Abstract
Background
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) could play carcinogenic roles in gastric cancer (GC) and have potential to be biomarkers for GC early diagnosis, which needs to be further excavated and supported by more evidence.
Aims
The study aims to identify more authentic circRNA expression profiles that could function as potential biomarkers in GC.
Methods
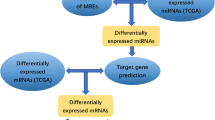
circRNA expression data in three microarrays were downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus datasets. A systematic meta-analysis based on an integrated dataset pre-processed from the three microarrays was conducted to identify a panel of differentially expressed circRNAs (DEcircs) by using the metaDE package. Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes term enrichment were used to note the corresponding functions of DEcircs. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was applied to verify the DEcircs expression in cancer tissues and adjacent paracancerous tissues. A GC risk-related circRNAs–miRNAs–mRNAs network was further constructed and analyzed.
Results
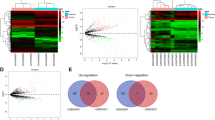
MetaDE analysis suggested 64 DEcircs between cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues. GO and KEGG analysis showed that the parental genes of these DEcircs were mainly associated with histone methylation, Wnt signalosome and histone methylation activity. Hsa_circ_0005927 and hsa_circ_0067934 were verified in GC tissues, and a GC risk-related network was constructed.
Conclusion
MetaDE-based circRNA expression profiles revealed a series of potential biomarkers involved in GC. Two circRNAs, hsa_circ_0005927 and hsa_circ_0067934, could be more authentic biomarkers for GC screening. The GC risk-related network of hsa_circ_0005927/hsa_circ_0067934 and their downstream targets will provide new genetic insights for GC research.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data are included in the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- GC:
-
Gastric cancer
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
- GEO:
-
Gene expression omnibus
- FC:
-
Fold change
- GO:
-
Gene ontology
- KEGG:
-
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
References
Theodoratou E, Timofeeva M, Li X, Meng X, Ioannidis JPA. Nature, nurture, and cancer risks: genetic and nutritional contributions to cancer. Ann Rev Nutr. 2017;37:293–320. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-071715-051004.
Yuan J, Yue H, Zhang M, et al. Transcriptional profiling analysis and functional prediction of long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:8131–8142. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6993.
Lasda E, Parker R. Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. RNA (New York, NY). 2014;20:1829–1842. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.047126.114.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495:384–388. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11993.
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR, et al. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol cell. 2014;56:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.019.
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2959.
Du WW, Yang W, Liu E, Yang Z, Dhaliwal P, Yang BB. Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:2846–2858. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw027.
Liu J, Liu T, Wang X, He A. Circles reshaping the RNA world: from waste to treasure. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0630-y.
Salzman J, Chen RE, Olsen MN, Wang PL, Brown PO. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet.. 2013;9:e1003777. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003777.
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11928.
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavac M, Glavac D. Circular RNAs: biogenesis, function, and a role as possible cancer biomarkers. Int J Genom. 2017;2017:6218353. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/6218353.
Chen J, Li Y, Zheng Q, et al. Circular RNA profile identifies circPVT1 as a proliferative factor and prognostic marker in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;388:208–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.12.006.
Li P, Chen S, Chen H, et al. Using circular RNA as a novel type of biomarker in the screening of gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta Int J Clin Chem. 2015;444:132–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2015.02.018.
Li WH, Song YC, Zhang H, et al. Decreased expression of Hsa_circ_00001649 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance. Dis Mark.. 2017;2017:4587698. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4587698.
Shao Y, Chen L, Lu R, et al. Decreased expression of hsa_circ_0001895 in human gastric cancer and its clinical significances. Tumour Biol.. 2017;39:1010428317699125. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317699125.
Liang Y, Wang W, Fang C, et al. Clinical significance and diagnostic value of serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA72-4 in patients with gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:49565–49573. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10391.
Wang J, Wang D, Wan D, et al. Circular RNA In invasive and recurrent clinical nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas: expression profiles and bioinformatic analysis. World Neurosurg.. 2018;. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.06.038.
