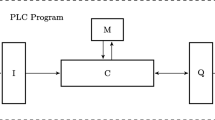
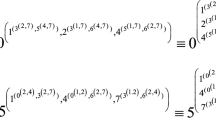Abstract
This paper presents a general framework for efficient synthesis of supervisors for discrete event systems. The approach is based on compositional minimisation, using concepts of process equivalence. In this context, a large number of ways are suggested how a finite-state automaton can be simplified such that the results of supervisor synthesis are preserved. The proposed approach yields a compact representation of a least restrictive supervisor that ensures controllability and nonblocking. The method is demonstrated on a simple manufacturing example to significantly reduce the number of states constructed for supervisor synthesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åkesson K, Flordal H, Fabian M (2002) Exploiting modularity for synthesis and verification of supervisors. In: Proceedings of the 15th IFAC world congress, Barcelona, Spain
Brandin BA, Malik R, Malik P (2004) Incremental verification and synthesis of discrete-event systems guided by counter examples. Trans Control Syst Technol 12(3):387–401
Cassandras CG, Lafortune S (1999) Introduction to discrete event systems. Kluwer
De Nicola R, Hennessy MCB (1984) Testing equivalences for processes. Theor Comp Sci 34(1–2): 83–133
de Queiroz MH, Cury JER (2000) Modular supervisory control of large scale discrete event systems. In: Boel R, Stremersch G (eds) Discrete event systems, analysis and control. Kluwer, pp 103–110
de Queiroz MH, Cury JER, Wonham WM (2005) Multitasking supervisory control of discrete-event systems. Discrete Event Dyn Syst 15(4):375–395
Dershowitz N, Jouannaud J-P (1990) Rewrite systems. In: van Leeuwen J (ed) Handbook of theoretical computer science, vol B. Elsevier, pp 243–320
Fabian M (1995) On object oriented nondeterministic supervisory control. PhD thesis, Control Engineering Laboratory, Chalmers University of Technology, Göteborg, Sweden
Feng L, Wonham WM (2006) Computationally efficient supervisor design: Abstraction and modularity. In: Proceedings of the 8th international workshop on discrete event systems, WODES ’06, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, pp 3–8
Flordal H, Malik R (2006) Supervision equivalence. In: Proceedings of the 8th international workshop on discrete event systems, WODES ’06, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, pp 155–160
Hill RC, Tilbury DM (2006) Modular supervisory control of discrete-event systems with abstraction and incremental hierarchical construction. In: Proceedings of the 8th international workshop on discrete event systems, WODES ’06. Ann Arbor, MI, USA, pp 399–406
Hoare CAR (1985) Communicating sequential processes. Series in Computer Science, Prentice-Hall
Lin F, Wonham WM (1990) Decentralized control and coordination of discrete-event systems with partial observation. IEEE Trans. Autom Control 35(12):1330–1337
Malik R, Streader D, Reeves S (2006) Conflicts and fair testing. Int J Found Comput Sci 17(4): 797–813
Milner R (1989) Communication and concurrency. Series in Computer Science, Prentice-Hall
Ramadge PJ, Wonham WM (1989) The control of discrete event systems. Proc IEEE 77(1):81–98
Song R, Leduc RJ (2006) Symbolic synthesis and verification of hierarchical interface-based supervisory control. In: Proceedings of the 8th international workshop on discrete event systems, WODES ’06 Ann Arbor, MI, USA, pp 419–426
Su R, Wonham WM (2004) Supervisor reduction for discrete-event systems. Discrete Event Dyn Syst 14(1):31–53
Wong KC, Wonham WM (1998) Modular control and coordination of discrete-event systems. Discrete Event Dyn Syst 8(3):247–297
Wonham WM (2006) Supervisory control of discrete event systems, Technical report. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flordal, H., Malik, R., Fabian, M. et al. Compositional Synthesis of Maximally Permissive Supervisors Using Supervision Equivalence. Discrete Event Dyn Syst 17, 475–504 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10626-007-0018-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10626-007-0018-z