Abstract
Background/Aims
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) as a newly identified biological agent has shown promising antitumor effects in a wide range of cancers. However, gastric cancer cells are less sensitive than other cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Here, we combined TRAIL with bortezomib, a proteasomal inhibitor to induce apoptosis in three gastric cancer cell lines.
Methods
After the cells were treated with TRAIL and/or bortezomib, the cell viability, apoptosis and cell cycle distribution were examined. The levels of death receptors and the mitochondrial membrane potential were also detected. The expression of apoptosis-associated proteins was determined by Western blot.
Results
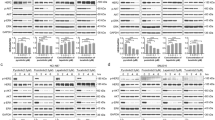
Bortezomib at low concentration significantly (P < 0.05) enhanced the cytotoxic effect of TRAIL by enhancing apoptosis as well as cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. The enhancement of efficiency of TRAIL by bortezomib involved up-regulation of death receptor 4 and 5, as well as reduction of the mitochondrial membrane potential. Further study showed that combined treatment with TRAIL and bortezomib down-regulated anti-apoptotic protein cIAP-1, and over expression of cIAP-1 significantly (P < 0.05) reduced the synergistic effect between TRAIL and bortezomib.
Conclusions
Bortezomib synergizes TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. The synergistic effect between these two drugs is associated with up-regulation of death receptors and down-regulation of cIAP-1. The combination of TRAIL and bortezomib might be an effective regimen for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajani JA, Mayer RJ, Ota DM, et al. Preoperative and postoperative combination chemotherapy for potentially resectable gastric carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:1839–1844.
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995;3:673–682.
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 1999;5:157–163.
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest. 1999;104:155–162.
Wang P, Zhang J, Bellail A, et al. Inhibition of RIP and c-FLIP enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Signal. 2007;19:2237–2246.
Song JH, Tse MC, Bellail A, et al. Lipid rafts and nonrafts mediate tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptotic and nonapoptotic signals in non small cell lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6946–6955.
Franco AV, Zhang XD, Van Berkel E, et al. The role of NF-kappa B in TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis of melanoma cells. J Immunol. 2001;166:5337–5345.
Chen W, Wang X, Zhuang J, Zhang L, Lin Y. Induction of death receptor 5 and suppression of survivin contribute to sensitization of TRAIL-induced cytotoxicity by quercetin in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:2114–2121.
Psahoulia FH, Drosopoulos KG, Doubravska L, Andera L, Pintzas A. Quercetin enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in colon cancer cells by inducing the accumulation of death receptors in lipid rafts. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:2591–2599.
Mühlethaler-Mottet A, Bourloud KB, Auderset K, Joseph JM, Gross N. Drug-mediated sensitization to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in caspase-8-complemented neuroblastoma cells proceeds via activation of intrinsic and extrinsic pathways and caspase-dependent cleavage of XIAP, Bcl-xL and RIP. Oncogene. 2004;23:5415–5425.
Nam SY, Jung GA, Hur GC, et al. Upregulation of FLIP(S) by Akt, a possible inhibition mechanism of TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancers. Cancer Sci. 2003;94:1066–1073.
Sterz J, von Metzler I, Hahne JC, et al. The potential of proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;17:879–895.
Liu X, Yue P, Chen S, et al. The proteasome inhibitor PS-341 (bortezomib) up-regulates DR5 expression leading to induction of apoptosis and enhancement of TRAIL-induced apoptosis despite up-regulation of c-FLIP and survivin expression in human NSCLC cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:4981–4988.
Saulle E, Petronelli A, Pasquini L, et al. Proteasome inhibitors sensitize ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2007;12:635–655.
Bai J, Sui J, Demirjian A, Vollmer CM Jr, Marasco W, Callery MP. Predominant Bcl-XL knockdown disables antiapoptotic mechanisms: tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-based triple chemotherapy overcomes chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2344–2352.
Hasegawa T, Suzuki K, Sakamoto C, et al. Expression of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family members in human neutrophils: up-regulation of cIAP2 by granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and overexpression of cIAP2 in chronic neutrophilic leukemia. Blood. 2003;101:1164–1171.
Van Geelen CM, de Vries EG, de Jong S. Lessons from TRAIL-resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer cells: paving the road to patient-tailored therapy. Drug Resist Updat. 2004;7:345–358.
Ishiguro K, Ando T, Maeda O, et al. Ginger ingredients reduce viability of gastric cancer cells via distinct mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;362:218–223.
Chaudhari AA, Seol JW, Kim SJ, et al. Reactive oxygen species regulate Bax translocation and mitochondrial transmembrane potential, a possible mechanism for enhanced TRAIL-induced apoptosis by CCCP. Oncol Rep. 2007;18:71–76.
Jin CY, Park C, Cheong J, et al. Genistein sensitizes TRAIL-resistant human gastric adenocarcinoma AGS cells through activation of caspase-3. Cancer Lett. 2007;257:56–64.
Xu L, Qu X, Zhang Y, et al. Oxaliplatin enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells by CBL-regulated death receptor redistribution in lipid rafts. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:943–948.
Balsas P, López-Royuela N, Galán-Malo P, Anel A, Marzo I, Naval J. Cooperation between Apo2L/TRAIL and bortezomib in multiple myeloma apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:804–812.
Wang S, El-Deiry WS. TRAIL and apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene. 2003;22:8628–8633.
Rowinsky EK. Targeted induction of apoptosis in cancer management: the emerging role of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor activating agents. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:9394–9407.
Conticello C, Adamo L, Giuffrida R, et al. Proteasome inhibitors synergize with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-induced ligand to induce anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell death. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1938–1942.
Nikrad M, Johnson T, Puthalalath H, Coultas L, Adams J, Kraft AS. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib sensitizes cells to killing by death receptor ligand TRAIL via BH3-only proteins Bik and Bim. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005;4:443–449.
Zhu H, Guo W, Zhang L, et al. Proteasome inhibitors-mediated TRAIL resensitization and Bik accumulation. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005;4:781–786.
Hideshima T, Catley L, Raje N, et al. Inhibition of Akt induces significant downregulation of survivin and cytotoxicity in human multiple myeloma cells. Br J Haematol. 2007;138:783–791.
Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, et al. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 1998;396:580–584.
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST, Giles FJ. Survivin: key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:5000–5005.
Dai Y, Lawrence TS, Xu L. Overcoming cancer therapy resistance by targeting inhibitors of apoptosis proteins and nuclear factor-kappa B. Am J Transl Res. 2009;1:1–15.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Ashwell (National Institutes of Health, USA) for kindly providing the Flag-tagged cIAP-1-expressing pCMVTag 2B plasmid. This work was supported by: Chinese National Foundation of National Sciences grants 30770993; Liaoning Province Foundation of National Sciences grants 20072100; China Postdoctor Foundation of Science grants 20070411081.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Qu, XJ., Xu, L. et al. Bortezomib Synergizes TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Gastric Cancer Cells. Dig Dis Sci 55, 3361–3368 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1191-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-010-1191-8