Abstract
Background
Huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) is a neuronal protein that is predominantly expressed in neurons in the brain. HAP1 is critical for maintenance of neuronal survival as well as regulation of food intake and body weight in animals. In addition to the critical role of HAP1 in the central nervous system, HAP1 is also found in endocrine cells, raising an interesting issue of whether HAP1 is expressed in the digestive system.
Aims
To examine the expression and localization of HAP1 in the human gastrointestinal tract and to compare the differences of the HAP1 expression between benign and malignant tissues in the digestive system.
Methods
We used Western blot and immunohistochemistry to examine the expression and distribution of HAP1 in the human gastrointestinal tract tissues.
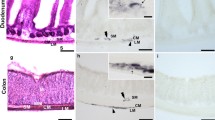
Results
We observed that the presence of HAP1-positive cells in the gastrointestinal tract was not uniform with immunohistochemistry staining. Western blot revealed that only one isoform (75KD) HAP1 was present in the human gastrointestinal system. Interestingly, the expression of HAP1 was higher in the stomach than other regions of the gastrointestinal tract and was at the lowest level in the intestine. We also found that HAP1 was unlikely altered in benign gastric polyps, but was downregulated in pancreatic cancer.
Conclusions
This is the first study showing the differential expression and location of HAP1 in the human digestive system. These findings suggested that HAP1 may have cell-type-dependent function in the gastrointestinal tract and may serve as a diagnostic marker for pancreatic cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li SH, Hosseini SH, Gutekunst CA, Hersch SM, Ferrante RJ, Li XJ. A human HAP1 homologue. Cloning, expression, and interaction with huntingtin. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19220–19227.
Gutekunst CA, Li SH, Yi H, Ferrante RJ, Li XJ, Hersch SM. The cellular and subcellular localization of huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1): comparison with huntingtin in rat and human. J Neurosci. 1998;18:7674–7686.
Li XJ, Li SH, Sharp AH, et al. A huntingtin-associated protein enriched in brain with implications for pathology. Nature. 1995;378:398–402.
Dragatsis I, Dietrich P, Zeitlin S. Expression of the huntingtin-associated protein 1 gene in the developing and adult mouse. Neurosci Lett. 2000;282:37–40.
Li SH, Yu ZX, Li CL, et al. Lack of huntingtin-associated protein-1 causes neuronal death resembling hypothalamic degeneration in Huntington’s disease. J Neurosci. 2003;23:6956–6964.
McGuire JR, Rong J, Li SH, Li XJ. Interaction of huntingtin-associated protein-1 with kinesin light chain: implications in intracellular trafficking in neurons. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:3552–3559.
Rong J, McGuire JR, Fang ZH, et al. Regulation of intracellular trafficking of huntingtin-associated protein-1 is critical for TrkA protein levels and neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci. 2006;26:6019–6030.
Rong J, Li S, Sheng G, et al. 14-3-3 Protein interacts with huntingtin-associated protein 1 and regulates its trafficking. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:4748–4756.
Takeshita Y, Fujinaga R, Zhao C, Yanai A, Shinoda K. Huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) interacts with androgen receptor (AR) and suppresses SBMA-mutant-AR-induced apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:2298–2312.
Liao M, Shen J, Zhang Y, Li SH, Li XJ, Li H. Immunohistochemical localization of huntingtin-associated protein 1 in endocrine system of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem. 2005;53:1517–1524.
Liao M, Chen X, Han J, Yang S, Peng T, Li H. Selective expression of huntingtin-associated protein 1 in {beta}-cells of the rat pancreatic islets. J Histochem Cytochem. 2010;58:255–263.
Martin EJ, Kim M, Velier J, et al. Analysis of huntingtin-associated protein 1 in mouse brain and immortalized striatal neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1999;403:421–430.
Pan JY, Yuan S, Yu T, et al. Regulation of L-type Ca2+ channel activity and insulin secretion by huntingtin-associated protein 1. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:26352–26363.
Sheng G, Chang GQ, Lin JY, et al. Hypothalamic huntingtin-associated protein 1 as a mediator of feeding behavior. Nat Med. 2006;12:526–533.
Lumsden AL, Young RL, Pezos N, Keating DJ. Huntingtin-associated protein 1: eutherian adaptation from a TRAK-like protein, conserved gene promoter elements, and localization in the human intestine. BMC Evol Biol. 2016;16:214.
Li J, Pandey V, Kessler T, Lehrach H, Wierling C. Modeling of miRNA and drug action in the EGFR signaling pathway. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e30140.
Zhu L, Song X, Tang J, et al. Huntingtin-associated protein 1: a potential biomarker of breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:1881–1887.
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by NIH Grants NS036232, NS095279. We thank Ning Xin for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Emory University. The objectives of the study were explained to each patient, and written informed consent was obtained prior to enrollment, in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. The ethics approval number is IRB00084524.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Li, S., Gao, X. et al. Expression and Localization of Huntingtin-Associated Protein 1 (HAP1) in the Human Digestive System. Dig Dis Sci 64, 1486–1492 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5425-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5425-5