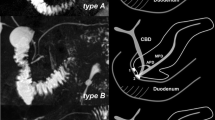
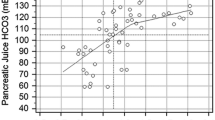
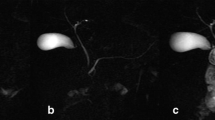
Abstract
Objectives The aim of this investigation was to evaluate the pancreatographic findings and dynamics of pancreatic duct diameter, as determined by secretin-enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (S-MRCP), in patients with acute alcoholic pancreatitis or chronic alcoholic pancreatitis and in a control group. Methods S-MRCP was performed in patients with acute alcoholic pancreatitis who did not manifest the functional and radiological (ultrasonography and computed tomography) criteria of chronic pancreatitis (n = 21), in patients with chronic alcoholic pancreatitis (n = 28) and in a control group (n = 16). The diameter of the main pancreatic duct (MPD) was monitored before secretin administration and at 3 and 10 min after secretin administration. Morphological features were also assessed before and after the administration of secretin. Results All ductal diameters were significantly larger in chronic alcoholic pancreatitis (P < 0.0001). There were no differences in MPD caliber between patients with acute alcoholic pancreatitis and the control group. The percentage of variation between basal MPD diameter and at 3 min post-secretin administration was lower in patients with chronic (35.5%) pancreatitis than in those with acute alcoholic pancreatitis (52.3%) and the control group (52.5%). There were no significant differences between patients with acute alcoholic pancreatitis and the control group in terms of the frequency of visualization of side branches, ductal narrowing, intraluminal filling defects, and ductal irregularity. One patient with acute alcoholic pancreatitis presented ductal criteria of chronic pancreatitis following the administration of secretin. Conclusions The dynamics of MPD visualized on S-MRCP in patients with acute alcoholic pancreatitis is similar to that observed in the control group and different from that observed in patients with chronic alcoholic pancreatitis. There were no significant differences between patients with acute alcoholic pancreatitis and the control group in terms of morphological pancreatographic features.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gullo L, Migliori M, Brunetti MA, Manca M (2005) Alcoholic pancreatitis: new insights into an old disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 7:96–100. doi:10.1007/s11894–005-0046-5
Sarles H (1991) Definitions and classifications of pancreatitis. Pancreas 6:470–474. doi:10.1097/00006676-199107000-00015
Blackstone MO (1990) Can alcohol cause true acute pancreatitis? Gastroenterology 99:1544–1546
Ammann RW, Muellhaupt B (1994) Progression of alcoholic acute to chronic pancreatitis. Gut 35:552–556. doi:10.1136/gut.35.4.552
Ammann RW, Heitz PU, Klöppel G (1996) Course of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis: a prospective clinicomorphological long-term study. Gastroenterology 111:224–231. doi:10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8698203
Apte MV, Wilson JS (2003) Alcohol-induced pancreatic injury. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17:593–612. doi:10.1016/S1521-6918(03)00050-7
Glasbrenner B, Kahl S, Malfertheiner P (2002) Moderns diagnostics of chronic pancreatitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:935–941. doi:10.1097/00042737-200209000-00003
Binmoeller KF, Soehendra N (2002) Pitfalls in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. In: Dimarino AJ, Benjamin SB (eds) Gastrointestinal disease. An endoscopic approach. Slack, Thorofare, pp 1049–1062
Barish MA, Yucel K, Ferrucci JT (1999) Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. N Eng J Med 341:258–264. doi:10.1056/NEJM199907223410407
Sica GT, Braver J, Cooney MJ, Miller FH, Chai JL, Admas DF (1999) Comparison of endoscopic cholangiopancreatography with MR cholangiopancreatography in patients with pancreatitis. Radiology 210:605–610
Matos C, Metens T, Devière J, Nicaise N, Braudé P, Van Yperen G, Cremer M, Stryuven J (1997) Pancreatic duct: morphologic and functional evaluation with dynamic MR pancreatography after secretin stimulation. Radiology 203:435–441
Manfredi R, Costamagna G, Brizi M, Maresca G, Vecchioli A, Colagrande C, Marano P (2000) Severe chronic pancreatitis versus suspected pancreatic disease: dynamic MR pancreatography after secretin stimulation. Radiology 214:849–855
