Abstract
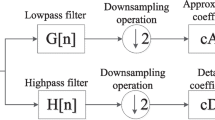
In this paper, we propose a high-performance audio fingerprinting system used in real-world query-by-example applications for acoustic audio-based content identification, especially for use in heterogeneous portable consumer devices or on-line audio distributed system. In the proposed method, audio fingerprints are generated using a modulated complex lapped transform-based non-repeating foreground audio extraction and an adaptive thresholding method for prominent peak detection. Effective matching is performed using a robust peak-pair-based hash function of non-repeating foreground audio to protect against noise, echo, artifacts from pitch-shifting, time-stretching, resampling, equalization, or compression. Experimental results confirm that the proposed method is quite robust in various distorted conditions and achieves preliminarily promising accuracy results.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cano, P., Batlle, E., Kalker, T., Haitsma, J.: A review of algorithms for audio fingerprinting. In: International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, pp. 169–173 (2002)
Li, W., Xiao, C., Liu, Y.: Low-order auditory Zernike moment: a novel approach for robust music identification in the compressed domain. EURASIP J. Adv. Sig. Process. 1, 1–15 (2013)
Sinitsyn, A.: Duplicate song detection using audio fingerprinting for consumer electronics devices. In: IEEE International Symposium on Consumer Electronics (ISCE06), St. Petersburg, Russia, pp. 1–6 (2006)
Cerquides, J.: A real time audio fingerprinting system for advertisement tracking and reporting in FM radio. In: 17th International Conference on Radioelektronika, Brno, Czech, pp. 1–4 (2007)
Haitsma, J., Kalker, T.: A highly robust audio fingerprinting system. In: 3rd International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Paris, France, pp. 107–115 (2002)
Liu, Y., Yun, H.-S., Kim, N.S.: Audio fingerprinting based on multiple hashing in DCT domain. IEEE Sig. Process. Lett. 6(6), 525–528 (2009)
Chandrasekhar, V., Sharifi, M., Ross, D.A.: Survey and evaluation of audio fingerprinting schemes for mobile query-by-example applications. In: 12th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Miami, USA, pp. 801–806 (2011)
Pan, X., Yu, X., Deng, J., Yang, W., Wang, H.: Audio fingerprinting based on local energy centroid. In: IET International Communication Conference on Wireless Mobile and Computing (CCWMC), Shanghai, China, pp. 351–354 (2011)
Baluja, S., Covel, M.: Audio fingerprinting: combining computer vision and data-stream processing. In: International Conference on Acoustic, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Honolulu, Hawaii, pp. 2:213–2:216 (2007)
Anguera, X., Garzon, A., Adamek, T.: MASK: robust local feature for audio fingerprinting. In: International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), pp. 455–460 (2012)
Wang, A.: An industrial strength audio search algorithm. In: 4th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), Baltimore, pp. 7–13 (2003)
Kim, H.-G., Kim, J.Y.: Robust audio fingerprinting method using prominent peak pair based on modulated complex lapped transform. ETRI J. 36(6), 999–1007 (2014)
Fenet, S., Richard, G., Grenier, Y.: A scalable audio fingerprint method with robustness to pitch-shifting. In: 12th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, pp. 121–126 (2011)
Malvar, H.: Fast algorithm for the modulated complex lapped transform. IEEE Sig. Process. Lett. 10(1), 8–10 (2003)
Rafii, Z., Pardo, B.: Repeating pattern extraction technique (REPET): a simple method for music/voice separation. EEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(1), 73–84 (2013)
Liutkus, A., Rafii, Z., Badeau, R., Pardo, B., Richard, G.: Adaptive filtering for music/voice separation exploiting the repeating musical structure. In: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Kyoto, Japan, pp. 53–56 (2012)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2013R1A1A2007601). And this research was supported by the MSIP (Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning), Korea, under the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program (IITP-2015-H8501-15-1016) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion), and Kwangwoon Research Grant 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HG., Cho, HS. & Kim, J.Y. Robust audio fingerprinting using peak-pair-based hash of non-repeating foreground audio in a real environment. Cluster Comput 19, 315–323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-015-0523-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-015-0523-z