Abstract
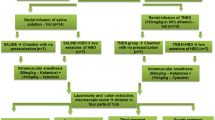
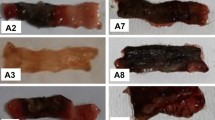
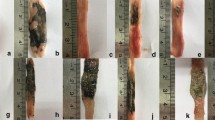
Aim Our aim was to investigate the effectiveness of aminoguanidine (AMG), an inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, and hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) treatment in an experimental colitis model. Methods We induced colitis in rats. In the control group, we applied 2 ml serum physiologic intraperitoneally for 7 days. In the HBO group, 100% oxygen at 2.4 atm pressure was applied for 7 days. In the AMG group, 100 mg/kg AMG was applied intraperitoneally for 7 days. In the HBO + AMG group, HBO and AMG were applied, respectively. At the end of 7 days, rats were sacrificed and the distal 10 cm part of colon was examined macro- and microscopically. Results Severity of colitis and NO activities were reduced by AMG, HBO, and HBO + AMG application. There was histologically significant improvement, especially in the HBO + AMG group Conclusions Both HBO and AMG were significantly effective in preventing weight loss, reducing NO activities, and severity of colitis, when comparing HBO and AMG separately.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pettersson S. Introduction: Inflammatory bowel disease: A complex systemic disease engaging multiple players outside the immune system. J Intern Med. 2008;263:574–576. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2008.01973.x.
Pavlick KP, Laroux FS, Fuseler J, et al. Role of reactive metabolities of oxygen and nitrogen in inflammatory bowel disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002;33:311–322. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00853-5.
Grisham MB. Oxidants and free radicals in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet. 1994;344:859–861. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(94)92831-2.
Harris ML, Schiller HJ, Reilly PM, Donowitz M, Grisham MB, Bulkley GB. Free radicals and other reactive oxygen metabolities in inflammatory bowel disease: Cause, consequence or epiphenomenon? Pharmacol Ther. 1992;53:375–408. doi:10.1016/0163-7258(92)90057-7.
Cross RK, Wilson KT. Nitric oxide in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2003;9:179–189. doi:10.1097/00054725-200305000-00006.
Singer II, Kawka DW, Scott S, et al. Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitrotyrosine in colonic epithelium in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1996;111:871–875. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(96)70055-0.
Grisham MB, Specian RD, Zimmerman TE. Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on the pathophysiology observed in a model of chronic granulomatous colitis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;271:1114–1121.
Rachmilewitz D, Karmeli F, Okon E, Bursztyn M. Experimental colitis is ameliorated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase activity. Gut. 1995;37:247–255. doi:10.1136/gut.37.2.247.
Rachmilewitz D, Karmeli F, Okon E. Sulfhydryl blocker-induced rat colonic inflammation is ameliorated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:98–106. doi:10.1016/0016-5085(95)90273-2.
Grim PS, Gottlieb LJ, Boddie A, Batson E. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy. JAMA. 1990;263:2216–2220. doi:10.1001/jama.263.16.2216.
Lavy A, Weisz G, Adir Y, Ramon Y, Melamed Y, Eidelman S. Hyperbaric oxygen for perianal Crohn’s disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1994;19:202–205. doi:10.1097/00004836-199410000-00006.
Rachmilewitz D, Karmeli F, Okon E, Rubenstein I, Better OS. Hyperbaric oxygen: A novel modality to ameliorate experimental colitis. Gut. 1998;43:512–518.
Colombel JF, Mathieu D, Bouault JM, et al. Hyperbaric oxygenation in severe perineal Crohn’s disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1995;38:609–614. doi:10.1007/BF02054120.
Jurjus AR, Khoury NN, Reimund JM. Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2004;50:81–92. doi:10.1016/j.vascn.2003.12.002.
Yuan H, Ji WS, Wu KX, Jiao JX, Sun LH, Feng YT. Anti-inflammatory effect of Diammonium Glycyrrhizinate in a rat model of ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:4578–4581.
Tsikas D. Analysis of nitrite and nitrate in biological fluids by assays based on the Griess reaction: Appraisal of the Griess reaction in the l-arginine/nitric oxide area of research. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2007;851:51–70. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.07.054.
Butler AR, Flitney FW, Williams DL. NO, nitrosonium ions, nitroxide ions, nitrosothiols and iron-nitrosyls in biology: a chemist’s perspective. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995;16:18–22. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(00)88968-3.
Takahashı T. Pathophysiological significance of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the gastrointestinal tract. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:421–430. doi:10.1007/s00535-003-1094-y.
Cuzzocrea S, McDonald MC, Mazzon E, et al. Tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, reduces dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;406:127–137. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(00)00623-3.
Zingarelli B, Cuzzocrea S, Szabo C, Salzman AL. Mercaptoethylguanidine, a combined inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase and peroxynitrite scavenger, reduces trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colonic damage in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998;287:1048–1055.