Hellerhoff KJ, Helmberger H, Rösch T, Settles MR, Link TM, Rummeny EJ (2002) Dynamic MR pancreatography after secretin administration. Image quality and diagnostic accuracy. Am J Roentgenol 179:121–129
Fukukura Y, Fujiyoshi F, Sasaki M, Nakajo M (2002) Pancreatic duct: morphologic evaluation with MR cholangiopancreatography after secretin stimulation. Radiology 222:674–680. doi:10.1148/radiol.2223010684
Cappeliez O, Delhaye M, Devière J, Le Moine O, Metens T, Nicaise N, Cremer M, Stryuven J (2000) Chronic pancreatitis: evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function with MR pancreatography after secretin stimulation. Radiology 215:358–364
Czakó L, Endes J, Takács T, Boda K, Lonovics J (2001) Evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function by secretin-enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. Pancreas 23:323–328. doi:10.1097/00006676-200110000-00015
Mariani A (2001) Is secretin magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography an effective guide for a diagnostic and/or therapeutic flow-chart in acute recurrent pancreatitis? J Pancreas 2:414– 421
Banks PA, Freeman ML (2006) Practice parameters committee of the American college of gastroenterology: practice guidelines in acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 101:2379–2400. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00856.x
Axon ATR, Classen M, Cotton PB, Cremer M, Freeny PC, Lees WR (1984) Pancreatography in chronic pancreatitis: international definitions. Gut 25:1107–1112. doi:10.1136/gut.25.10.1107
Bradley EL 3rd (1993) A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis. Arch Surg 128:586–590
Homma T, Harada H, Koizimi M (1997) Diagnostic criteria for chronic pancreatitis by the Japan pancreas society. Pancreas 15:14–15. doi:10.1097/00006676-199707000-00002
Ladas SD, Tassios PS, Giorgiotis K, Rokkas T, Theodosiou P, Raptis SA (1993) Pancreatic duct width: its significance as a diagnostic criterion for pancreatic disease. Hepatogastroenterology 40:52–55
Fogel EL, Sherman S, Lehman G (2002) Pancreatic diseases. In: Classen M, Tytgat GNJ, Lightdale CJ (eds) Gastroenterological endoscopy. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 634–663
Osawa S, Kataoka K, Sakagami J, Sogame Y, Kawasaki C, Takaoka K, Yasuda H, Takatera A (2002) Relation between morphologic changes in the main pancreatic duct and exocrine pancreatic function after a secretin test. Pancreas 25:12–19. doi:10.1097/00006676-200207000-00005
Forsmark CE, Toskes PP (1995) What does a normal pancreatogram mean? Gastrointest Endosc Clin North Am 5:105–23
Pareja E, Artigues E, Mir J, Fabra R, Martínez A, Vázquez A, Trullenque R (2003) Main pancreatic duct : morphology after acute biliary pancreatitis with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography after secretin stimulation. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 95:389–394
Etemad B, Whitcomb D (2001) Chronic pancreatitis: diagnosis, classification, and new genetic developments. Gastroenterology 120:682–707. doi:10.1053/gast.2001.22586
Kahl S, Glasbrenner B, Leodolter A, Pross M, Schulz HU, Malfertheiner P (2002) EUS in the diagnosis of early chronic pancreatitis: a prospective follow-up study. Gastrointest Endosc 55:507–11. doi:10.1067/mge.2002.122610
Wallace MB, Hawes RH (2001) Endoscopic ultrasound in the evaluation and treatment of chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 23:26–35. doi:10.1097/00006676-200107000-00004
Tamura R, Ishibashi T, Takahashi S (2006) Chronic pancreatitis: MRCP versus ERCP for quantitative caliber measurement and qualitative evaluation. Radiology 238:920–928. doi:10.1148/radiol.2382041527
Czakó L (2007) Diagnosis of early-stage chronic pancreatitis by secretin-enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. J Gastroenterol 42[suppl XVII]:113–117. doi:10.1007/s00535-006-1919-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pascual, I., Soler, J., Peña, A. et al. Morphological and Functional Evaluation of the Pancreatic Duct with Secretin-Stimulated Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography in Alcoholic Pancreatitis Patients. Dig Dis Sci 53, 3234–3241 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0284-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-008-0284-0