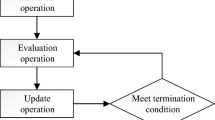
Abstract
This paper deals with the on-line design of a supervisor to coordinate an automated guided vehicle (AGV) fleet. This supervisor ensures the system safety (no collision) and a good coordination between vehicles (no blocking situations). It is the so-called Wonham-Ramadge supervisor, it is the least restrictive, and ensures controllability and nonblocking. We propose a compositional procedure to resolve this problem allowing an efficient on-line synthesis. A calculation on the fly is made at every attribution of a new mission for an AGV, to actualize the supervisor and adapt it to the new situation. This compositional approach allows to increase the number of AGV taken on compared to the monolithic approach. We show on some tests the efficiency of this method for the on-line synthesis of supervisor to coordinate a fleet of mobile robots for real cases.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In this paper, we consider automata with either a unique or an empty initial state, i.e., q 0 ∈ Q or q 0 = ∅. Therefore, we denote q 0 = x 0 instead of q 0 = {x 0} as a shorthand for the initial state.
In this paper, we consider automata with either a unique or an empty initial state. Therefore, we denote q 0, A B = (q 0, A , q 0, B ) as a shorthand for the initial state.
References
Arnaud Y, Cury JER, Loiseau JJ, Martinez C (2009) Pilotage sûr et optimal d’une flotte de véhicules autoguidés. In: JD-JN-MACS 2009. Angers, France
Breton L, Maza S, Castagna P (2006) A multi-agent based conflict-free routing approach of bi-directional automated guided vehicles. In: American Control Conference, 2006
Cai K, Wonham WM (2010) Supervisor localization: A top-down approach to distributed control of discrete-event systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control 55(3):605–618. doi:10.1109/TAC.2009.2039237
Cassandras CG, Lafortune S (2006) Introduction to Discrete Event Systems. Springer-Verlag New York, Inc., Secaucus
Clarke EM, Emerson EA, Sistla AP (1986) Automatic verification of finite-state concurrent systems using temporal logic specifications. ACM Trans Program Lang Syst 8(2):244–263. doi:10.1145/5397.5399
Flordal H, Malik R, Fabian M, Åkesson K (2007) Compositional synthesis of maximally permissive supervisors using supervision equivalence. Discrete Event Dynamic Systems 17(4):475–504. doi:10.1007/s10626-007-0018-z
Girault J, Loiseau JJ, Roux OH (2013) Synthèse en ligne de superviseur compositionnel pour flotte de robots mobiles. In: European Journal of Automation, MSR’13, vol 47/1-3, pp 195–210
Hill RC, Tilbury DM (2006) Modular supervisory control of discrete-event systems with abstraction and incremental hierarchical construction. In: 2006 8th International Workshop on Discrete Event Systems, pp 399–406. doi:10.1109/WODES.2006.382507, (to appear in print)
Komenda J, Van Schuppen J, Gaudin B, Marchand H (2008) Supervisory control of modular systems with global specification languages. Automatica 44:1127–1134. doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2007.09.004
Krogh BH, Holloway LE (1991) Synthesis of feedback control logic for discrete manufacturing systems. Automatica 27(4):641–651
Malik R, Flordal H (2008) Yet another approach to compositional synthesis of discrete event systems. In: 9th International Workshop on Discrete Event Systems, 2008. WODES 2008. pp 16–21. doi:10.1109/WODES.2008.4605916, (to appear in print)
Maza S (2003) Analyse du comportement d’un système de transport par chariot bidirectionnels en vue de sa commande. PhD thesis, Université de Nantes
Mohajerani S, Malik R, Ware S, Fabian M (2011) Compositional synthesis of discrete event systems using synthesis abstraction. In: 2011 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), pp 1549–1554. doi:10.1109/CCDC.2011.5968439, (to appear in print)
Queiroz MHD, Cury JER (2000) Modular supervisory control of large scale discrete event systems. In: Proceedings of the WODES’00 International Workshop on Discrete Event Systems: Analysis and Control. Kluwer Academic, pp 103–110
Ramadge PJ, Wonham WM (1987) Supervisory control of a class of discrete event processes. SIAM J Control Optim 25(1):206–230
Ramadge PJ, Wonham WM (1989) The control of discrete event systems. Proc IEEE 77(1):81–98
Reveliotis SA (2000) Conflict resolution in agv systems. IIE Trans 32:200–0
Wonham WM, Ramadge PJ (1984) On the supremal controllable sublanguage of a given language. In: The 23rd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, 1984, vol 23, pp 1073–1080
Wonham WM, Ramadge PJ (1988) Modular supervisory control of discrete-event systems. Mathematics of Control, Signals and Systems 1(1):13–30
Acknowledgments
This paper is an extended version of Girault et al. (2013) and was selected by the conference MSR’13 for this submission to the journal DEDS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girault, J., Loiseau, JJ. & Roux, O.H. On-line compositional controller synthesis for AGV. Discrete Event Dyn Syst 26, 583–610 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10626-015-0222-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10626-015-0222-1