Abstract
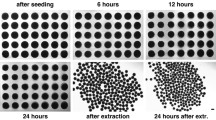
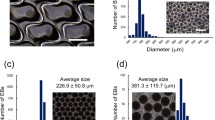
Pluripotent human embryonic stem cell (hESC) lines are a promising model system in developmental and tissue regeneration research. Differentiation of hESCs towards the three germ layers and finally tissue specific cell types is often performed through the formation of embryoid bodies (EBs) in suspension or hanging droplet culture systems. However, these systems are inefficient regarding embryoid body (EB) formation, structural support to the EB and long term differentiation capacity. The present study investigates if agarose, as a semi solid matrix, can facilitate EB formation and support differentiation of hESC lines. The results showed that agarose culture is able to enhance EB formation efficiency with 10% and increase EB growth by 300%. The agarose culture system was able to maintain expression of the three germ layers over 8 weeks of culture. All of the four hESC lines tested developed EBs in the agarose system although with a histological heterogeneity between cell lines as well as within cell lines. In conclusion, a 3-D agarose culture of spherical hESC colonies improves EB formation and growth in a cost effective, stable and non-laborious technique.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- hESC:
-
Human embryonic stem cell
- EB:
-
Embryoid body
- EBs:
-
Embryoid bodies
- SCID:
-
Severe combined immunodeficiency
- 3-D:
-
Three dimensional
- MEF:
-
Mouse embryonic fibroblast
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- AFP:
-
Alpha fetoprotein
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- Bfgf:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- PPD11:
-
p-Phenylenediamine anti-fade solution
- IgG:
-
Immuno globulin G
References
Amit M, Carpenter MK, Inokuma MS, Chiu CP, Harris CP, Waknitz MA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Thomson JA (2000) Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture. Dev Biol 227:271–278
Benya PD, Shaffer JD (1982) Dedifferentiated chondrocytes reexpress the differentiated collagen phenotype when cultured in agarose gels. Cell 30:215–224
Bongso A, Fong CY, Ng SC, Ratnam S (1994) Isolation and culture of inner cell mass cells from human blastocysts. Hum Reprod 9:2110–2117
Chen SS, Revoltella RP, Papini S, Michelini M, Fitzgerald W, Zimmerberg J, Margolis L (2003) Multilineage differentiation of rhesus monkey embryonic stem cells in 3-D culture systems. Stem Cells 21:281–295. doi:10.1634/stemcells.21-3-281
Cooke MJ, Stojkovic M, Przyborski SA (2006) Growth of teratomas derived from human pluripotent stem cells is influenced by the graft site. Stem Cells Dev 15:254–259
Dang SM, Kyba M, Perlingeiro R, Daley GQ, Zandstra PW (2002) Efficiency of embryoid body formation and hematopoietic development from embryonic stem cells in different culture systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 78:442–453
Dang SM, Gerecht-Nir S, Chen J, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Zandstra PW (2004) Controlled, scalable embryonic stem cell differentiation culture. Stem Cells 22:275–282
Gerecht S, Burdick JA, Ferreira LS, Townsend SA, Langer R, Vunjak-Novakovic G (2007) Hyaluronic acid hydrogel for controlled self-renewal and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11298–11303
Heins N, Englund MC, Sjoblom C, Dahl U, Tonning A, Bergh C, Lindahl A, Hanson C, Semb H (2004) Derivation, characterization, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 22:367–376
Hopfl G, Gassmann M, Desbaillets I (2004) Differentiating embryonic stem cells into embryoid bodies. Methods Mol Biol 254:79–98. doi:1-59259-741-6:07910.1385/1-59259-741-6:079
Itskovitz-Eldor J, Schuldiner M, Karsenti D, Eden A, Yanuka O, Amit M, Soreq H, Benvenisty N (2000) Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into embryoid bodies compromising the three embryonic germ layers. Mol Med 6:88–95
Keller GM (1995) In vitro differentiation of embryonic stem cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:862–869. doi:0955-0674(95)80071-9