Zhao J, Li L, Wang Q, Han H, Zhan Q, Xu M. circRNA expression profile in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma patients. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;44:2138–2146. https://doi.org/10.1159/000485953.
Liu W, Zhang J, Zou C, et al. Microarray expression profile and functional analysis of circular RNAs in osteosarcoma. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2017;43:969–985. https://doi.org/10.1159/000481650.
Ein-Dor L, Kela I, Getz G, Givol D, Domany E. Outcome signature genes in breast cancer: is there a unique set? Bioinformatics. 2005;21:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth469.
Ntzani EE, Ioannidis JP. Predictive ability of DNA microarrays for cancer outcomes and correlates: an empirical assessment. Lancet. 2003;362:1439–1444. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14686-7.
Pashaei E, Pashaei E, Ahmady M, Ozen M, Aydin N. Meta-analysis of miRNA expression profiles for prostate cancer recurrence following radical prostatectomy. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0179543. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0179543.
Wang X, Kang DD, Shen K, et al. An R package suite for microarray meta-analysis in quality control, differentially expressed gene analysis and pathway enrichment detection. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:2534–2536. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts485.
Lu S, Li J, Song C, Shen K, Tseng GC. Biomarker detection in the integration of multiple multi-class genomic studies. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:333–340. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp669.
Zhao R, Ni J, Lu S, et al. CircUBAP2-mediated competing endogenous RNA network modulates tumorigenesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Aging. 2019;11:8484. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102334.
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:79. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0827-8.
Wang X, Lin Y, Song C, Sibille E, Tseng GC. Detecting disease-associated genes with confounding variable adjustment and the impact on genomic meta-analysis: with application to major depressive disorder. BMC Bioinf. 2012;13:52. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-13-52.
Tseng GC, Ghosh D, Feingold E. Comprehensive literature review and statistical considerations for microarray meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:3785–3799. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1265.
Qi C, Hong L, Cheng Z, Yin Q. Identification of metastasis-associated genes in colorectal cancer using metaDE and survival analysis. Oncol Lett. 2016;11:568–574. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2015.3956.
Cheng M, An S, Li J. Identifying key genes associated with acute myocardial infarction. Medicine. 2017;96:e7741. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007741.
Dudekula DB, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, De S, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M. CircInteractome: a web tool for exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and microRNAs. RNA Biol. 2016;13:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2015.1128065.
Pasquinelli AE. MicroRNAs and their targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3162.
Backes C, Kehl T, Stockel D, et al. miRPathDB: a new dictionary on microRNAs and target pathways. Nucleic acids Res. 2017;45:D90–D96. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw926.
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL, Ideker T. Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:431–432. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq675.
Wang J, Li H. circRNA circ_0067934 silencing inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of NSCLC cells and correlates with unfavorable prognosis in NSCLC. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:3053–3060. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201805_15063.
Zhu Q, Lu G, Luo Z, et al. circRNA circ_0067934 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma through regulation of miR-1324/FZD5/Wnt/beta-catenin axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497:626–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.119.
Xia W, Qiu M, Chen R, et al. Circular RNA has_circ_0067934 is upregulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promoted proliferation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35576. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35576.
Xin J, Zhang XY, Sun DK, Tian LQ, Xu P. Up-regulated circular RNA hsa_circ_0067934 contributes to glioblastoma progression through activating PI3K-AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:3447–3454. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201904_17709.
Wang H, Yan X, Zhang H, Zhan X. circRNA circ_0067934 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis and promotes thyroid carcinoma progression. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:1342–1349. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.913463.
Hu C, Wang Y, Li A, Zhang J, Xue F, Zhu L. Overexpressed circ_0067934 acts as an oncogene to facilitate cervical cancer progression via the miR-545/EIF3C axis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:9225–9232. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27601.
Zou Q, Wang T, Li B, et al. Overexpression of circ-0067934 is associated with increased cellular proliferation and the prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2018;16:5551–5556. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9357.
Zhou GK, Zhang GY, Yuan ZN, Pei R, Liu DM. Has_circ_0008274 promotes cell proliferation and invasion involving AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:8772–8780. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201812_16644.
