (SC97 and SC245), which are full antagonists of the wild type and the clinically-relevant T877A, W741C and H874Y mutated ARs. Here, we discovered SC97 and SC245 also inhibit NF-κB. By synthesizing a series of derivatives of these two compounds, we have discovered a novel compound 3b that potently inhibits both AR and NF-κB signalling, including the AR F876L mutant. Compound 3b showed low micromolar antiproliferative activites in C4-2B and 22Rv1 cells, which express mutated ARs and are androgen-independent, as well as DU-145 and PC-3 cells, which exhibit constitutively activated NF-κB signalling. Our studies indicate 3b is effective against the CRPC cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Androgen receptor
- Bic:
-
Bicalutamide
- CRPC:
-
Castration-resistant prostate cancer
- DHT:
-
Di-hydrotestosterone
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Taplin ME, Ho SM (2001) The endocrinology of prostate cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3467–3477
Tannock IF, de Wit R, Berry WR et al (2004) Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 351:1502–1512
Petrylak DP, Tangen CM, Hussain MH et al (2004) Docetaxel and estramustine compared with mitoxantrone and prednisone for advanced refractory prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 351:1513–1520
Ang JE, Olmos D, de Bono JS (2009) CYP17 blockade by abiraterone: further evidence for frequent continued hormone-dependence in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 100:671–675
Scher HI, Beer TM, Higano CS et al (2008) Phase I/II study of MDV3100 in patients (pts) with progressive castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC). J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 26:5006
Tran C, Ouk S, Clegg NJ et al (2009) Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science 324:787–790
Scher HI, Beer TM, Higano CS et al (2010) Antitumour activity of MDV3100 in castration-resistant prostate cancer: a phase 1–2 study. Lancet 375:1437–1446
Attard G, Cooper CS, de Bono JS (2009) Steroid hormone receptors in prostate cancer: a hard habit to break? Cancer Cell 16:458–462
Taplin ME (2008) Androgen receptor: role and novel therapeutic prospects in prostate cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 8:1495–1508
Yoshida T, Kinoshita H, Segawa T et al (2005) Antiandrogen bicalutamide promotes tumor growth in a novel androgen-dependent prostate cancer xenograft model derived from a bicalutamide-treated patient. Cancer Res 65:9611–9616
Steketee K, Timmerman L, Ziel-van der Made AC et al (2002) Broadened ligand responsiveness of androgen receptor mutants obtained by random amino acid substitution of H874 and mutation hot spot T877 in prostate cancer. Int J Cancer 100:309–317
Taplin ME, Rajeshkumar B, Halabi S et al (2003) Androgen receptor mutations in androgen-in dependent prostate cancer: cancer and leukemia group B study 9663. J Clin Oncol 21:2673–2678
Urushibara M, Ishioka J, Hyochi N et al (2007) Effects of steroidal and non-steroidal antiandrogens on wild-type and mutant androgen receptors. Prostate 67:799–807
Joseph JD, Lu N, Qian J et al (2013) A clinically relevant androgen receptor mutation confers resistance to second-generation antiandrogens enzalutamide and ARN-509. Cancer Discov 3:1020–1029
Korpal M, Korn JM, Gao X et al (2013) An F876L mutation in androgen receptor confers genetic and phenotypic resistance to MDV3100 (Enzalutamide). Cancer Discov 3:1030–1043
Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM (2004) The IKK NF-kappa B system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:17–26
Shen HM, Tergaonkar V (2009) NF + ¦B signaling in carcinogenesis and as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. Apoptosis 14:348–363
Setlur SR, Royce TE, Sboner A et al (2007) Integrative microarray analysis of pathways dysregulated in metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res 67:10296–10303
Gasparian AV, Yao YJ, Kowalczyk D et al (2002) The role of IKK in constitutive activation of NF- + ¦B transcription factor in prostate carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci 115:141–151
Lee DF, Hung MC (2008) Advances in targeting IKK and IKK-related kinases for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 14:5656–5662
Zhang L, Altuwaijri S, Deng F et al (2009) NF- + ¦B regulates androgen receptor expression and prostate cancer growth. Am J Pathol 175:489–499
Malinowska K, Neuwirt H, Cavarretta IT et al (2009) Interleukin-6 stimulation of growth of prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo through activation of the androgen receptor. Endocr Relat Cancer 16:155–169
Chun JY, Nadiminty N, Dutt S et al (2009) Interleukin-6 regulates androgen synthesis in prostate cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 15:4815–4822
Feng S, Tang Q, Sun M et al. (2009) Interleukin-6 increases prostate cancer cells resistance to bicalutamide via TIF2. Mol Cancer Ther
Drachenberg DE, Elgamal AA, Rowbotham R et al (1999) Circulating levels of interleukin-6 in patients with hormone refractory prostate cancer. Prostate 41:127–133
Jin RJ, Lho Y, Connelly L et al (2008) The nuclear factor- NF-kB pathway controls the progression of prostate cancer to androgen-independent growth. Cancer Res 68:6762–6769
Zhou J, Geng G, Shi Q et al (2009) Design and synthesis of androgen receptor antagonists with bulky side chains for overcoming antiandrogen resistance. J Med Chem 52:5546–5550
Zhou JM, Geng GY, Wu JH (2010) Synthesis and in vitro characterization of ionone-based chalcones as novel antiandrogens effective against multiple clinically relevant androgen receptor mutants. Invest New Drugs 28:291–298
Zhou J, Geng G, Batist G et al (2009) Syntheses and potential anti-prostate cancer activities of ionone-based chalcones. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:1183–1186
Attard G, Reid AHM, Olmos D et al (2009) Antitumor activity with CYP17 blockade indicates that castration-resistant prostate cancer frequently remains hormone driven. Cancer Res 69:4937–4940
Shen HC, Balk SP (2009) Development of androgen receptor antagonists with promising activity in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 15:461–463
Eichholz A, Ferraldeschi R, Attard G et al (2012) Putting the brakes on continued androgen receptor signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol 360:68–75
Krishnan AV, Zhao XY, Swami S et al (2002) A glucocorticoid-responsive mutant androgen receptor exhibits unique ligand specificity: therapeutic implications for androgen-independent prostate cancer. Endocrinology 143:1889–1900
Eder IE, Haag P, Bartsch G et al (2005) Targeting the androgen receptor in hormone-refractory prostate cancer–new concepts. Future Oncol 1:93–101
Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C et al (2004) Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med 10:33–39
Yemelyanov A, Gasparian A, Lindholm P et al (2006) Effects of IKK inhibitor PS1145 on NF- + ¦B function, proliferation, apoptosis and invasion activity in prostate carcinoma cells. Oncogene 25:387–398
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Cancer Research Society (J.W.). Postdoctoral fellowship from the CIHR/MCETC Strategic Training Program is grateful acknowledged (J.Z.).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Synthesis, 1H NMR and mass spectral analyses of 1b, 1d, 2a−2d and 4a−4f as well as cell lines and western blot analysis.
ESM 1
(DOC 352 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Zhou, J., Geng, G. et al. Synthesis and in vitro characterization of ionone-based compounds as dual inhibitors of the androgen receptor and NF-κB. Invest New Drugs 32, 227–234 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-013-0040-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-013-0040-y