Levenberg S, Huang NF, Lavik E, Rogers AB, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Langer R (2003) Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells on 3-D polymer scaffolds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12741–12746. doi:10.1073/pnas.17354631001735463100
Martin GR, Evans MJ (1975) Differentiation of clonal lines of teratocarcinoma cells: formation of embryoid bodies in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1441–1445
Powers DE, Millman JR, Huang RB, Colton CK (2008) Effects of oxygen on mouse embryonic stem cell growth, phenotype retention, and cellular energetics. Biotechnol Bioeng 101:241–254. doi:10.1002/bit.21986
Prokhorova TA, Harkness LM, Frandsen U, Ditzel N, Burns JS, Schroeder HD, Kassem M (2008) Teratoma Formation by Human Embryonic Stem Cells is site-dependent and enhanced by the presence of Matrigel. Stem Cells Dev 18:47–54. doi:10.1089/scd.2007.0266
Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, Trounson A, Bongso A (2000) Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol 18:399–404
Sakai S, Hashimoto I, Kawakami K (2008) Production of cell-enclosing hollow-core agarose microcapsules via jetting in water-immiscible liquid paraffin and formation of embryoid body-like spherical tissues from mouse ES cells enclosed within these microcapsules. Biotechnol Bioeng 99:235–243. doi:10.1002/bit.21624
Schuldiner M, Yanuka O, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Melton DA, Benvenisty N (2000) Effects of eight growth factors on the differentiation of cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11307–11312
Sjogren-Jansson E, Zetterstrom M, Moya K, Lindqvist J, Strehl R, Eriksson PS (2005) Large-scale propagation of four undifferentiated human embryonic stem cell lines in a feeder-free culture system. Dev Dyn 233:1304–1314. doi:10.1002/dvdy.20459
Strom S, Inzunza J, Grinnemo KH, Holmberg K, Matilainen E, Stromberg AM, Blennow E, Hovatta O (2007) Mechanical isolation of the inner cell mass is effective in derivation of new human embryonic stem cell lines. Hum Reprod 22:3051–3058. doi:dem33510.1093/humrep/dem335
Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, Waknitz MA, Swiergiel JJ, Marshall VS, Jones JM (1998) Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282:1145–1147
Valbuena D, Galan A, Sanchez E, Poo ME, Gomez E, Sanchez-Luengo S, Melguizo D, Garcia A, Ruiz V, Moreno R, Pellicer A, Simon C (2006) Derivation and characterization of three new Spanish human embryonic stem cell lines (VAL −3 −4 −5) on human feeder and in serum-free conditions. Reprod Biomed Online 13:875–886
Wu H, Xu J, Pang ZP, Ge W, Kim KJ, Blanchi B, Chen C, Sudhof TC, Sun YE (2007) Integrative genomic and functional analyses reveal neuronal subtype differentiation bias in human embryonic stem cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:13821–13826. doi:070619910410.1073/pnas.0706199104
Wu H, Kim KJ, Mehta K, Paxia S, Sundstrom A, Anantharaman T, Kuraishy AI, Doan T, Ghosh J, Pyle AD, Clark A, Lowry W, Fan G, Baxter T, Mishra B, Sun Y, Teitell MA (2008) Copy number variant analysis of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 26:1484–1489. doi:2007-099310.1634/stemcells.2007-0993
Yu X, Dillon GP, Bellamkonda RB (1999) A laminin and nerve growth factor-laden three-dimensional scaffold for enhanced neurite extension. Tissue Eng 5:291–304
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by: Swedish Research Council grant no. 2005-7544, The ALF/LUA research grant from the Sahlgrenska University Hospital. The Inga Britt and Arne Lundberg Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
All work with the human embryonic stem cells was conducted according to the ISSCR Guidelines for the Conduct of Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research and with the approval of the local ethics committees at the University of Gothenburg and the University of Uppsala.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stenberg, J., Elovsson, M., Strehl, R. et al. Sustained embryoid body formation and culture in a non-laborious three dimensional culture system for human embryonic stem cells. Cytotechnology 63, 227–237 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-011-9344-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-011-9344-y