Roediger WE, Lawson MJ, Nance SH, Radcliffe BC. Detectable colonic nitrite levels in inflammatory bowel disease-mucosal or bacterial mulfunction? Digestion. 1986;35:199–204.
Middleton SJ, Shorthouse M, Hunter JO. Increased nitric oxide synthesis in ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 1993;341:465–466. doi:10.1016/0140-6736(93)90211-X.
Rachmilewitz D, Stamler JS, Bachwich D, Karmeli F, Ackerman Z, Podolsky DK. Enhanced colonic nitric oxide generation and nitric oxide synthase activity in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut. 1995;36:718–723. doi:10.1136/gut.36.5.718.
Rachmilewitz D, Eliakim R, Ackerman Z, Karmeli F. Direct determination of colonic nitric oxide level—a sensitive marker of disease activity in ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:409–412.
Hogaboam CM, Jacobson K, Collins SM, Blennerhassett MG. The selective beneficial effects of nitric oxide inhibition in experimental colitis. Am J Physiol. 1995;268:G673–G684.
Perner A, Andresen L, Normark M, et al. Expression of nitric oxide synthases and effects of L-arginine and L-NMMA on nitric oxide production and fluid transport in collagenous colitis. Gut. 2001;49:387–394. doi:10.1136/gut.49.3.387.
Kankuri E, Hamalainen M, Hukkanen M, et al. Suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine release by selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase in mucosal explants from patients with ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:186–192. doi:10.1080/00365520310000681.
Pilichos CJ, Kouerinis IA, Zografos GC, et al. The effect of nitric oxide synthases inhibitors on inflammatory bowel disease in a rat model. In Vivo. 2004;18:513–516.
Dudhgaonkar SP, Tandan SK, Kumar D, Raviprakash V, Kataria M. Influence of simultaneous inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in experimental colitis in rats. Inflammopharmacol. 2007;15:188–195. doi:10.1007/s10787-007-1603-3.
Nakamura H, Tsukada H, Oya M, et al. Aminoguanidine has both an anti-inflammatory effect on experimental colitis and a proliferative effect on colonic mucosal cells. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999;34:1117–1122. doi:10.1080/003655299750024922.
Cuthbertson CM, Christophi C. Potential effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in acute pancreatitis. ANZ J Surg. 2006;76:625–630. doi:10.1111/j.1445-2197.2006.03793.x.
Christophi C, Millar I, Nikfarjam M, Muralidharan V, Malcontenti-Wilson C. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:2042–2046. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.03380.x.
Alex J, Laden G, Cale AR, et al. Pretreatment with hyperbaric oxygen and its effect on neuropsychometric dysfunction and systemic inflammatory response after cardiopulmonary bypass: A prospective randomized double-blind trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;130:1623–1630. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2005.08.018.
Marshall GT, Thirlby RC, Bredfeldt JE, Hampson NB. Treatment of gastrointestinal radiation injury with hyperbaric oxygen. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2007;34:35–42.
Filntisis GA, Moon RE, Kraft KL, Farmer JC, Scher RL, Piantadosi CA. Laryngeal radionecrosis and hyperbaric oxygen therapy: Report of 18 cases and review of the literature. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2000;109:554–562.
Gürbüz AK, Elbüken E, Yazgan Y, Yildiz S. A different therapeutic approach in patients with severe ulcerative colitis: Hyperbaric oxygen treatment. South Med J. 2003;96:632–633. doi:10.1097/01.SMJ.0000074507.31006.79.
Gorgulu S, Yagci G, Kaymakcioglu N, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen enhances the efficiency of 5-aminosalicylic acid in acetic acid-induced colitis in rats. Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51:480–487. doi:10.1007/s10620-006-3159-2.
Demirtürk L, Ozel M, Yazgan Y, Buchman AL. Therapeutic efficacy of hyperbaric oxygenation in ulcerative colitis refractory to medical treatment. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;35:286–287. doi:10.1097/00004836-200209000-00021.
Buchman AL, Fife C, Torres C, Smith L, Aristizibal J. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for severe ulcerative colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;33:337–339. doi:10.1097/00004836-200110000-00018.
Gulec B, Yasar M, Yildiz S, et al. Effect of hyperbaric oxygen on experimental acute distal colitis. Physiol Res. 2004;53:493–499.
Atug O, Hamzaoglu H, Tahan V, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is as effective as dexamethasone in the treatment of TNBS-E-induced experimental colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53:481–485. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-9956-4.
Akin ML, Gulluoglu BM, Uluutku H, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen improves healing in experimental rat colitis. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2002;29:279–285.
Lin HC, Wan FJ, Wu CC, Tung CS, Wu TH. Hyperbaric oxygen protects against lipopolysaccharide-stimulated oxidative stress and mortality in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;508:249–254. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.12.021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Cemal Nuri Ercin and Zeki Yesilova contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ercin, C.N., Yesilova, Z., Korkmaz, A. et al. The Effect of iNOS Inhibitors and Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment in a Rat Model of Experimental Colitis. Dig Dis Sci 54, 75–79 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0498-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0498-1