Afzali F, Salimi M. Unearthing regulatory axes of breast cancer circRNAs networks to find novel targets and fathom pivotal mechanisms. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci. 2019;. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-019-00339-6.
Deng N, Li L, Gao J, et al. Hsa_circ_0009910 promotes carcinogenesis by promoting the expression of miR-449a target IL6R in osteosarcoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;495:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.11.028.
Ping L, Jian-Jun C, Chu-Shu L, Guang-Hua L, Ming Z. Silencing of circ_0009910 inhibits acute myeloid leukemia cell growth through increasing miR-20a-5p. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2019;75:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcmd.2018.12.006.
Liu M, Liu KD, Zhang L, et al. Circ_0009910 regulates growth and metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22:8248–8256. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201812_16519.
Guo JN, Li J, Zhu CL, et al. Comprehensive profile of differentially expressed circular RNAs reveals that hsa_circ_0000069 is upregulated and promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in colorectal cancer. Onco Targets Therapy. 2016;9:7451–7458. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S123220.
Bian L, Zhi X, Ma L, et al. Hsa_circRNA_103809 regulated the cell proliferation and migration in colorectal cancer via miR-532-3p/FOXO4 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;505:346–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.073.
Hao S, Lv J, Yang Q, et al. Identification of key genes and circular RNAs in human gastric cancer. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2019;25:2488–2504. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.915382.
Li T, Shao Y, Fu L, et al. Plasma circular RNA profiling of patients with gastric cancer and their droplet digital RT-PCR detection. J Mol Med (Berlin, Germany). 2018;96:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-017-1600-y.
Iparraguirre L, Munoz-Culla M, Prada-Luengo I, Castillo-Trivino T, Olascoaga J, Otaegui D. Circular RNA profiling reveals that circular RNAs from ANXA2 can be used as new biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26:3564–3572. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx243.
Wu N, Jin L, Cai J. Profiling and bioinformatics analyses reveal differential circular RNA expression in hypertensive patients. Clin Exp Hypertens (New York, NY: 1993). 2017;39:454–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/10641963.2016.1273944.
Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, et al. Roles of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5:e1039. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.515.
Song X, Xin N, Wang W, Zhao C. Wnt/beta-catenin, an oncogenic pathway targeted by H. pylori in gastric carcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 2015;6:35579–35588. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5758.
Wan L, Zhang L, Fan K, Cheng ZX, Sun QC, Wang JJ. Circular RNA-ITCH suppresses lung cancer proliferation via inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. BioMed Res Int. 2016;2016:1579490. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1579490.
Patel TN, Roy S, Ravi R. Gastric cancer and related epigenetic alterations. Ecancermedicalscience. 2017;11:714. https://doi.org/10.3332/ecancer.2017.714.
Du Y, Jiang B, Song S, et al. Metadherin regulates actin cytoskeletal remodeling and enhances human gastric cancer metastasis via epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol. 2017;51:63–74. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2017.4002.
Xu X, Jia SZ, Dai Y, et al. The relationship of circular RNAs with ovarian endometriosis. Reprod Sci (Thousand Oaks, Calif). 2018;2018:1933719118759439. https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719118759439.
Sun T, Du W, Xiong H, et al. TMEFF2 deregulation contributes to gastric carcinogenesis and indicates poor survival outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:4689–4704. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0315.
Cai W, Chen G, Luo Q, et al. PMP22 regulates self-renewal and chemoresistance of gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer Therap. 2017;16:1187–1198. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0750.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Ref No. 81772987) and Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province in China (Ref No. 20170540987).
Funding
This work is supported partly by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Ref No. 81772987) and Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province in China (Ref No. 20170540987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY and QX provided direction and guidance throughout the preparation of this manuscript. DH and WB performed data extraction and analysis. DH performed experiments and drafted the manuscript. LZ corrected the grammatical errors in this article. YY reviewed the manuscript and made significance revisions on the drafts. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors approved publication of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Hx., Xu, Q., Wang, Bg. et al. MetaDE-Based Analysis of circRNA Expression Profiles Involved in Gastric Cancer. Dig Dis Sci 65, 2884–2895 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-06014-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-06014-6